Team:Harvard/Results/Zinc Finger Binders
From 2011.igem.org
(→Color Blindness (CB) Bottom Hits) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
We did not have time to test all 6 targets as planned: we chose to focus on zinc finger binders to DNA tripplet TGG, which is found in the color blindness gene bottom target. | We did not have time to test all 6 targets as planned: we chose to focus on zinc finger binders to DNA tripplet TGG, which is found in the color blindness gene bottom target. | ||
| - | =Color Blindness (CB) Bottom Hits= | + | =Color Blindness (CB) Bottom Hits: 15 Possible Novel Zinc Fingers= |
We assembled the Color Blindness Bottom library, transformed it into the proper selection strain, and plated on incomplete media with varying concentrations of 3-AT. We saw colonies form, with more on the less stringent plates (NM) and fewer colonies on the higher 3-AT concentrations. Several colonies were picked and tested under varying concentrations of 3-AT in plate reader overnight, and there was a clear difference in growth between the colonies and the negative control (CB bottom binding site with Zif268). | We assembled the Color Blindness Bottom library, transformed it into the proper selection strain, and plated on incomplete media with varying concentrations of 3-AT. We saw colonies form, with more on the less stringent plates (NM) and fewer colonies on the higher 3-AT concentrations. Several colonies were picked and tested under varying concentrations of 3-AT in plate reader overnight, and there was a clear difference in growth between the colonies and the negative control (CB bottom binding site with Zif268). | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
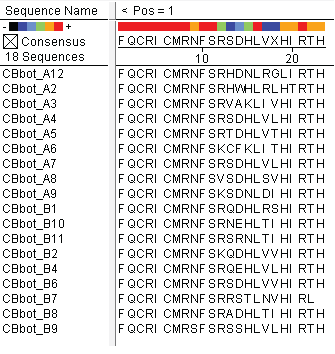
| - | These colonies were then sequenced to discover which of our library zinc fingers was successfully binding to the 5'-GTG GGA TGG-3' sequence. So far, | + | These colonies were then sequenced to discover which of our library zinc fingers was successfully binding to the 5'-GTG GGA TGG-3' sequence. So far, preliminary results indicate that 15 of the colonies have sequences consistent with the DNA sequences on the chip that was submitted, meaning that '''we have discovered up to 15 novel zinc fingers'''. The sequences consistent with the chip are CBBot_A1, A3, A4 (same as A7), A6, A8, A9, B1, B10, B11, B2, B4, B6, B7, B8, and B9. |
| + | |||
| + | All of the sequenced colonies used the Zif268 backbone, but since the TGG codon is not unlike known Zif268-based zinc finger binding sequences, this may imply that Zif268 is the optimal backbone for such a base triplet. The actual DNA-binding helix is much more variable, and we will continue to test the strength of the binding interactions of these zinc fingers and look for trends in their amino acid make-up. | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:56, 29 September 2011
We did not have time to test all 6 targets as planned: we chose to focus on zinc finger binders to DNA tripplet TGG, which is found in the color blindness gene bottom target.
Color Blindness (CB) Bottom Hits: 15 Possible Novel Zinc Fingers
We assembled the Color Blindness Bottom library, transformed it into the proper selection strain, and plated on incomplete media with varying concentrations of 3-AT. We saw colonies form, with more on the less stringent plates (NM) and fewer colonies on the higher 3-AT concentrations. Several colonies were picked and tested under varying concentrations of 3-AT in plate reader overnight, and there was a clear difference in growth between the colonies and the negative control (CB bottom binding site with Zif268).
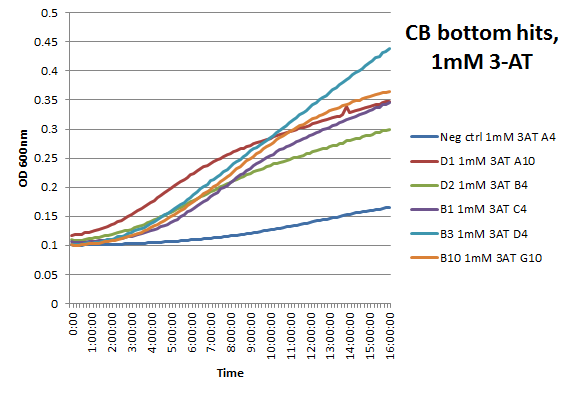 | | 
|
These colonies were then sequenced to discover which of our library zinc fingers was successfully binding to the 5'-GTG GGA TGG-3' sequence. So far, preliminary results indicate that 15 of the colonies have sequences consistent with the DNA sequences on the chip that was submitted, meaning that we have discovered up to 15 novel zinc fingers. The sequences consistent with the chip are CBBot_A1, A3, A4 (same as A7), A6, A8, A9, B1, B10, B11, B2, B4, B6, B7, B8, and B9.
All of the sequenced colonies used the Zif268 backbone, but since the TGG codon is not unlike known Zif268-based zinc finger binding sequences, this may imply that Zif268 is the optimal backbone for such a base triplet. The actual DNA-binding helix is much more variable, and we will continue to test the strength of the binding interactions of these zinc fingers and look for trends in their amino acid make-up.
 "
"








