Team:MIT/Results/
From 2011.igem.org
| (84 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
$('.col_list li').hover(function() { | $('.col_list li').hover(function() { | ||
| - | $(this).css('background-color','# | + | $(this).css('background-color','#a3abae'); |
}, function() { | }, function() { | ||
| - | $(this).css('background-color','# | + | $(this).css('background-color','#e1e6e9'); |
}); | }); | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
<h2>Navigation</h2> | <h2>Navigation</h2> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | + | <li id="ov">Overview</li> | |
| - | <li id="parts"> | + | <li id="parts">BioBricks</li> |
| - | <li id="char"> | + | <li id="char">Transcription Factor Characterizations</li> |
| + | <li id="multi">Multi-input Logic Characterization</li> | ||
<li id="patt">Patterning Modeling Results</li> | <li id="patt">Patterning Modeling Results</li> | ||
<li id="patte">Patterning Experimental Results</li> | <li id="patte">Patterning Experimental Results</li> | ||
| - | <li id="adh"> | + | <li id="adh">Mammalian Cell Adhesion Results</li> |
| + | <li id="deliv">DNA Delivery</li> | ||
<li id="attr">Attributions</li> | <li id="attr">Attributions</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 67: | ||
<div id="col_left"> | <div id="col_left"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="content" id="ovcontent"> | ||
| + | <center><b>Communication between engineered HEK Notch senders and CHO Delta receivers.</b><br> Top: fluorescent. Bottom: brightfield. Note that due to high red-fluorescence bleed-through in the imaging process, the red fluorescence does not delineate a regular cell's morphology. However, the activation effect of delta-expressing cells communicating with notch-expressing cells is shown by the yellow fluorescence of adjacent receiver cells.</center> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/d/d0/HEK_DeltaSenders_CHO_NotchReceivers.png" style="max-width:100%; padding:5px;"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/2/23/ | ||
| + | HEKCHO_coculture_bw.png" style="max-width:100%; padding:5px;"><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><b>Timelapse of CHO cells transfected with CMV:tTA and TRE:Delta-mCherry with dox<iframe width="420" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/oHJhDiTZZCI" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></center> | ||
| + | </b> | ||
| + | <p> The video is a timelapse of CHO cells transfected with CMV:tetR and CMV-TO:Delta-mCherry. At t=0, 100ug/mL dox is added to the media. The movie is a timelapse sped up such that one second of movie time is one hour of real time. </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br>See detailed results and controls by navigating on the left!</div> | ||
<div class="content" id="delivcontent"> | <div class="content" id="delivcontent"> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 100: | ||
<p>B</p> | <p>B</p> | ||
<img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/1/1c/Specimen_001_Charles_2.fcs_gated.jpg" style="max-width:550px; margin-right:10px;"/> | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/1/1c/Specimen_001_Charles_2.fcs_gated.jpg" style="max-width:550px; margin-right:10px;"/> | ||
| + | <p>C</p> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/c/c3/MIT_fluorescence.jpg" style="max-width:100%; padding:10px;"/> | ||
<p> Figure 2: Hek293 cells were transfected with equal amounts by weight of Hef1a:mKate and Hef1a-LacO:eYFP plasmids. | <p> Figure 2: Hek293 cells were transfected with equal amounts by weight of Hef1a:mKate and Hef1a-LacO:eYFP plasmids. | ||
| - | (2A) Scatterplot displaying fluorescence levels of events as measured by flow cytometry. Events falling below the basal threshold for red fluorescence were omitted to observe "red" population. We observe that along the FITC axis, more than 99% of the red population fall above the threshold. (2B) Histogram of the same data | + | (2A) Scatterplot displaying fluorescence levels of events as measured by flow cytometry. Events falling below the basal threshold for red fluorescence were omitted to observe "red" population. We observe that along the FITC axis, more than 99% of the red population fall above the threshold. (2B) Histogram of the same data. (2C) A three plasmid cotransfection. |
<p>Many of our circuit designs involve multiple prmoter gene pairs which means multiple plasmid transfections. We run into the issue that we cannot be sure which cells received the plasmids of interest. From this excellent correlation we can be confident that most cells with one plasmid have received others. Throughout our project, we include constitutively fluorescence expressing plasmids in transfections, allowing us to gate our data based on this constitutive color. Although this method is far from perfect, it allows us to remove untransfected background from our data and obtain a reasonable profile of our tranfected population. | <p>Many of our circuit designs involve multiple prmoter gene pairs which means multiple plasmid transfections. We run into the issue that we cannot be sure which cells received the plasmids of interest. From this excellent correlation we can be confident that most cells with one plasmid have received others. Throughout our project, we include constitutively fluorescence expressing plasmids in transfections, allowing us to gate our data based on this constitutive color. Although this method is far from perfect, it allows us to remove untransfected background from our data and obtain a reasonable profile of our tranfected population. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 126: | ||
Hek293 cells display good levels of transfection efficiencies with Lipofectamine 2000. However, we found during the summer that cadherins are endogenously expressed in Hek cells, and this limits their experimental flexibility when it comes to cell-cell adhesion. CHO cells, however, do not naturally express significant levels of cadherins. Seeing also that the Notch-Delta system was previously characterized by the Elowitz group using CHO cells, we decided to port our parts into CHO cells. As documented above (3A), however, we were unable to obtain acceptable efficiency with lipofectamine in CHO cells. We then investigated alternative methods of transient transfection. | Hek293 cells display good levels of transfection efficiencies with Lipofectamine 2000. However, we found during the summer that cadherins are endogenously expressed in Hek cells, and this limits their experimental flexibility when it comes to cell-cell adhesion. CHO cells, however, do not naturally express significant levels of cadherins. Seeing also that the Notch-Delta system was previously characterized by the Elowitz group using CHO cells, we decided to port our parts into CHO cells. As documented above (3A), however, we were unable to obtain acceptable efficiency with lipofectamine in CHO cells. We then investigated alternative methods of transient transfection. | ||
<p> Nucleofection was suggested as a good alternative. We made us of the Lonza Nucleofection technology to transfect our CHO cells. The results are shown below: | <p> Nucleofection was suggested as a good alternative. We made us of the Lonza Nucleofection technology to transfect our CHO cells. The results are shown below: | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/3/3f/9-22_eyfp_4xff4_yellow.jpg' style="width:45%"> | ||
| + | <img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/0/0a/9-22_gfp_green.jpg' style="width:45%"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>The above shows the fluorescent images of CHO cells transfected with constitutive EYFP and constitutive GFP.</p> | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 136: | ||
<div class="content" id="partscontent"> | <div class="content" id="partscontent"> | ||
| - | <h1> | + | <h1>BioBricks</h1> |
| + | Total Parts Count: 68 | ||
<h2>Our Favorite Parts</h2> | <h2>Our Favorite Parts</h2> | ||
<div class="part"> | <div class="part"> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 157: | ||
<div class="end"> | <div class="end"> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| - | + | See Transcription Factor Characterizations for characterization! | |
<!--IF THE CHARACTERIZATION DOES NOT EXIST FOR THE PART, REMOVE THE ABOVE LINK.--> | <!--IF THE CHARACTERIZATION DOES NOT EXIST FOR THE PART, REMOVE THE ABOVE LINK.--> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 159: | Line 180: | ||
<div class="end"> | <div class="end"> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| - | + | See Transcription Factor Characterizations for characterization! | |
<!--IF THE CHARACTERIZATION DOES NOT EXIST FOR THE PART, REMOVE THE ABOVE LINK.--> | <!--IF THE CHARACTERIZATION DOES NOT EXIST FOR THE PART, REMOVE THE ABOVE LINK.--> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 186: | ||
<div class="part"> | <div class="part"> | ||
| - | <span class="name"><b>Name:</b> | + | <span class="name"><b>Name:</b> Delta-mCherry MammoBlock</span> |
<span class="id"> | <span class="id"> | ||
<b>ID:</b> | <b>ID:</b> | ||
| - | <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part: | + | <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511302"> |
| - | + | BBa_K511302 | |
</a> | </a> | ||
