Team:Calgary/Project
From 2011.igem.org
Emily Hicks (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
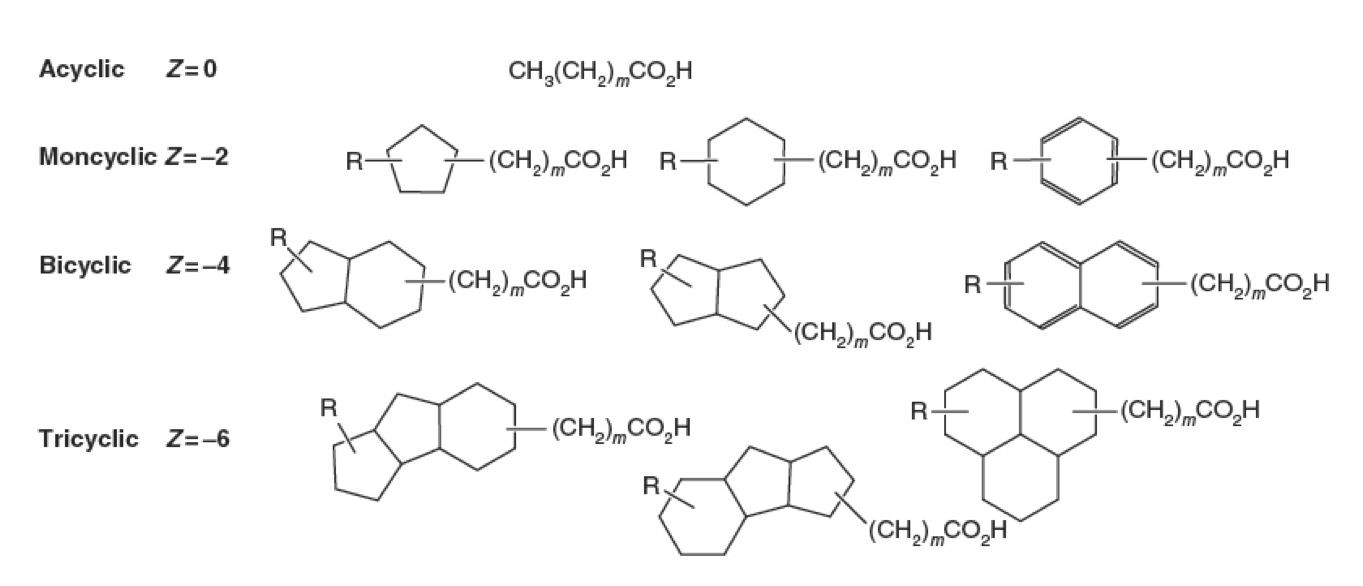
<p>Naphthenic Acids (NAs) are a group of recalcitrant, hydrophobic, compounds comprising a variety of structures. All NAs contain a conserved carboxylic acid group followed by a hydrocarbon chain. Attached to this hydrophobic chain can be between one and four hydrogenated ring systems. The classification of what defines an NA continues to be debated in the scientific community. With such diversity within this chemical class, the biodegradation of NAs is difficult to define due to the likelihood of biodegradation pathways interacting with very specific topological structures. Thus one pathway likely does not degrade all NAs, and NA research has yet to define any NA degrading pathways.</p> | <p>Naphthenic Acids (NAs) are a group of recalcitrant, hydrophobic, compounds comprising a variety of structures. All NAs contain a conserved carboxylic acid group followed by a hydrocarbon chain. Attached to this hydrophobic chain can be between one and four hydrogenated ring systems. The classification of what defines an NA continues to be debated in the scientific community. With such diversity within this chemical class, the biodegradation of NAs is difficult to define due to the likelihood of biodegradation pathways interacting with very specific topological structures. Thus one pathway likely does not degrade all NAs, and NA research has yet to define any NA degrading pathways.</p> | ||
| + | |||
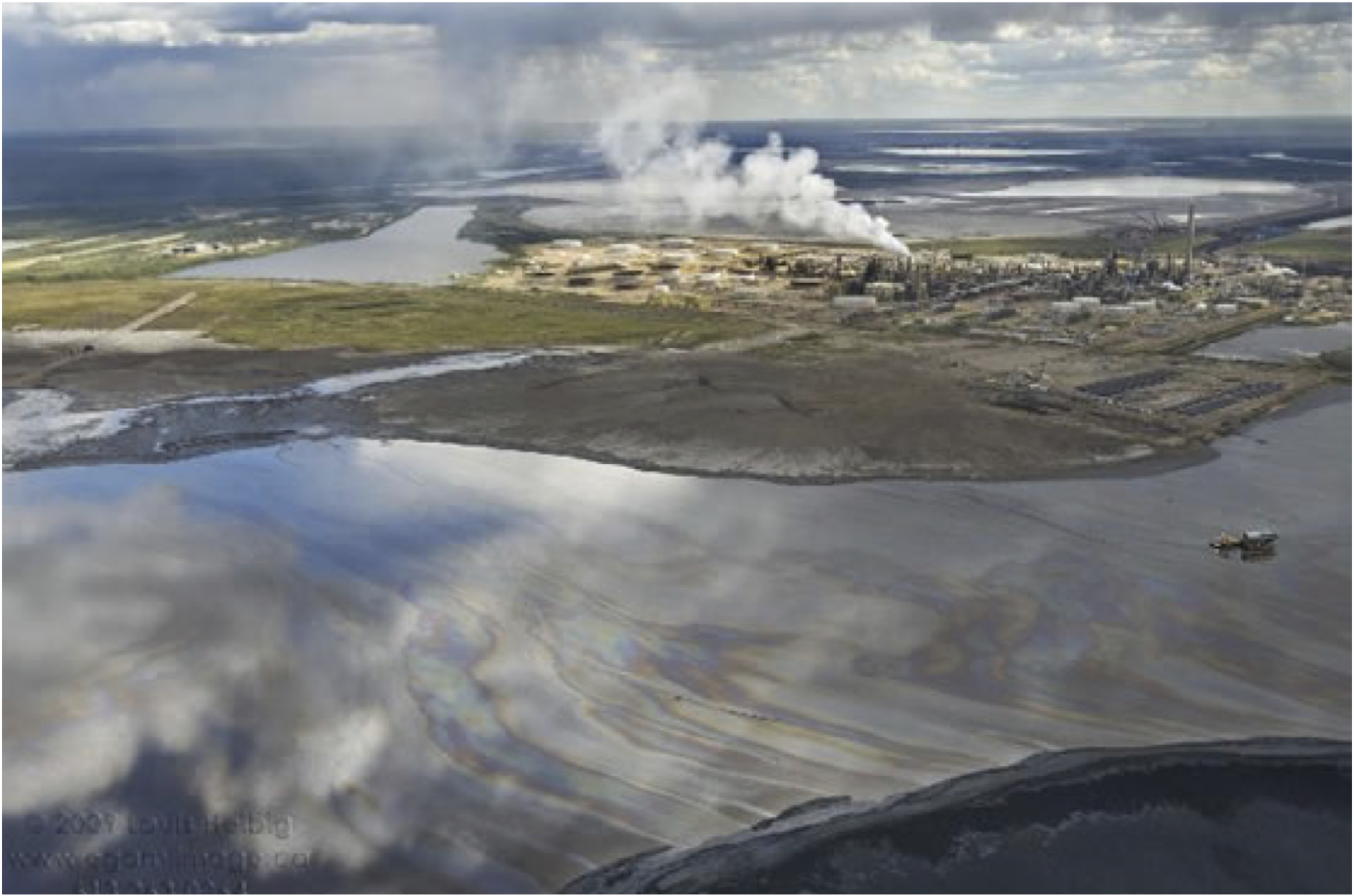
<p>NAs are naturally found in oil sands deposits and their surfactant quality aids in a higher efficiency of oil sands recovery in the hot water extraction process. Post processing, the majority of NAs from the tar sands are deposited into the waste water, collected in large tailings ponds along with a variety of other toxic by-products of bitumen extraction. The NAs continuously accumulate in these large tailings ponds and are allowed to settle to the bottom of these pools.