Team:NTNU Trondheim/Project
From 2011.igem.org
(→Project description) |
|||
| (12 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{:Team:NTNU_Trondheim/NTNU_header}} | ||
| - | + | ==Project description== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | '''The idea''' | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | The stringent response in bacteria is caused by amino-acid starvation, fatty acid limitation, iron limitation, heat shock and other stress conditions. As a response under these conditions, ''in vitro'' studies have suggested that the alarmone guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) increase to modulate transcription to promote survival. The increase in ppGpp levels causes a redirection of transcription so that genes important for survival are favoured at the expense of those required for growth and proliferation [1]. | ||
| + | So, could we use ppGpp as signal molecule to find out when cells are stressed? | ||
| + | '''The solution''' | ||
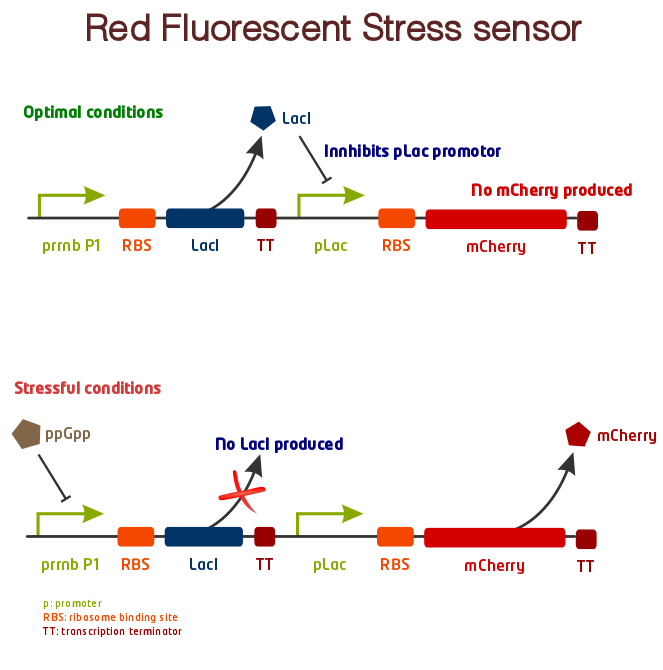
| - | + | Our system will be based on a promoter that is important for regulating growth and proliferation. At the moment we are trying to use the ''rrnB-p1'' promoter, which has been shown in earlier studies to be highly regulated by the ppGpp molecule. Hopefully the promoter will be down regulated enough by increased levels of ppGpp to turn the repressor ''lacI'' it controls completely off. The lacI represses a second promoter ''lacP'' that induces the production of a red fluorescent protein (mCherry) and turns the cells red. For a detailed overview of our system, see the figure below. | |
| - | |||
| + | [[File:NTNU2011 system.png|center|Optimal conditions: Under optimal conditions the rrnB P1 promoter promotes transcription of green fluorescent protein (GFP) and lacI. LacI represses the lacI/pL promoter and leads to no further transcription. Green germs. | ||
| + | Stressful conditions: Under stressful conditions the ppGpp concentration of the cells will increase and lead to repression of the rrnB P1 promoter. The lacI/pL promoter will no longer be repressed and start the transcription of mCherry. Red germs. | ||
| + | ]] | ||
| + | Optimal conditions: Under optimal conditions the ''rrnB P1'' lacI, which represses the ''pLac'' promoter and leads to no further transcription. | ||
| + | Stressful conditions: Under stressful conditions the ppGpp concentration of the cells will increase and lead to repression of the ''rrnB P1'' promoter. The ''pLac'' promoter will no longer be repressed and start the transcription of ''mCherry''. Red germs. | ||
| + | To see how the stress sensor turned out visit [[:Team:NTNU_Trondheim/Data|Our Data page]] | ||
| + | Reference: | ||
| - | + | [[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966842X05000788 1]] Magnusson, L. U., A. Farewell, et al. (2005). "ppGpp: a global regulator in Escherichia coli." Trends Microbiol 13(5): 236-242 | |
| - | + | {{:Team:NTNU_Trondheim/NTNU_footer}} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Latest revision as of 09:34, 21 September 2011

Project description
The idea
The stringent response in bacteria is caused by amino-acid starvation, fatty acid limitation, iron limitation, heat shock and other stress conditions. As a response under these conditions, in vitro studies have suggested that the alarmone guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) increase to modulate transcription to promote survival. The increase in ppGpp levels causes a redirection of transcription so that genes important for survival are favoured at the expense of those required for growth and proliferation [1].
So, could we use ppGpp as signal molecule to find out when cells are stressed?
The solution
Our system will be based on a promoter that is important for regulating growth and proliferation. At the moment we are trying to use the rrnB-p1 promoter, which has been shown in earlier studies to be highly regulated by the ppGpp molecule. Hopefully the promoter will be down regulated enough by increased levels of ppGpp to turn the repressor lacI it controls completely off. The lacI represses a second promoter lacP that induces the production of a red fluorescent protein (mCherry) and turns the cells red. For a detailed overview of our system, see the figure below.
Optimal conditions: Under optimal conditions the rrnB P1 lacI, which represses the pLac promoter and leads to no further transcription.
Stressful conditions: Under stressful conditions the ppGpp concentration of the cells will increase and lead to repression of the rrnB P1 promoter. The pLac promoter will no longer be repressed and start the transcription of mCherry. Red germs.
To see how the stress sensor turned out visit Our Data page
Reference:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966842X05000788 1 Magnusson, L. U., A. Farewell, et al. (2005). "ppGpp: a global regulator in Escherichia coli." Trends Microbiol 13(5): 236-242
 "
"