</span> | </span> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | <span class="type"><b>Type:</b> | + | <span class="type"><b>Type:</b> Signaling</span> |
| - | <span class="length"><b>Length:</b> | + | <span class="length"><b>Length:</b> 2853</span> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<div class="desc"> | <div class="desc"> | ||
| - | <p>This part encodes a | + | <p>This part encodes a fusion between the Delta-3 ligand and the monomeric mCherry red fluorescent protein.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<b>Description/Usage:</b> | <b>Description/Usage:</b> | ||
<div class="end"> | <div class="end"> | ||
<hr /> | <hr /> | ||
| - | + | See Multi-input Logic Characterization for characterization! | |
<!--IF THE CHARACTERIZATION DOES NOT EXIST FOR THE PART, REMOVE THE ABOVE LINK.--> | <!--IF THE CHARACTERIZATION DOES NOT EXIST FOR THE PART, REMOVE THE ABOVE LINK.--> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 189: | Line 210: | ||
<h2>Other Parts We Like</h2> | <h2>Other Parts We Like</h2> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511001"> |
| + | <b>BBa_K511001</b> | ||
| + | </a> minCMV-1xCI434 Promoter MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511002"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511002</b> | ||
| + | </a> minCMV-4xMnt Promoter MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511004"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511004</b> | ||
| + | </a> TRE-Tight-LacOid Promoter MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511100"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511100</b> | ||
| + | </a> EBFP2 MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511101"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511101</b> | ||
| + | </a> EYFP-FF4x4 MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511102"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511102</b> | ||
| + | </a> mKate MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511103"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511103</b> | ||
| + | </a> amCyan-miRFF4 MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511200"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511200</b> | ||
| + | </a> CI434-VP16 Transactivator MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511201"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511201</b> | ||
| + | </a> Mnt-VP16 Transactivator MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511202"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511202</b> | ||
| + | </a> rtTA-DD Transactivator MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511203"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511203</b> | ||
| + | </a> rtTA3 Tetracycline-Inducible Transactivator MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511204"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511204</b> | ||
| + | </a> LacI Repressor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511205"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511205</b> | ||
| + | </a> LacI-KRAB Repressor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511206"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511206</b> | ||
| + | </a> LacI-miRFF4 Repressor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511207"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511207</b> | ||
| + | </a> Gal4-VP16 Transactivator MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511300"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511300</b> | ||
| + | </a> Notch-Gal4-ESN Juxtacrine Signaling Receptor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511301"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511301</b> | ||
| + | </a> Notch-Gal4-VP16 Juxtacrine Signaling Receptor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511303"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511303</b> | ||
| + | </a> Delta-mCherry-4xFF4 Juxtacrine Signaling Ligand MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511400"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511400</b> | ||
| + | </a> AVPR2-TEVs-Gal4-VP16 Signaling Receptor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511401"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511401</b> | ||
| + | </a> HRH4-TEVs-GV16 Signaling Receptor MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511500"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511500</b> | ||
| + | </a> pDisplay-Vasopressin-MYC Ligand MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511600"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511600</b> | ||
| + | </a> N-Cadherin-2A-EYFP Cell Adhesion MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511700"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511700</b> | ||
| + | </a> TEV Protease MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511701"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511701</b> | ||
| + | </a> B-Arrestin-2-TEV-Protease MammoBlock</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511800"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511800</b> | ||
| + | </a> Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511801"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511801</b> | ||
| + | </a> Red Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-mKate) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511802"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511802</b> | ||
| + | </a> Red Fluorescent Delta Ligand Generator (Hef1a-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511803"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511803</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Fluorescence/Repression Generator (Hef1a-LacO-AmCyan-miRFF4) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511804"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511804</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Enhanced Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-LacO-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511805"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511805</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Yellow Fluorescence Generator (Hef1a-LacO-EYFP-4xFF4) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511806"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511806</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Red Fluorescent Ligand Generator (Hef1a-LacO-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511807"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511807</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Red Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-LacO-mKate) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511808"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511808</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-LacO-EYFP) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511809"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511809</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Tango Ligand Generator (Hef1a-LacO-pDisplay-Vasopressin-MYC) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511810"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511810</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible Tango Receptor Generator (Hef1a-LacO-AVPR2-TEVs-Gal4-VP16) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511811"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511811</b> | ||
| + | </a> Notch-Gal4-ESN Juxtacrine Receptor Generator (CMV-Notch-Gal4-ESN) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511812"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511812</b> | ||
| + | </a> CI434-VP16-Inducible Red Fluorescence Generator (minCMV-1xCI434-mKate) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511813"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511813</b> | ||
| + | </a> Mnt-VP16-Inducible Red Fluorescence Generator (minCMV-4xMnt-mKate) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511814"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511814</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Red Fluorescent Ligand Generator (TRE-Tight-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511815"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511815</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Red Fluorescent Protein Generator (TRE-Tight-mKate) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511816"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511816</b> | ||
