Team:Glasgow/BiofilmResults
From 2011.igem.org
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| + | <p>The diagrams below show two 24-hour RFP Nissle biofilms compared to non-transformed Nissle and Nissle transformed with the puC19 vector. They show the distinct red fluorescence of RFP, as well as what appears to be innate green fluorescence of Nissle. Due to this property of <i>E. coli</i> Nissle, using GFP or YFP is not recommended. <p> | ||
| + | <p>More details on these diagrams can be found in the lab book section.</p> | ||
| + | |||
<table> | <table> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 46: | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
<img src="http://farm7.static.flickr.com/6175/6170690387_75d453a871_z.jpg"> | <img src="http://farm7.static.flickr.com/6175/6170690387_75d453a871_z.jpg"> | ||
Revision as of 02:40, 22 September 2011

Results
Back to Biofilms
Back to Results
The images below show a selection of stages of biofilm formation. Starting with Image 1 showing a lab strain of E.colithat has no fimbriae, and is not forming a biofilm.
Image 2 shows an EM of E.coli Nissle 1917 in the early stages of biofilm formation. The fimbriae that allow the cells to cling to each other are clearly visible.
Image 3 shows a Nissle biofilm in the later stages of formation, with the cells densely packed and the extracellular matrix that holds them together showing.
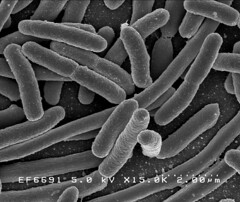
Image 1: 15,000x EM of E.coli for comparison. No fimbriae or EPS is visible. (courtesy of Rocky Mountain Laboratories) |
 Image 2: 10,000x SEM image of Nissle showing the fimbriae |
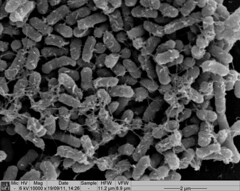 Image 3: SEM image of Nissle biofilm showing the extracellular matrix |
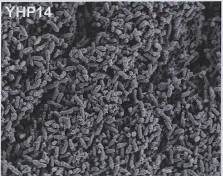
Image 4: 1000x EM of P. aeruginosa biofilm, showing its densely packed structure (courtesy of Dan Walker, University of Glasgow) |
The diagrams below show two 24-hour RFP Nissle biofilms compared to non-transformed Nissle and Nissle transformed with the puC19 vector. They show the distinct red fluorescence of RFP, as well as what appears to be innate green fluorescence of Nissle. Due to this property of E. coli Nissle, using GFP or YFP is not recommended.
More details on these diagrams can be found in the lab book section.
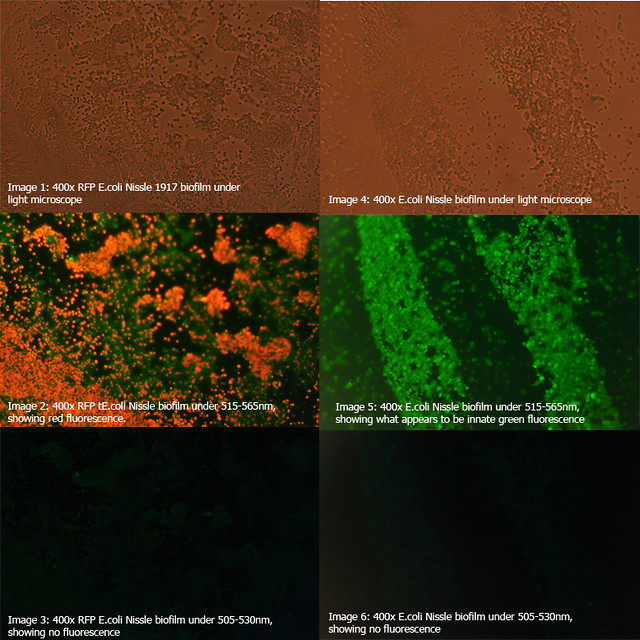
Figure 1: Comparison of RFP E.coli Nissle biofilms to untransformed E.coli Nissle bioflims under light microscope and under excitatory and non-excitatory wavelengths |
|
|
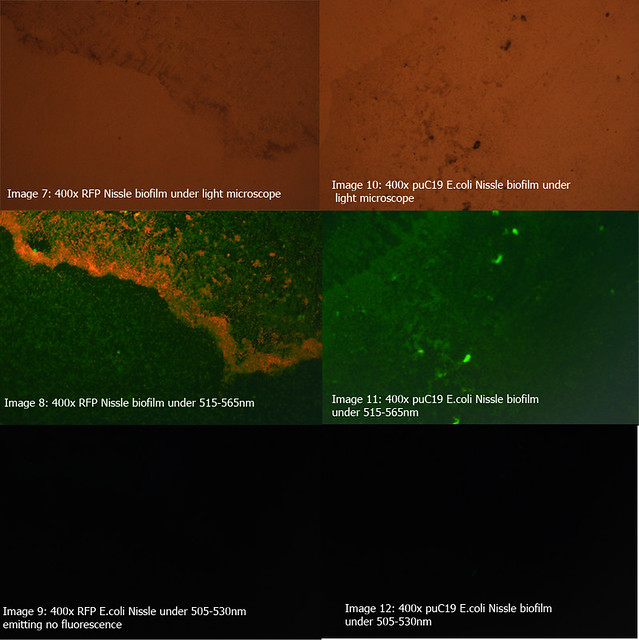
Figure 2: Comparison of RFP E.coli Nissle biofilms to puC19 E.coli Nissle biofilms under light microscope and under excitatory and non-excitatory wavelengths |
Summary
- New Chassis
-Transformable
- Forms biofilms
- Non-pathogenic and compatible with majority of biobricks
-No shuttle vector necessary
-Time series shows that biofilm grows at similar speed to planktonic cells
Well suited for biofilm investigation, especially when intending to transform the biofilm
 "
"
