Team:HKU-Hong Kong/Lab Diaries
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| (28 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|style="width:900px;"|'''Week 1''' | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 1''' | ||
| + | Transformation of reporter DNA (pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp) into DH10B (non-virulent strain E. coli) with antibiotic resistance (Chloramphenicol – Cm) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 2''' | ||
<OL> | <OL> | ||
| - | <LI> | + | <LI>tetO2 -1 (DNA binding site) |
| - | < | + | <OL> |
| + | <LI>Reverse PCR was used to insert tetO2 -1 into pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp (template DNA) by using forward and reverse primers which are with the tetO2 -1. By using reverse PCR, we can insert the tetO2 -1 site into the pEGFP while the plasmid produced is still in double-stranded circular form. | ||
| + | <LI>pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp-tetO2-1 was then transformed into DH10B to greatly amplify the product by using bacterial cells. | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>tetO2 -2 (DNA biding site) | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Reverse PCR was used to insert tetO2 -2 into pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp. | ||
| + | <LI>2uL of 10-fold diluted pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp- tetO2 -2 was transformed into DH10B to greatly amplify the product by using bacterial cells. | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>tetO2 – 3 (DNA binding site) | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Reverse PCR was used to insert tetO2 – 3 into pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp. | ||
| + | <LI>2uL of 10-fold diluted pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp- tetO2 – 3 was transformed into DH10B to greatly amplify the product by using bacterial cells. | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 3''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Overlap PCR (involving 3 steps) was carried out to produce the fusion protein [tetR-HNS (any length)]. | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>PCR was carried out separately for 2 genes, tetR and HNS (full length, in this case). | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Primers used were as below: | ||
| + | <LI>tetR: [forward] R-H-out-F; [reverse] R-H-tetR-R | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (FL): [forward] R-H-tetR-F-out; [reverse] R-H(FL)-2-R | ||
| + | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="width:254px;background:#99EE63;text-align:center;font-family: georgia, helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#000000;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:KAREN_Fusion_protein_gene.png|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Fusion protein genes produced separately using PCR | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Another PCR was carried out using primers with linker to insert the linker DNA to the tetR and HNS (FL) for the fusion of the 2 genes. | ||
| + | <LI>PCR was used to further amplify the product from step 2 (fusion protein gene). | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
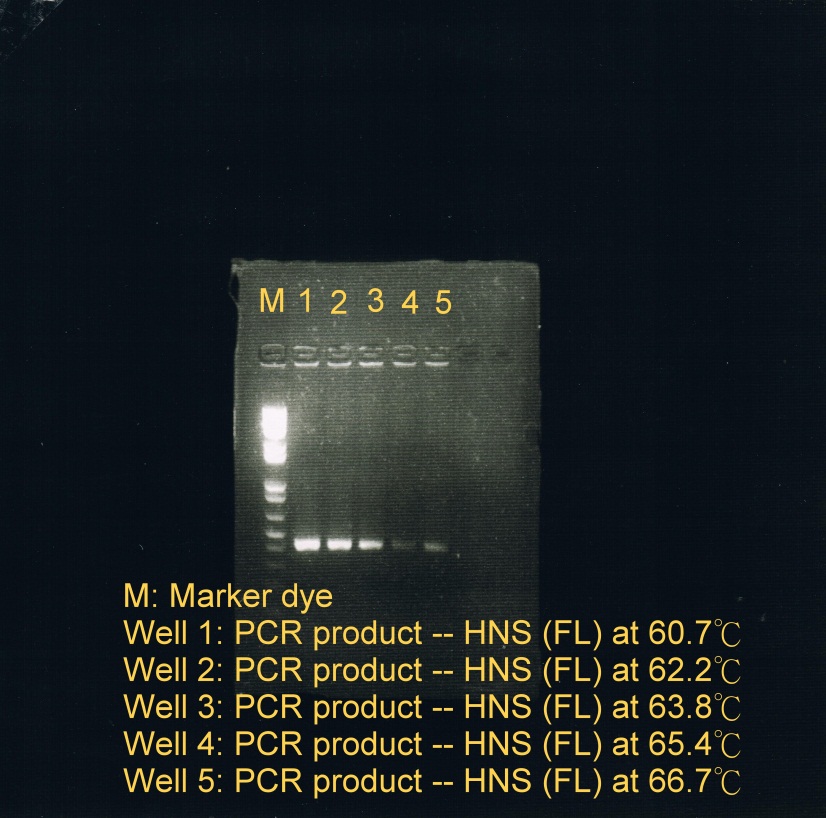
| + | <LI>PCR was used to obtain HNS(FL) at 5 different temperatures to test which temperature is optimal for annealing. | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Annealing phase at 5 different temperatures: | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>60.7C | ||
| + | <LI>62.2C | ||
| + | <LI>63.8C | ||
| + | <LI>65.4C | ||
| + | <LI>66.7C (less sample) | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Electrophoresis was carried to determine which temperature best suit the annealing phase. From the gel image, it was observed that a high concentration of products was resulted at annealing temperature between 60.7C and 62.2C. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="width:254px;background:#99EE63;text-align:center;font-family: georgia, helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#000000;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:KAREN_fusion_ptn_2.jpg|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Fusion protein genes annealed at 5 different temperatures | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 4-5''' | ||
| + | tetO2 – 0 and tetO2 – 4 | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Reverse PCR was used to insert tetO2 -0 and tetO2 – 4 into pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp. | ||
| + | <LI>2uL of pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp- tetO2 – 0 and pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp- tetO2 – 4 were transformed into DH10B separately to greatly amplify the product by using bacterial cells. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 6''' | ||
| + | Overlap PCR was carried out to produce fusion protein gene | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>HNS::tetR | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (1-46) | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (1-83) | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (1-90) | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (FL) | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>tetR::HNS | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (2-46) | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (2-83) | ||