| + | </a>Inducible Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (TRE-Tight-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511817"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511817</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (TRE-Tight-EYFP-FF4x4) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511818"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511818</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Notch-Gal4-ESN Receptor Generator (TRE-Tight-Notch-Gal4-ESN) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511819"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511819</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-Citrine) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511820"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511820</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511821"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511821</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Fluorescence/Repression Generator (UAS-Gal4-amCyan-miRFF4) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511822"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511822</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-EYFP-FF4x4) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511823"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511823</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Rd Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-mKate) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511824"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511824</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Red Fluorescent Ligand Generator (UAS-Gal4-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511825"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511825</b> | ||
| + | </a>Inducible Notch-Gal4-ESN Receptor Generator (UAS-Gal4-Notch-Gal4-ESN) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511826"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511826</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible N-Cadherin-2A-EYFP Generator (UAS-Gal4-N-Cadherin-2A-EYFP) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511900"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511900</b> | ||
| + | </a> Gal4-VP16 Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-Gal4-VP16) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511901"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511901</b> | ||
| + | </a> LacI Repressor Generator (Hef1a-LacI) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511902"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511902</b> | ||
| + | </a> rtTA3 Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511903"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511903</b> | ||
| + | </a> rtTA-DD Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-rtTA-DD) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511904"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511904</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible LacI Repressor Generator (Hef1a-LacO-LacI) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511905"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511905</b> | ||
| + | </a> Repressible rtTA3 Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-LacO-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511906"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511906</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible CI434-VP16 Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-CI434-VP16) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511907"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511907</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Mnt-VP16 Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-Mnt-VP16) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511908"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511908</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible Gal4-VP16 Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-Gal4-VP16) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511909"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511909</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible LacI Repressor Generator (TRE-Tight-LacI) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511910"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511910</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible LacI-KRAB Repressor Generator (TRE-Tight-LacI-KRAB) MammoBlock Device</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511911"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511911</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible rtTA Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511912"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511912</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible LacI Repressor Generator (UAS-Gal4-LacI) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511913"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511913</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible LacI Repressor Generator (UAS-Gal4-LacI-KRAB) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511914"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511914</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible rtTA3 Transactivator Generator (UAS-Gal4-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K511915"> | ||
| + | <b>BBa_K511915</b> | ||
| + | </a> Inducible rtTA-DD Transactivator Generator (UAS-Gal4-rtTA-DD) MammoBlock Device </p> | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | ||
<div class="content" id="charcontent"> | <div class="content" id="charcontent"> | ||
| - | <h1> | + | <h1>Transcription Factor Characterizations</h1> |
<p>The characterization of newly constructed biological parts as described below.</p> | <p>The characterization of newly constructed biological parts as described below.</p> | ||
<h2>List of characterizations</h2> | <h2>List of characterizations</h2> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | + | ||
<li><a href="#tre">rtTA3/TRE promoter</a></li> | <li><a href="#tre">rtTA3/TRE promoter</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="#gal4">Gal4/UAS promoter</a></li> | <li><a href="#gal4">Gal4/UAS promoter</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="#laci">LacI/Hef1a-LacO repressor</a></li> | <li><a href="#laci">LacI/Hef1a-LacO repressor</a></li> | ||
| - | |||
<li><a href="#cmv-to">CMV-TetO promoter</a></li> | <li><a href="#cmv-to">CMV-TetO promoter</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="#mnt">Mnt-VP16/Mnt promoter</a></li> | <li><a href="#mnt">Mnt-VP16/Mnt promoter</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="#ci434">CI434-VP16/CI434 promoter</a></li> | <li><a href="#ci434">CI434-VP16/CI434 promoter</a></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<h3><a id="tre">rtTA3/TRE promoter</a></h3> | <h3><a id="tre">rtTA3/TRE promoter</a></h3> | ||
| + | <center><img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/d/d7/TRE_Delta_mCherry_Ladder.png' style="width:50%"> | ||
<img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/thumb/c/c0/TRE_Delta-mCherry_Dox_ladder.jpg/800px-TRE_Delta-mCherry_Dox_ladder.jpg' style="width:500px"> | <img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/thumb/c/c0/TRE_Delta-mCherry_Dox_ladder.jpg/800px-TRE_Delta-mCherry_Dox_ladder.jpg' style="width:500px"> | ||
| - | < | + | <iframe width="420" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/oHJhDiTZZCI" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></center> |
<h4>Explanation:</h4> | <h4>Explanation:</h4> | ||
<p>The rtTA3 system relies on two elements: the rtTA3 gene which encodes an activator and the TRE promoter which rtTA3 binds to. Upon doxcycline binding to rtTA3, it is able to to bind to TRE and activate expression of downstream genes. In this particular experiment, we transfected Hek293 cells with 266 ng each of Hef1a:eBFP2, Hef1a:rtTA3, and TRE:delta-mCherry constructs. Cells were then induced with varying levels of doxycycline for 48 hours before FACS. Because we generally observe >50% transfection efficiency with Lipofectamine in Hek293 cells, we took only the top 50% of cells by TxRed signal for the displayed data. We display the mean TxRed intensity for the top 50% of events verus doxycycline concentration. Control cells were given the same set of DNA but without Hef1a:rtTA3.</p> | <p>The rtTA3 system relies on two elements: the rtTA3 gene which encodes an activator and the TRE promoter which rtTA3 binds to. Upon doxcycline binding to rtTA3, it is able to to bind to TRE and activate expression of downstream genes. In this particular experiment, we transfected Hek293 cells with 266 ng each of Hef1a:eBFP2, Hef1a:rtTA3, and TRE:delta-mCherry constructs. Cells were then induced with varying levels of doxycycline for 48 hours before FACS. Because we generally observe >50% transfection efficiency with Lipofectamine in Hek293 cells, we took only the top 50% of cells by TxRed signal for the displayed data. We display the mean TxRed intensity for the top 50% of events verus doxycycline concentration. Control cells were given the same set of DNA but without Hef1a:rtTA3.</p> | ||
| - | <p> We can clearly observe a steep increase in red signal which levels off at dox levels above 0.5 ug/mL. Meanwhile the control cells remain at baseline, showing that doxycyline itself does not affect fluoresence levels. | + | <p> We can clearly observe a steep increase in red signal which levels off at dox levels above 0.5 ug/mL. Meanwhile the control cells remain at baseline, showing that doxycyline itself does not affect fluoresence levels.</p> |
| + | <p> The video is a timelapse of CHO cells transfected with CMV:tTA and TRE:Delta-mCherry. At t=0, 100ug/mL dox is added to the media. The movie is a timelapse sped up such that one second of movie time is one hour of real time. | ||
<h3><a id="gal4">Gal4/UAS promoter</a></h3> | <h3><a id="gal4">Gal4/UAS promoter</a></h3> | ||
| Line 235: | Line 519: | ||