</p> | <p>NAs are naturally found in oil sands deposits and their surfactant quality aids in a higher efficiency of oil sands recovery in the hot water extraction process. Post processing, the majority of NAs from the tar sands are deposited into the waste water, collected in large tailings ponds along with a variety of other toxic by-products of bitumen extraction. The NAs continuously accumulate in these large tailings ponds and are allowed to settle to the bottom of these pools.</p> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
<h2>Bitumen Extraction Process</h2> | <h2>Bitumen Extraction Process</h2> | ||
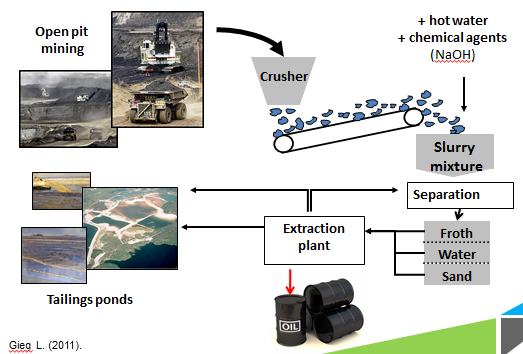
| - | <p>Naphthenic acids are found naturally in the bitumen that is extracted from the ground, but is not one of the desired products in refined petroleum. During the refining process, excess hot water and chemical agents such as NaOH are added to aid in the separation of contaminants such as | + | <p>Naphthenic acids are found naturally in the bitumen that is extracted from the ground, but is not one of the desired products in refined petroleum. During the refining process, excess hot water and chemical agents such as NaOH are added to aid in the separation of contaminants, such as NAs, from the desired hydrocarbons. These contaminants are then stored in the tailings ponds that are shown above.</p> |
</html>[[Image:UofC_Extraction.png|thumb|600px|center|<b>Figure 3.</b>The extraction process from bitumen to oil, showing where waste like naphthenic acids is extracted]]<html> | </html>[[Image:UofC_Extraction.png|thumb|600px|center|<b>Figure 3.</b>The extraction process from bitumen to oil, showing where waste like naphthenic acids is extracted]]<html> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