| + | <LI>HNS (FL) | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 7''' | ||
| + | Overlap PCR was carried out to produce fusion protein gene tetR::HNS (2-90) | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>The sticky ends of the enzyme products was transformed into blunt ends using PCR. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 8''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>pROT-HNS (for BioBricks) was produced | ||
| + | <LI>Double enzyme digestion was carried out to digest the fusion protein genes and ligate them to pBS1C3 (plasmid backbone) | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>3 samples were transformed | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tetR::HNS (2-83) | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tetR::HNS (2-90) | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tetR::HNS (FL) | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Enzyme digestion was carried out for the extracted and purified plasmid tetO2-0 and tetO2-3 | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>0.5uL of CIP alkaline phosphatase was added to prevent self-ligation to each enzyme digest reaction mixture. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 9''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>tetO2 – 0 and tetO2 – 3 were ligated to form tetO2 – 0 – 3. | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>tetO2 – 0 – 3 was transformed to DH10b competent cells. | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
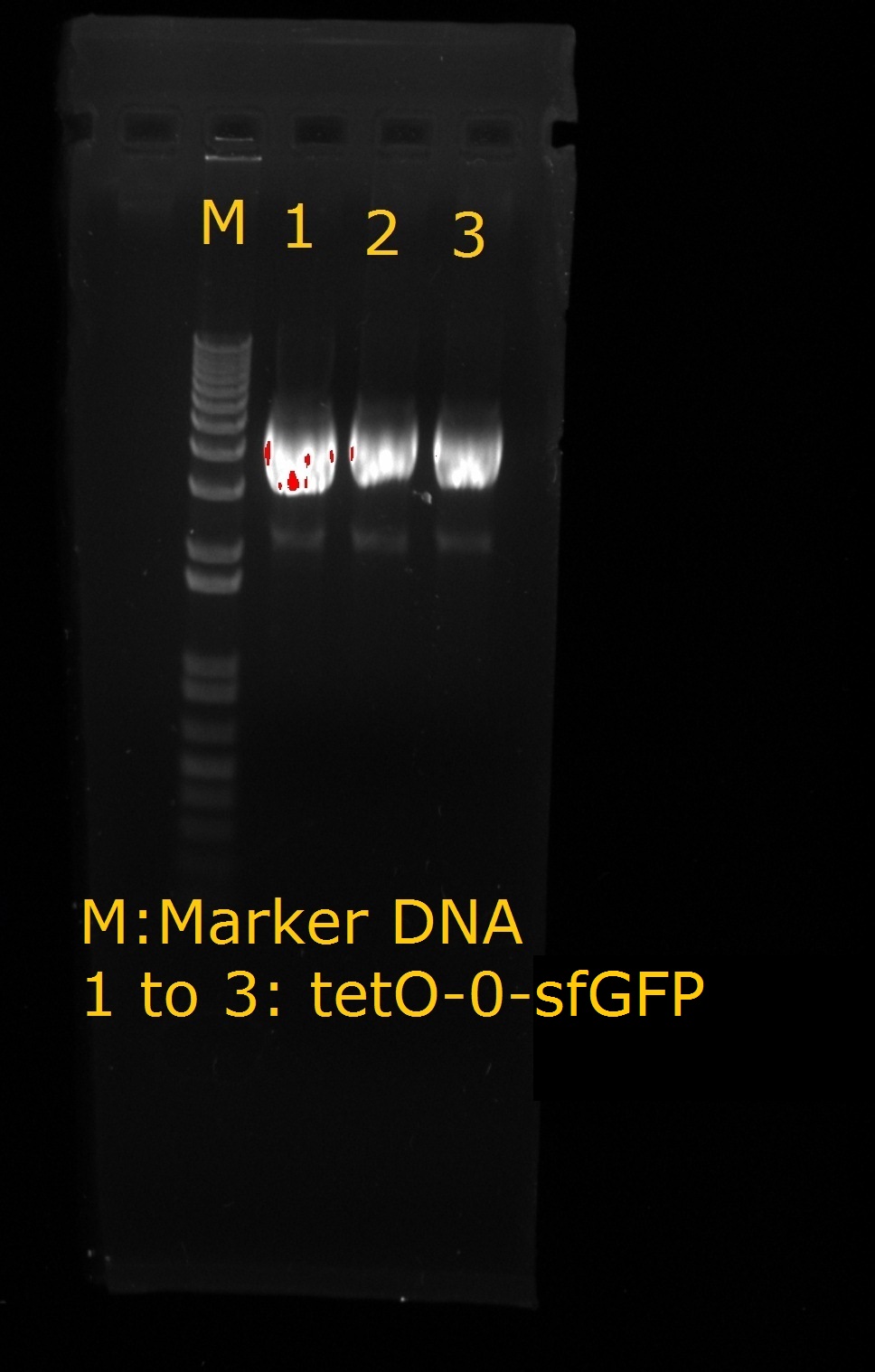
| + | <LI>Production of tetO2 – 0 –sfGFP | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="width:254px;background:#99EE63;text-align:center;font-family: georgia, helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#000000;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:TetO2-0-sfGFP.jpg|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |tetO2-0-sfGFP | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 10''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>EcoRI and PstI enzyme cut sites were added to both ends of HNS using PCR (for BioBricks construction). | ||
| + | <LI>Production of | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>J23103RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23106RH; J23106RHH | ||
| + | <LI>J23116RH; J23116RHH | ||
