Team:Glasgow
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Chris Wood (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
<h3><a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/Nissle"><i>E.coli</i> Nissle 1917</a></h3> - our new transformable, non-pathogenic, biofilm-forming chassis | <h3><a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/Nissle"><i>E.coli</i> Nissle 1917</a></h3> - our new transformable, non-pathogenic, biofilm-forming chassis | ||
</br> | </br> | ||
| - | + | <h3><a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:Glasgow/PDE">c-di-GMP Phosphodiesterase</h3> | |
| + | c-di-GMP Phosphodiesterase breaks down c-di-GMP, which is a secondary messenger which regulates many behaviours such as motility and biofilm formation. Over-expressing this phosphodiesterase should decrease the levels of c-di-GMP, increasing cellular motility and causing biofilm dispersal. c-di-GMP has many more functions making this biobrick useful in a wide range of applications | ||
| + | </br> | ||
<h2>Sponsors</h2> | <h2>Sponsors</h2> | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 20 September 2011

DISColi: Bio-photolithography in Device Engineering Using Different Wavelengths of Light
Highlights!
In the course of our project we have created many noteworthy biobricks and have made a series of very interesting discoveries. Here are our personal highlights, including our favourite biobricks, our new chassis, and our public presence. Have a look!
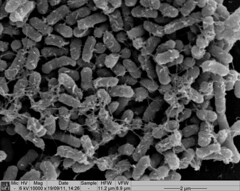
E.coli Nissle 1917
- our new transformable, non-pathogenic, biofilm-forming chassisc-di-GMP Phosphodiesterase
c-di-GMP Phosphodiesterase breaks down c-di-GMP, which is a secondary messenger which regulates many behaviours such as motility and biofilm formation. Over-expressing this phosphodiesterase should decrease the levels of c-di-GMP, increasing cellular motility and causing biofilm dispersal. c-di-GMP has many more functions making this biobrick useful in a wide range of applicationsSponsors
With many thanks to our generous sponsors, without whom this project would not have been possible.
 "
"