<h2>The Toxicity of Naphthenic Acids</h2> | <h2>The Toxicity of Naphthenic Acids</h2> | ||
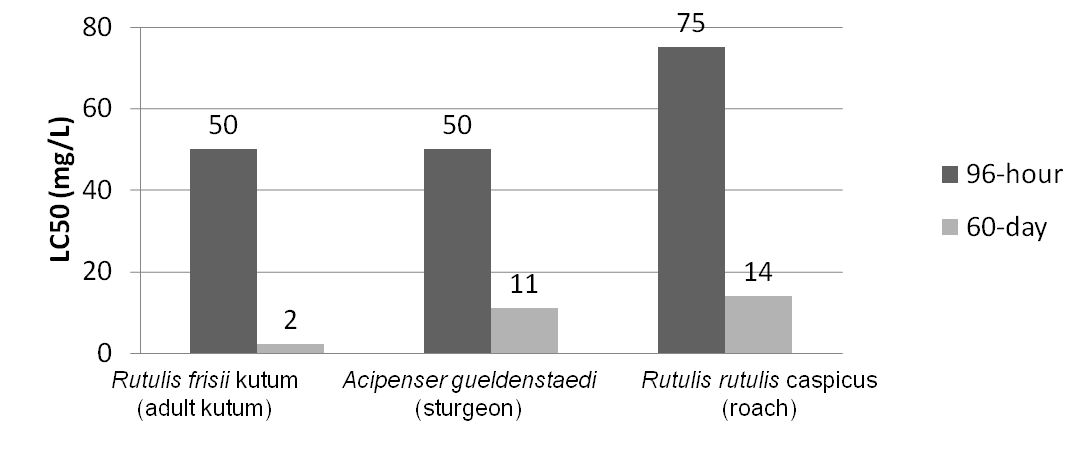
| - | <p>One of the major industry concerns with NAs is their contribution to corrosion | + | <p>One of the major industry concerns with NAs is their contribution to corrosion of equipment and pipelines. In addition, their surfactant nature also makes them toxic in mammalian systems allowing them to pass through and potentially disrupt cell membranes. NAs with a higher molecular weight are typically less toxic than those with a lower molecular weight, however, the lower molecular weight compounds still have significant toxicity with LC<sub>50</sub> values of less than 50 mg/L in freshwater systems. The higher the concentration of NAs in the environment the greater the potential harm to the local ecosystem, in particular, potential contamination of biological communities surrounding the tailings ponds.</p> |
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 22:22, 28 September 2011








A Biosensor for Naphthenic Acids

Naphthenic Acids in the Oil Sands
Naphthenic Acids (NAs) are a group of recalcitrant, hydrophobic, compounds comprising a variety of structures. All NAs contain a conserved carboxylic acid group followed by a hydrocarbon chain. Attached to this hydrophobic chain can be between one and four hydrogenated ring systems. The classification of what defines an NA continues to be debated in the scientific community. With such diversity within this chemical class, the biodegradation of NAs is difficult to define due to the likelihood of biodegradation pathways interacting with very specific topological structures. Thus one pathway likely does not degrade all NAs, and NA research has yet to define any NA degrading pathways.