| + | <LI>pET28a | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tdRema | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Checking fluorescence intensity of sfGFP and EGFP | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>3 colonies from sfGFP streak plate and 1 colony from EGFP streak plate were picked. Each was inoculated into 0.5mL LB broth with 0.5uL Cm in 37C on rotary machine in warm room for around 3 hours. | ||
| + | <LI>Samples were then diluted 1:50 in fresh 2mL LB broth with 2uL Cm in 37C on rotary machine in warm room for around 3 hours. | ||
| + | <LI>Fluorescence intensity were checked at OD600 using spectrophotometer | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 11''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Production of | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>J23103R | ||
| + | <LI>J23106R | ||
| + | <LI>J23109R | ||
| + | <LI>J23116R | ||
| + | <LI>J23103RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23106RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23109RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23116RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23103RHH | ||
| + | <LI>J23106RHH | ||
| + | <LI>J23109RHH | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tetR::HNS (2-83) | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tetR::HNS (2-90) | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-tetR::HNS (FL) | ||
| + | <LI>pSB1C3-HNS | ||
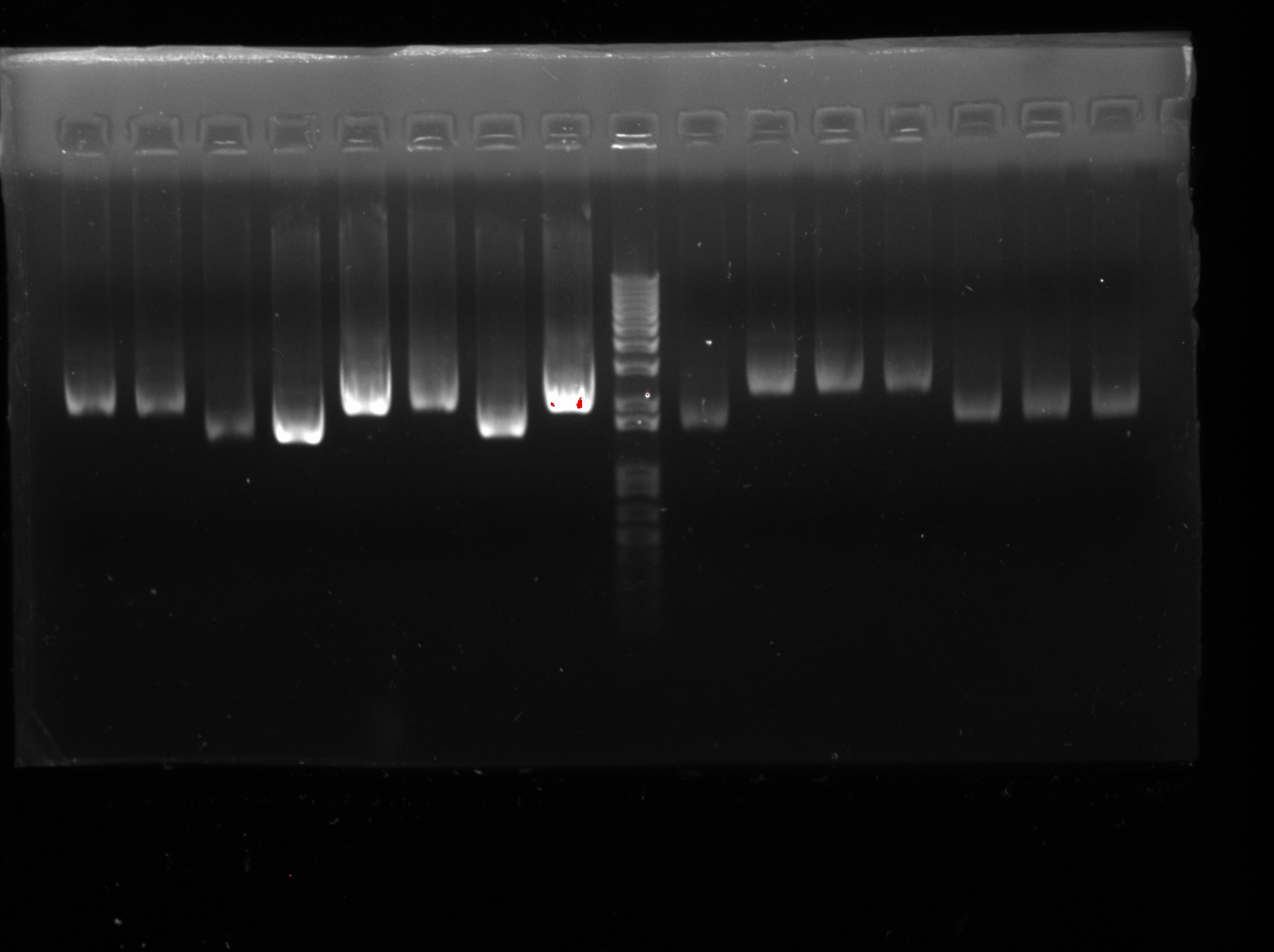
| + | <LI>Electrophoresis was carried out to confirm the success of extraction) (except J23116RH) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="width:254px;background:#99EE63;text-align:center;font-family: georgia, helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#000000;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Week_11.jpg|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Confirmation of successful extraction | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div ALIGN=CENTER> | ||
| + | {| style="width:254px;background:#99EE63;text-align:center;font-family: georgia, helvetica, arial, sans-serif;color:#000000;margin- top:5px;padding: 2px;" cellspacing="5"; | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Week_11_(2).jpg|250px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Confirmation of successful extraction | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Purification of NdeI digested pET28a | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 12''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Production of | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Bio-83 | ||
| + | <LI>Bio-90 | ||
| + | <LI>Bio-FL | ||