As can be seen in the figure above, we see significant inhibition of eYFP expression with addition of a Hef1a:lacI construct (around 20 fold decrease). Finally, as we increase IPTG levels, we see mean yellow fluorescence increase as lacI inhibition is relieved. We also incorporate our UAS/Gal4 system by putting lacI expression under control of UAS, thus giving us a different constitutive level of lacI production. Again we observe inhibition of lacO by lacI relieved by IPTG. | As can be seen in the figure above, we see significant inhibition of eYFP expression with addition of a Hef1a:lacI construct (around 20 fold decrease). Finally, as we increase IPTG levels, we see mean yellow fluorescence increase as lacI inhibition is relieved. We also incorporate our UAS/Gal4 system by putting lacI expression under control of UAS, thus giving us a different constitutive level of lacI production. Again we observe inhibition of lacO by lacI relieved by IPTG. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<h3><a id="mnt">Mnt-VP16/minCMV-4xMnt promoter</a></h3> | <h3><a id="mnt">Mnt-VP16/minCMV-4xMnt promoter</a></h3> | ||
| Line 267: | Line 536: | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="content" id="multicontent"> | ||
| + | <h1>Multi-input Logic Characterization</h1> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Here we show an experimental result of an example of what we call our internal processing module, which is essentially a 2 input chemical AND gate. Taking the individual functional transcription factor systems characterized above, we integrated them into an AND gate with two inputs: IPTG and doxycycline levels. The system integrates the UAS/GV16, rtTA3/TRE, and lacI/lacO systems described above. As discussed earlier, IPTG can bind to lacI and relieve its repression of lacO. Thus in this particular circuit, IPTG relieves inhibition of rtTA3 expression. Then, only in the presence of doxycycline can rtTA3 activate expression of the TRE controlled reporter. Therefore, we require both IPTG and dox to achieve expression of our final Delta-mCherry reporter. | ||
| + | <p>The data show the desired 2 input AND behavior. We see maximum Delta-mCherry expression at the highest levels of both dox and IPTG. We also observe significant activation at high dox levels even in the absence of IPTG. This suggests some leakiness in the lacI inhibition, allowing for some rtTA3 to be produced and activated by dox. This behavior can be addressed using a different inhibitor such as lacI-KRAB which exhibits a much stronger repression.</p> | ||
| + | <h3><a id="cascade">2-input AND Gate: Gal4-VP16→LacI¬rtTA3</a></h3> | ||
| + | <img src="http://i1087.photobucket.com/albums/j476/MITiGEM/Screenshot2011-10-28at51824PM.png" border="0" alt="Photobucket"> | ||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/thumb/0/0c/Doxiptg2inputandgate.jpg/800px-Doxiptg2inputandgate.jpg' style="width:100%"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/6/6d/Circuit_Diagram_Cascade_A.jpg' style="width:100%"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>The above graph displays flow cytometry measuring mCherry fluorescence of transfected Hek293 cells in the presence of different IPTG and doxycycline concentrations. We observe highest reporter levels at max IPTG and dox concentrations. Meanwhile, we see decreasing levels of reporter expression as we decrease either dox or IPTG levels. Note the high background, especially at high dox levels due to leakiness of lacI inhibition. </p> | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 272: | Line 558: | ||
<div class="content" id="pattcontent"> | <div class="content" id="pattcontent"> | ||
<h1>Patterning Modeling Results</h1> | <h1>Patterning Modeling Results</h1> | ||
| - | + | <p>All simulations were done using our modeling framework, <em><a href="http://igem.mit.edu/mcell.zip">mcell</a></em>. For more information on <em>mcell</em>, please look in the Tools section. Some sample runs can be downloaded from here: <a href="http://igem.mit.edu/simulations.zip">here</a>. | |
| + | |||
| + | <p>Most of our modeling was done on the following circuit:</p> | ||
| + | <p><img src="http://i.imgur.com/I96GX.png" /></p> | ||
| + | <p>MODERATE is a promoter that has moderate activity under the experimental conditions; for instance, TRE without any rtTA3 in the system would work. All cells contain this circuit; the values of all proteins are 0 at start. </p> | ||
| + | <p>We followed the model of Delta-Notch interaction proposed by Elowitz[1]. In it, Delta and Notch in the same cell cis-inhibit at a rate proportional to their amounts; Delta in one cell can bind to Notch in another cell (at a rate proportional to the available Notch and Delta), destroying both proteins and releasing the Notch Intracellular Domain (NICD), which then goes on bind to a promoter and stimulated production of genes.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Applying this model, along with standard mass action to model protein binding events and Hill equations to model promoter stimulation (along with the standard set of simplifying assumptions that go along with these methods), we arrive at the following series of differential equations: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | d[NCis]/dt = n_prod - k_cis*[NCis]*[DCis] - k_trans*[NCis]*[DTrans] | ||
| + | d[DCis]/dt = d_min + d_prod/(1+[LacI]*b_L) - k_cis*[NCis]*[DCis] | ||
| + | - k_trans*[NTrans]*[DCis] | ||
| + | d[NICD]/dt = k_trans*[NCis]*[DTrans] | ||
| + | d[Reporter]/dt = d[NCAD]/dt = d[LacI]/dt = V_max*(Gal4^h)/(k_d+Gal4^h) | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | DTrans is the amount of Delta in neighboring cells touching the current cell; likewise, NTrans is the amount of Notch in neighboring cells touching the current cell. We assumed that Delta and Notch are all located on the cell surface and are evenly distributed. NCis is the amount of Notch inside the given cell; DCis is the amount of Delta inside the given cell. The values for V_max, h, and k_d were taken from [1]; for the simulations shown on this page, n_prod = 5, d_min = 1, d_prod = 9 (so that the Delta production rate varies between 1 and 10); k_cis = 1, k_trans = 0.04, and b_L = 10. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Bimodality in HEK cells</h2> | ||
| + | <p>Running this circuit in HEK cells (modeled by setting the energy of contact between cells in CompuCell3D to -10.0 and initializing the cells with no gaps) produces stunning bimodality.</p> | ||
| + | <h3>Video</h3> | ||
| + | <iframe width="480" height="360" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/9bLE5TTHqWU?rel=0&hd=1" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> | ||
| + | <h3>Analysis</h3> | ||
| + | <p>What happens here is that, initially, all the cells develop a large amount of Delta. However, some Notch still remains in the cells, and is strongly activated; Delta production rates begin to drop because of the LacI. Some cells gain significant amounts of Notch before others, due to the random movements of the cells. Once a cell gains a significant amount of Notch, it's Delta level drops off sharply, and it ceases to activate cells in its vincinity. Thus, once a cell is fully "activated", other cells around it are much less likely to be. The stable state of such dynamics is a mosaic pattern, in which single cells are activated and are surrounded by a sea of inactivated cells.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>But what if they are not sticky?</h2> | ||
| + | <p>There is a very large discrepancy between the behavior of the circuit in HEK cells in CHO cells, which are modeled with no adhesion and are initialized with gaps in between them. In CHO cells, the following ensues: | ||
| + | <h3>Movie</h3> | ||
| + | <iframe width="480" height="360" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/BSpxpVqDULY?rel=0&hd=1" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> | ||
| + | <h3>Analysis</h3> | ||
| + | Bimodality almost completely drops off in this model. This is clear from the video; looking at the histograms, we can see that only an extremely small hump develops at the end in place of where the hump for the activated mode should be. The cells drift around randomly, most of the far away from others and thus inactivated; sometimes they bump in to one another, and a cell or two begins the road to activation, but they never stay together for long enough for the dominance of the activated cell to be established and for bimodality to be enforced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Adding in NCAD</h2> | ||
| + | <p>Now, we add in the NCad. Using the AdhesionFlex plugin, we set the adhesion strength of NCad to 1 (modifying this within reasonable bounds does not really change things much) and set the amount of NCad in CompuCell3D to equal the amount of Reporter in our BionetSolver circuit. This created the following results: | ||
| + | <h3>Movie</h3> | ||
| + | <p><iframe width="480" height="360" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/dbz4VegsJOw?rel=0&hd=1" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe><br/> | ||
| + | <h3>Analysis</h3> | ||