NAs are naturally found in oil sands deposits and their surfactant quality aids in a higher efficiency of oil sands recovery in the hot water extraction process. Post processing, the majority of NAs from the tar sands are deposited into the waste water, collected in large tailings ponds along with a variety of other toxic by-products of bitumen extraction. The NAs continuously accumulate in these large tailings ponds and are allowed to settle to the bottom of these pools.
Bitumen Extraction Process
Naphthenic acids are found naturally in the bitumen that is extracted from the ground, but is not one of the desired products in refined petroleum. During the refining process, excess hot water and chemical agents such as NaOH are added to aid in the separation of contaminants, such as NAs, from the desired hydrocarbons. These contaminants are then stored in the tailings ponds that are shown above.
The Toxicity of Naphthenic Acids
One of the major industry concerns with NAs is their contribution to corrosion of equipment and pipelines. In addition, their surfactant nature also makes them toxic in mammalian systems allowing them to pass through and potentially disrupt cell membranes. NAs with a higher molecular weight are typically less toxic than those with a lower molecular weight, however, the lower molecular weight compounds still have significant toxicity with LC50 values of less than 50 mg/L in freshwater systems. The higher the concentration of NAs in the environment the greater the potential harm to the local ecosystem, in particular, potential contamination of biological communities surrounding the tailings ponds.
Monitoring Naphthenic Acids
Having the ability to monitor the levels of NAs is mandated by Canadian law and would be useful in assessing whether or not any future detoxification or remediation efforts are effective. Other applications include examining the surrounding areas for seepage of NAs into ground water, and determining the extent of damage caused by oil based chemical spills. Currently, the only ways to test for the presence of NAs are mass spectrometry and gas chromatography. These methods are costly, require the experience of a trained technician, must be shipped to a facility to be processed, and takes up to several hours per analysis. The University of Calgary’s iGEM team is working on developing a novel electrochemical biosensor which would allow for cheap, quick, and convenient on site monitoring of NAs. The bacteria used to sense the naphthenic acids would be contained inside a device, and respond specifically to these compounds. Their response would signal a change in electrochemical potential in the solution which could be used as a read-out for our device in a quantitative manner.
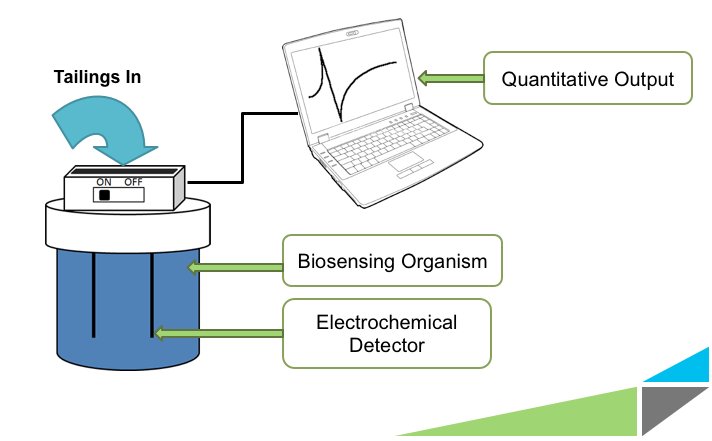
Engineering the Biosensor
Engineering the biosensor involved three main components: finding an appropriate sensory element, characterizing a novel reporter and selecting and designing tools for an appropriate chassis for our system. Information on the sensory element can be found on our Promoter Project page. More details on our reporter can be found on the Reporter Project page. More details on our chassis can be found on our Chassis Project page.

 "
"