Team:ITESM Mexico/Experimental design
From 2011.igem.org
| (10 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Team:ITESM_Mexico/Top}} | {{Team:ITESM_Mexico/Top}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | :: | + | <html><h1 class="myowntitle">Experimental design</h1> </html> |
| + | ------ | ||
| + | ::'''Concentration and photoreceptor''' | ||
| - | |||
| - | :: | + | ::''Basic steps:'' |
| - | + | *'''Transformation of competent cells with iGEM parts and our own designed parts ''' | |
| + | For both constructs parts need to be transformed. The best strain to perform the transformation is with DH5-α. The transformation is performed by the kit TransformAid Bacterial Transformation kit from Fermentas. The parts must be transformed, cultured and subcultured. There are parts with different resistances; two of the antibiotics were dissolved in water (ampicillin and kanamycin), and chloramphenicol was dissolved in absolute ethanol. The transformation is performed with synthesized parts from Genscript and the plates sent by IGEM. Then the parts are grown in bacteria by incubating them at 37°C overnight. | ||
| - | + | *'''Plasmid isolation of each part ''' | |
| + | After the transformation of bacteria the parts have to be taken to miniprep, the minipreps are proven to be better when the plasmid isolation is performed by the kit PureYield Plasmid Miniprep System from Promea, which is better than the manual method of alkaline lysis with “home-made” solutions. This kit improves the quantity of DNA obtained. This data can be compared with spectrophotometer tests by comparing the absorbance at 280 nm and 260 nm. | ||
| + | *'''Digestion of the pieces with EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI, PstI enzymes''' | ||
| + | After the quantity of DNA is determined digestion has to be made, to obtain the pieces of interest, thus the ligation can take place and the construct can be built. For this assembly we decided to follow a parallel assembly where several parts are cleaved with two enzymes and the other part with two enzymes to obtain the parts desired without complications. | ||
| + | There are pieces that are only cut by EcoRI and SpeI, and there are other parts that are cut by EcoRI and Xbal. But for the final assembly and the assembly of the individual pieces, the backbone, which has resistance to chloramphenicol, is cut by EcoRI and PstI. | ||
| + | Digestion is followed by the kit Biobrick Assembly from New England | ||
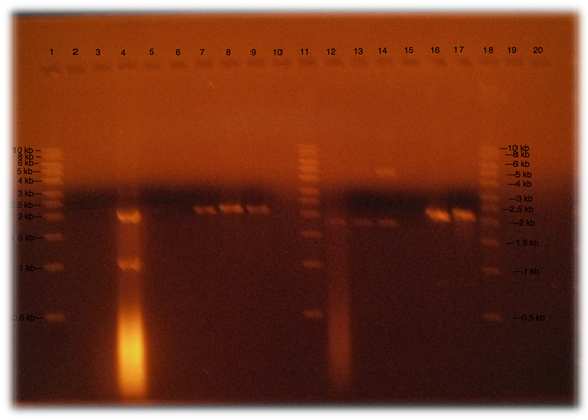
| + | *'''Run an electrophoresis gel to detect the presence of DNA''' | ||
| + | [[File:Experimental.jpg|center]] | ||
| + | After digestion an electrophoresis gel must be run. There are pieces from 35 bp to 3 kb in the construct; therefore gel must be run at different concentrations of agarose. Also we found a method that helps us to run gels 20 times faster than normal gels. This by applying lithium acetate and lithium buffer. | ||
| + | *'''Purification of gel bands to get the parts of interest''' | ||
| + | According to the kit from New England there is no need of Gel electrophoresis after digestion but is also recommended to do it to assure the presence of the parts by the presence of a band in a gel. If the gel is run a purification must be performed to obtain the DNA from the bands | ||
| + | *'''Ligation of the pieces''' | ||
| + | Pieces are ligated with the kit Biobrick Assembly from New England. Then a gel has to be performed to obtain the DNA. And after that gel is obtained a new purification and digestion can be done or a transformation in new bacteria. | ||
| + | *'''Repeat of the process of digestion and ligation to put together the whole construct ''' | ||
| - | + | *'''Confirmatory test''' | |
| - | + | To confirm the correct functioning of the construct tests with fluorocytometer must be performed, to quantify the expression when all the parts are activated or just some of the parts. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Latest revision as of 03:15, 29 September 2011
Experimental design
- Concentration and photoreceptor
- Basic steps:
- Transformation of competent cells with iGEM parts and our own designed parts
For both constructs parts need to be transformed. The best strain to perform the transformation is with DH5-α. The transformation is performed by the kit TransformAid Bacterial Transformation kit from Fermentas. The parts must be transformed, cultured and subcultured. There are parts with different resistances; two of the antibiotics were dissolved in water (ampicillin and kanamycin), and chloramphenicol was dissolved in absolute ethanol. The transformation is performed with synthesized parts from Genscript and the plates sent by IGEM. Then the parts are grown in bacteria by incubating them at 37°C overnight.
- Plasmid isolation of each part
After the transformation of bacteria the parts have to be taken to miniprep, the minipreps are proven to be better when the plasmid isolation is performed by the kit PureYield Plasmid Miniprep System from Promea, which is better than the manual method of alkaline lysis with “home-made” solutions. This kit improves the quantity of DNA obtained. This data can be compared with spectrophotometer tests by comparing the absorbance at 280 nm and 260 nm.
- Digestion of the pieces with EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI, PstI enzymes
After the quantity of DNA is determined digestion has to be made, to obtain the pieces of interest, thus the ligation can take place and the construct can be built. For this assembly we decided to follow a parallel assembly where several parts are cleaved with two enzymes and the other part with two enzymes to obtain the parts desired without complications. There are pieces that are only cut by EcoRI and SpeI, and there are other parts that are cut by EcoRI and Xbal. But for the final assembly and the assembly of the individual pieces, the backbone, which has resistance to chloramphenicol, is cut by EcoRI and PstI. Digestion is followed by the kit Biobrick Assembly from New England
- Run an electrophoresis gel to detect the presence of DNA
After digestion an electrophoresis gel must be run. There are pieces from 35 bp to 3 kb in the construct; therefore gel must be run at different concentrations of agarose. Also we found a method that helps us to run gels 20 times faster than normal gels. This by applying lithium acetate and lithium buffer.
- Purification of gel bands to get the parts of interest
According to the kit from New England there is no need of Gel electrophoresis after digestion but is also recommended to do it to assure the presence of the parts by the presence of a band in a gel. If the gel is run a purification must be performed to obtain the DNA from the bands
- Ligation of the pieces
Pieces are ligated with the kit Biobrick Assembly from New England. Then a gel has to be performed to obtain the DNA. And after that gel is obtained a new purification and digestion can be done or a transformation in new bacteria.
- Repeat of the process of digestion and ligation to put together the whole construct
- Confirmatory test
To confirm the correct functioning of the construct tests with fluorocytometer must be performed, to quantify the expression when all the parts are activated or just some of the parts.
 "
"