| + | <p>This circuit never really settles down into any clear behavior. Looking at the histograms, we can see that there is a fairly large gap between most "activated" and "non-activated" cells, but the "activated" cells have a much wider range of Reporter values and the range drifts over time. Looking at the video, one can see certain cells that end up always being unactivated, certain cells that are always activated, and certain cells with a moderate Reporter level that oscillates in a complicated fashion. What seems to be happening is that as a cell randomly becomes activated, it causes other cells to stick to it; this creates enough cells in close proximity to one another to cause more cells to activate, which weakens the aggregate structure, causing the cells to start drifting apart. Analysis of this model is ongoing. We tried clustering the cells, but standard algorithms did not do a very good job in clustering cells into groups that share the same behavior. This may be because cells seem to change behaviors -- a cell that looks like it is always off can, in the middle of the simulation, become an always on cell. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <hr/> | ||
| + | <p>[1] Sprinzak, et al. Cis-interactions between Notch and Delta generate mutually exclusive signalling states. <em>Nature</em> 465:86-90</p> | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 279: | Line 603: | ||
<h1>Patterning Experimental Results</h1> | <h1>Patterning Experimental Results</h1> | ||
| - | One of the key modules in our self-organizing cell | + | One of the key modules in our self-organizing cell project is intercellular communication. We achieved this through the use of the Notch/Delta signalling system. As described under the Project page, Notch/Delta is a cell-cell contact based signalling system with Delta acting as the sending ligand and Notch as the receiver. |
| - | The Notch we used was a fusion of the Notch extracellular domain with an intracellular Gal4 domain. Upon Delta binding, the intracellular domain is cleaved and Gal4 can migrate to the nucleus and activate UAS. In the following experiments, we tested out this interaction | + | The Notch we used was a fusion of the Notch extracellular domain with an intracellular Gal4 domain. Upon Delta binding, the intracellular domain is cleaved and Gal4 can migrate to the nucleus and activate UAS. In the following experiments, we tested out this interaction |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 297: | Line 619: | ||
<p>Purpose: These cells express Notch constitutively and inhibit Delta expression in the absence of doxycycline. In this state, they are effectively receiver type. However, as dox levels increase, we see more and more Delta expression and due to cis-inhibition, we see a switch to sender state. Because these cells allow us to observe and modulate cis-inhibition, we termed them "cis-inhibitor type". | <p>Purpose: These cells express Notch constitutively and inhibit Delta expression in the absence of doxycycline. In this state, they are effectively receiver type. However, as dox levels increase, we see more and more Delta expression and due to cis-inhibition, we see a switch to sender state. Because these cells allow us to observe and modulate cis-inhibition, we termed them "cis-inhibitor type". | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | <p> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/d/d0/HEK_DeltaSenders_CHO_NotchReceivers.png" style="max-width:49%; padding:0px;"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/0/08/Fluorescent_SendReceiver.png" style="max-width:49%;"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/2/23/ | ||
| + | HEKCHO_coculture_bw.png" style="max-width:49%; padding:0px;"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2011/b/b4/Brightfield_SendReceiver.png" style="max-width:49%; padding:0px;"> | ||
<img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/9/9a/Hek_Sender_CHO_Receiver.jpg' style="width:500px"> | <img src='https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/9/9a/Hek_Sender_CHO_Receiver.jpg' style="width:500px"> | ||
| + | <h4>Explanation:</h4> | ||
| + | <p>We decided to test our Notch/Delta constructs by performing a co-culture experiment. We transfected our Hef1a:Delta-mCherrry construct into Hek293 cells. We mixed these Hek sender cells with receiver CHO cells in the specified ratios. The results of flow cytometry are displayed above. | ||
| + | <p> From the microscopy images above, we can see clear expression of Delta-mCherry by our HEK cells. In addition, we can see activation of Notch on adjacent CHO receiver cells as seen by the presence of Citrine (yellow signal). This spatial correlation is strong evidence showing Notch activation by Delta. </p> | ||
| + | <p>The above bar chart displays average FITC signal of our cells as determined by flow cytometry. We can see an increase in fluorescence in the test samples compared to the controls. This suggests that our Delta construct is also capable of signaling to Notch.</p> | ||
| + | |||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| Line 312: | Line 637: | ||
<div class="content" id="adhcontent"> | <div class="content" id="adhcontent"> | ||
| - | <h1> | + | <h1>Mammalian Cell Adhesion Results</h1> |
| - | <p>Cadherins are | + | <p>Cadherins are a medically important calcium-dependent surface protein that can bind to same-type cadherins on other cells. The existence of different types of cadherins allows for the development of highly organized tissues, as the differential expression of different types of cadherins in various cells drives the development of complex three-dimensional structures. </p> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <p>We incorporated cadherins into our existing characterized signaling work, with the goal of achieving control of cadherin expression in mammalian cells. By integrating cadherins into our pattern-formation mechanism, we will be able to create patterns based on differential adhesion strengths between cells.</p> | ||
| + | <a href="http://s1087.photobucket.com/albums/j476/MITiGEM/?action=view&current=ncad.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://i1087.photobucket.com/albums/j476/MITiGEM/ncad.jpg" border="0" alt="Photobucket"style="max-width:100%"></a> | ||
| + | <center>Constitutive expression of NCad-eGFP.</center> | ||
| + | <p>The construct shown above uses a Ncadherin eGFP fusion protein that allows us to visualize localization of Ncadherin. Using confocal microscopy, we were able to observe membrane localization of our Ncadherin protein as expected. Additionally, we can also observe very bright signal at the cell interfaces, showing clustering of Ncad at these interfaces and thus adhesion.</p> | ||
| + | <a href="http://s1087.photobucket.com/albums/j476/MITiGEM/?action=view&current=kasj.jpg" target="_blank"><img src="http://i1087.photobucket.com/albums/j476/MITiGEM/kasj.jpg" border="0" alt="Photobucket" style="max-width:100%"></a> | ||
| + | <center>Constitutive expression of eGFP.</center> | ||
| + | <p>Meanwhile, in our control, we transfected a constitutive GFP construct. We can see diffuse cytoplasmic localization versus membrane localization. </p> | ||
| + | <p> This series of experiments show that our Ncad construct does display expected behavior and provides a promising start to incorporating adhesion into our designs. We observe membrane localization and sticking which is what we were looking for.</p> | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 325: | Line 656: | ||
The training for tissue culture work was conducted by <b>Linda Stockdale</b> in the Griffiths lab. | The training for tissue culture work was conducted by <b>Linda Stockdale</b> in the Griffiths lab. | ||
Gibson assembly techniques and FACS training from <b>Deepak Mishra</b>, one of our instructors. | Gibson assembly techniques and FACS training from <b>Deepak Mishra</b>, one of our instructors. | ||
| - | + | <b>Jonathan Babb</b>, another one of our instructors helped us with setting up the robot. | |
| - | <p>Other than the initial training, all work was done by our undergraduate team. <p> | + | <br> |
| - | Special credit belongs to <b>Semon Rezchikov</b> for simulations and modeling, <b>Jenny Cheng</b> for animations, and <b>Tiffany Huang</b> for wiki design. | + | <p>Other than the initial training, all programming, DNA, and transfection work was done by our undergraduate team. <p> |
| - | < | + | Special credit belongs to <b>Semon Rezchikov</b> for simulations and modeling, <b>Jenny Cheng</b> for animations, and <b>Tiffany Huang</b> and <b>Jenny Cheng</b> for wiki design. |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <p>Special thanks to <b>Michael Elowitz</b> for generously providing not only the CMV:hN1ECD-Gal4esn, CMV-TO:Delta-mCherry, and UAS:H2B-Citrine constructs, but also the stably integrated cell lines. We could not have implemented the Notch-Delta system without these valuable contributions. | ||
<div class="clear"></div> | <div class="clear"></div> | ||
| - | |||
</div><!--end col_left--> | </div><!--end col_left--> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Latest revision as of 04:02, 29 October 2011
Top: fluorescent. Bottom: brightfield. Note that due to high red-fluorescence bleed-through in the imaging process, the red fluorescence does not delineate a regular cell's morphology. However, the activation effect of delta-expressing cells communicating with notch-expressing cells is shown by the yellow fluorescence of adjacent receiver cells.