| + | <LI>Bio-HNS | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Transformation to competent cells using electroporation | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>tetO2 – 0 | ||
| + | <LI>tetO2 – 1 | ||
| + | <LI>sfGFP | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 13''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Production of | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Bio-HNS | ||
| + | <LI>Bio-HNS | ||
| + | <LI>pET28a-tetR | ||
| + | <LI>pET29a-HNS | ||
| + | <LI>pET28a-tetR::HNS (2-90) | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Transformation of | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>J23106RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23103R | ||
| + | <LI>J23109RHH | ||
| + | <LI>J23106R | ||
| + | <LI>J23109R | ||
| + | <LI>J23103RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23116R | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |style="width:900px;"|'''Week 14''' | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Production of J23116-tetR::HNS (2-90) | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Colony PCR was used to confirm the success of production | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Fluorescence of our samples were tested [in M1655 (with tetO-0, tetO-1 or tetO-0-sfGFP)] | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>J23109R | ||
| + | <LI>J23109RH | ||
| + | <LI>J23109RHH | ||
| + | <LI>J23116R | ||
| + | <LI>J23116RHH | ||
| + | </OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Check for the OD488 to OD510 (green fluorescence); OD600 (cell concentration in the solution) | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>With 1 set for CTC | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>Procedures | ||
| + | <OL> | ||
| + | <LI>A colony of the above samples was incubated in 3mL LB broth with antibiotics overnight. | ||
| + | <LI>1:50 diluted in M9 solution (10mL) (for CTC set: add CTC 20ug/mL). | ||
| + | <LI>Samples were then incubated at 37C for 6 hours in dark. | ||
| + | <LI>Each sample was then concentrated to 200uL. | ||
| + | <LI>Samples were loaded into a 96-well plate to check for OD using spectrophotometer. | ||
Latest revision as of 06:59, 5 October 2011
| Lab Diaries |
| Week 1
Transformation of reporter DNA (pEGFP-loxp-km-loxp) into DH10B (non-virulent strain E. coli) with antibiotic resistance (Chloramphenicol – Cm) |
Week 2
|
Week 3
|
| Week 4-5
tetO2 – 0 and tetO2 – 4
|
| Week 6
Overlap PCR was carried out to produce fusion protein gene
|
| Week 7
Overlap PCR was carried out to produce fusion protein gene tetR::HNS (2-90)
|
Week 8
|
Week 9
|
Week 10
|
Week 11
|
Week 12
|
Week 13
|
Week 14
|
 "
"