The video is a timelapse of CHO cells transfected with CMV:tetR and CMV-TO:Delta-mCherry. At t=0, 100ug/mL dox is added to the media. The movie is a timelapse sped up such that one second of movie time is one hour of real time.
See detailed results and controls by navigating on the left!
DNA Delivery Systems and Data Collection
Transfection Using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen)
To introduce our engineered genetic parts into mammalian cells, we employed the Lipofectamine 2000 reagent from Invitrogen, and obtained at best an 80% transfection efficiency for Hek293 cells and 10% transfection efficiency for CHO cells.Figure 1: Hek293 Lipofectamine Transfection Results
A

B

C

(1A) This scatter plot shows the distribution of the Hek293 population after it was transfected with the following DNA parts: Hef1a-LacO:eYFP and Hef1a:mKate, both of which were constitutively active, expressing yellow and red fluorescent proteins respectively. We observe a distinct shift of approximately 83% of the population in their eYFP fluorescence (FITC channel), while we observe a 69% shift in mKate fluorescence (PE-TexasRed channel). (1B) Histogram of signal intensities of the above data. (1C) The negative control sample was transfected with plasmids containing no functional promotor-gene pairs.
We were then interested in the efficiency of multiple plasmid transfections. Previous work suggests that the probabilities of uptaking different plasmids is not independent. Cells that have been succesfully transfected with one plasmid are more likely to also have been transfected with another. To show this correlation, we decided to see what percentage of cells that took up the Hef1a:mKate plasmid also took up the Hef1a-LacO:eYFP plasmid. In order to evaluate the correlation, we took all events above the observed basal PE-TexasRed fluorescence level and examined their FITC profile. We observe in the below graph that more than 99% of the red population display yellow fluorescence above basal levels (2A). We make use of this high level of correlation later.
Figure 2: Hek293 Lipofectamine Multiplasmid Transfection Results
A

B

C

Figure 2: Hek293 cells were transfected with equal amounts by weight of Hef1a:mKate and Hef1a-LacO:eYFP plasmids. (2A) Scatterplot displaying fluorescence levels of events as measured by flow cytometry. Events falling below the basal threshold for red fluorescence were omitted to observe "red" population. We observe that along the FITC axis, more than 99% of the red population fall above the threshold. (2B) Histogram of the same data. (2C) A three plasmid cotransfection.
Many of our circuit designs involve multiple prmoter gene pairs which means multiple plasmid transfections. We run into the issue that we cannot be sure which cells received the plasmids of interest. From this excellent correlation we can be confident that most cells with one plasmid have received others. Throughout our project, we include constitutively fluorescence expressing plasmids in transfections, allowing us to gate our data based on this constitutive color. Although this method is far from perfect, it allows us to remove untransfected background from our data and obtain a reasonable profile of our tranfected population.
Figure 3: CHO Lipofectamine Transfection Results
A

B

C

D

Figure 3: In the flow cytometry scatter plot and histogram above we see the fluorescence distribution of a population of CHO cells transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 and Hef1a_eBFP2, a constitutive blue color. We note that CHOs naturally emit autofluorescence, as seen in the small tail pointing upwards in the DAPI (blue) channel. This tail accounts for 8% of the population, so subtracting this from the 14.5% we observe in the transfected cells, we obtain approximately 6.5% transfection efficiency.
Transfection By Nucleofection
Hek293 cells display good levels of transfection efficiencies with Lipofectamine 2000. However, we found during the summer that cadherins are endogenously expressed in Hek cells, and this limits their experimental flexibility when it comes to cell-cell adhesion. CHO cells, however, do not naturally express significant levels of cadherins. Seeing also that the Notch-Delta system was previously characterized by the Elowitz group using CHO cells, we decided to port our parts into CHO cells. As documented above (3A), however, we were unable to obtain acceptable efficiency with lipofectamine in CHO cells. We then investigated alternative methods of transient transfection. Nucleofection was suggested as a good alternative. We made us of the Lonza Nucleofection technology to transfect our CHO cells. The results are shown below:


The above shows the fluorescent images of CHO cells transfected with constitutive EYFP and constitutive GFP.
BioBricks
Total Parts Count: 68Our Favorite Parts
Type: Regulatory Length: 1275
This part encodes a promoter with low-level, constitutive activity that can be repressed by variants of the LacI transcriptional repressor. Repression by LacI-KRAB through chromatin packing is quite effective.
See Transcription Factor Characterizations for characterization!
Type: Regulatory Length: 220
This part encodes a promoter that is inducible by variants of the Gal4 transactivator and off otherwise.
See Transcription Factor Characterizations for characterization!
Type: Signaling Length: 2853
This part encodes a fusion between the Delta-3 ligand and the monomeric mCherry red fluorescent protein.
See Multi-input Logic Characterization for characterization!
Other Parts We Like
BBa_K511001 minCMV-1xCI434 Promoter MammoBlock
BBa_K511002 minCMV-4xMnt Promoter MammoBlock
BBa_K511004 TRE-Tight-LacOid Promoter MammoBlock
BBa_K511100 EBFP2 MammoBlock
BBa_K511101 EYFP-FF4x4 MammoBlock
BBa_K511102 mKate MammoBlock
BBa_K511103 amCyan-miRFF4 MammoBlock
BBa_K511200 CI434-VP16 Transactivator MammoBlock
BBa_K511201 Mnt-VP16 Transactivator MammoBlock
BBa_K511202 rtTA-DD Transactivator MammoBlock
BBa_K511203 rtTA3 Tetracycline-Inducible Transactivator MammoBlock
BBa_K511204 LacI Repressor MammoBlock
BBa_K511205 LacI-KRAB Repressor MammoBlock
BBa_K511206 LacI-miRFF4 Repressor MammoBlock
BBa_K511207 Gal4-VP16 Transactivator MammoBlock
BBa_K511300 Notch-Gal4-ESN Juxtacrine Signaling Receptor MammoBlock
BBa_K511301 Notch-Gal4-VP16 Juxtacrine Signaling Receptor MammoBlock
BBa_K511303 Delta-mCherry-4xFF4 Juxtacrine Signaling Ligand MammoBlock
BBa_K511400 AVPR2-TEVs-Gal4-VP16 Signaling Receptor MammoBlock
BBa_K511401 HRH4-TEVs-GV16 Signaling Receptor MammoBlock
BBa_K511500 pDisplay-Vasopressin-MYC Ligand MammoBlock
BBa_K511600 N-Cadherin-2A-EYFP Cell Adhesion MammoBlock
BBa_K511700 TEV Protease MammoBlock
BBa_K511701 B-Arrestin-2-TEV-Protease MammoBlock
BBa_K511800 Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511801 Red Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-mKate) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511802 Red Fluorescent Delta Ligand Generator (Hef1a-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511803 Repressible Fluorescence/Repression Generator (Hef1a-LacO-AmCyan-miRFF4) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511804 Repressible Enhanced Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-LacO-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511805 Repressible Yellow Fluorescence Generator (Hef1a-LacO-EYFP-4xFF4) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511806 Repressible Red Fluorescent Ligand Generator (Hef1a-LacO-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511807 Repressible Red Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-LacO-mKate) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511808 Repressible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (Hef1a-LacO-EYFP) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511809 Repressible Tango Ligand Generator (Hef1a-LacO-pDisplay-Vasopressin-MYC) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511810 Repressible Tango Receptor Generator (Hef1a-LacO-AVPR2-TEVs-Gal4-VP16) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511811 Notch-Gal4-ESN Juxtacrine Receptor Generator (CMV-Notch-Gal4-ESN) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511812 CI434-VP16-Inducible Red Fluorescence Generator (minCMV-1xCI434-mKate) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511813 Mnt-VP16-Inducible Red Fluorescence Generator (minCMV-4xMnt-mKate) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511814 Inducible Red Fluorescent Ligand Generator (TRE-Tight-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511815 Inducible Red Fluorescent Protein Generator (TRE-Tight-mKate) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511816 Inducible Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (TRE-Tight-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511817 Inducible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (TRE-Tight-EYFP-FF4x4) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511818 Inducible Notch-Gal4-ESN Receptor Generator (TRE-Tight-Notch-Gal4-ESN) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511819 Inducible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-Citrine) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511820 Inducible Blue Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-EBFP2) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511821 Inducible Fluorescence/Repression Generator (UAS-Gal4-amCyan-miRFF4) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511822 Inducible Yellow Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-EYFP-FF4x4) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511823 Inducible Rd Fluorescent Protein Generator (UAS-Gal4-mKate) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511824 Inducible Red Fluorescent Ligand Generator (UAS-Gal4-Delta-mCherry) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511825 Inducible Notch-Gal4-ESN Receptor Generator (UAS-Gal4-Notch-Gal4-ESN) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511826 Inducible N-Cadherin-2A-EYFP Generator (UAS-Gal4-N-Cadherin-2A-EYFP) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511900 Gal4-VP16 Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-Gal4-VP16) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511901 LacI Repressor Generator (Hef1a-LacI) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511902 rtTA3 Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511903 rtTA-DD Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-rtTA-DD) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511904 Repressible LacI Repressor Generator (Hef1a-LacO-LacI) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511905 Repressible rtTA3 Transactivator Generator (Hef1a-LacO-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511906 Inducible CI434-VP16 Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-CI434-VP16) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511907 Inducible Mnt-VP16 Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-Mnt-VP16) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511908 Inducible Gal4-VP16 Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-Gal4-VP16) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511909 Inducible LacI Repressor Generator (TRE-Tight-LacI) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511910 Inducible LacI-KRAB Repressor Generator (TRE-Tight-LacI-KRAB) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511911 Inducible rtTA Transactivator Generator (TRE-Tight-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511912 Inducible LacI Repressor Generator (UAS-Gal4-LacI) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511913 Inducible LacI Repressor Generator (UAS-Gal4-LacI-KRAB) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511914 Inducible rtTA3 Transactivator Generator (UAS-Gal4-rtTA3) MammoBlock Device
BBa_K511915 Inducible rtTA-DD Transactivator Generator (UAS-Gal4-rtTA-DD) MammoBlock Device
Transcription Factor Characterizations
The characterization of newly constructed biological parts as described below.
List of characterizations
- rtTA3/TRE promoter
- Gal4/UAS promoter
- LacI/Hef1a-LacO repressor
- CMV-TetO promoter
- Mnt-VP16/Mnt promoter
- CI434-VP16/CI434 promoter
rtTA3/TRE promoter


Explanation:
The rtTA3 system relies on two elements: the rtTA3 gene which encodes an activator and the TRE promoter which rtTA3 binds to. Upon doxcycline binding to rtTA3, it is able to to bind to TRE and activate expression of downstream genes. In this particular experiment, we transfected Hek293 cells with 266 ng each of Hef1a:eBFP2, Hef1a:rtTA3, and TRE:delta-mCherry constructs. Cells were then induced with varying levels of doxycycline for 48 hours before FACS. Because we generally observe >50% transfection efficiency with Lipofectamine in Hek293 cells, we took only the top 50% of cells by TxRed signal for the displayed data. We display the mean TxRed intensity for the top 50% of events verus doxycycline concentration. Control cells were given the same set of DNA but without Hef1a:rtTA3.
We can clearly observe a steep increase in red signal which levels off at dox levels above 0.5 ug/mL. Meanwhile the control cells remain at baseline, showing that doxycyline itself does not affect fluoresence levels.
The video is a timelapse of CHO cells transfected with CMV:tTA and TRE:Delta-mCherry. At t=0, 100ug/mL dox is added to the media. The movie is a timelapse sped up such that one second of movie time is one hour of real time.
Gal4/UAS promoter

Explanation:
Another activator promoter pair we make use of is the Gal4-UAS system. Gal4VP16 is an activator capable of binding to UAS promoter site and activating expression of downstream genes. Here we characterize this interaction with a set of transfections. Cells were transfected with UAS:(mKate, eYFP-FF4, eBFP2, or H2B-citrine) and Hef1a:GV16. Controls lack the Hef1a:GV16 plasmid. The above graph displays mean fluoresence in the denoted channels.
As can be clearly seen, Hef1a:GV16 results in significant activation of the UAS promoter. This results in the observed increases in mean fluoresence compared to control populations. With the exception of UAS:eBFP2, we see more than 20-fold increase in mean fluorescence.
LacI/Hef1a-LacO repressor

Explanation:
In order to implement inhibition into our circuit designs, we made use of the lacO/lacI system. lacI binds a lacO site and can inhibit transcription of downstream genes. This inhibition can be relieved by binding lacI with IPTG. In order to test this part, we constructed a Hef1a-lacO promoter which is normally constitutively active until inhibition by lacI.
As can be seen in the figure above, we see significant inhibition of eYFP expression with addition of a Hef1a:lacI construct (around 20 fold decrease). Finally, as we increase IPTG levels, we see mean yellow fluorescence increase as lacI inhibition is relieved. We also incorporate our UAS/Gal4 system by putting lacI expression under control of UAS, thus giving us a different constitutive level of lacI production. Again we observe inhibition of lacO by lacI relieved by IPTG.
Mnt-VP16/minCMV-4xMnt promoter

Explanation:
Mnt is similar in role to Gal4-VP16. It binds to Mnt sites and can activate expression of downstream genes. We made a minCMV-4xMnt promoter upstream of the mKate gene. Mnt presence should activate expression of mKate and thus an increase in red fluorescence. We transfected Hek293 cells with Hef1a:rtTA3, TRE:Mnt-VP16, and minCMV-4xMnt:mKate.
From the data shown, we can clearly see an increase in mean red fluorescence upon dox addition
CI434-VP16/minCMV-1xCI434 promoter

Explanation:
CI434 is another transcriptional activator that we characterized. In order to test it, we transfected Hek293 cells with Hef1a:rtTA3, TRE:CI434-VP16, and minCMV-1xCI434:mKate. This allowed us to use dox induction to activate expression of CI434 which in turn should activate mKate expression.
The results above show a clear increase in red fluorescent signal upon dox addition. We observe around a 1.25 fold increase. We believe this is an underestimate of the actual activation strength due to lack of gating and low transfection efficiency for this experiment.
Multi-input Logic Characterization
Here we show an experimental result of an example of what we call our internal processing module, which is essentially a 2 input chemical AND gate. Taking the individual functional transcription factor systems characterized above, we integrated them into an AND gate with two inputs: IPTG and doxycycline levels. The system integrates the UAS/GV16, rtTA3/TRE, and lacI/lacO systems described above. As discussed earlier, IPTG can bind to lacI and relieve its repression of lacO. Thus in this particular circuit, IPTG relieves inhibition of rtTA3 expression. Then, only in the presence of doxycycline can rtTA3 activate expression of the TRE controlled reporter. Therefore, we require both IPTG and dox to achieve expression of our final Delta-mCherry reporter.
The data show the desired 2 input AND behavior. We see maximum Delta-mCherry expression at the highest levels of both dox and IPTG. We also observe significant activation at high dox levels even in the absence of IPTG. This suggests some leakiness in the lacI inhibition, allowing for some rtTA3 to be produced and activated by dox. This behavior can be addressed using a different inhibitor such as lacI-KRAB which exhibits a much stronger repression.
2-input AND Gate: Gal4-VP16→LacI¬rtTA3
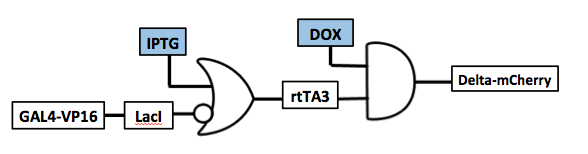


The above graph displays flow cytometry measuring mCherry fluorescence of transfected Hek293 cells in the presence of different IPTG and doxycycline concentrations. We observe highest reporter levels at max IPTG and dox concentrations. Meanwhile, we see decreasing levels of reporter expression as we decrease either dox or IPTG levels. Note the high background, especially at high dox levels due to leakiness of lacI inhibition.
Patterning Modeling Results
All simulations were done using our modeling framework, mcell. For more information on mcell, please look in the Tools section. Some sample runs can be downloaded from here: here.
Most of our modeling was done on the following circuit:

MODERATE is a promoter that has moderate activity under the experimental conditions; for instance, TRE without any rtTA3 in the system would work. All cells contain this circuit; the values of all proteins are 0 at start.
We followed the model of Delta-Notch interaction proposed by Elowitz[1]. In it, Delta and Notch in the same cell cis-inhibit at a rate proportional to their amounts; Delta in one cell can bind to Notch in another cell (at a rate proportional to the available Notch and Delta), destroying both proteins and releasing the Notch Intracellular Domain (NICD), which then goes on bind to a promoter and stimulated production of genes.
Applying this model, along with standard mass action to model protein binding events and Hill equations to model promoter stimulation (along with the standard set of simplifying assumptions that go along with these methods), we arrive at the following series of differential equations:
d[NCis]/dt = n_prod - k_cis*[NCis]*[DCis] - k_trans*[NCis]*[DTrans]
d[DCis]/dt = d_min + d_prod/(1+[LacI]*b_L) - k_cis*[NCis]*[DCis]
- k_trans*[NTrans]*[DCis]
d[NICD]/dt = k_trans*[NCis]*[DTrans]
d[Reporter]/dt = d[NCAD]/dt = d[LacI]/dt = V_max*(Gal4^h)/(k_d+Gal4^h)
DTrans is the amount of Delta in neighboring cells touching the current cell; likewise, NTrans is the amount of Notch in neighboring cells touching the current cell. We assumed that Delta and Notch are all located on the cell surface and are evenly distributed. NCis is the amount of Notch inside the given cell; DCis is the amount of Delta inside the given cell. The values for V_max, h, and k_d were taken from [1]; for the simulations shown on this page, n_prod = 5, d_min = 1, d_prod = 9 (so that the Delta production rate varies between 1 and 10); k_cis = 1, k_trans = 0.04, and b_L = 10.
Bimodality in HEK cells
Running this circuit in HEK cells (modeled by setting the energy of contact between cells in CompuCell3D to -10.0 and initializing the cells with no gaps) produces stunning bimodality.
Video
Analysis
What happens here is that, initially, all the cells develop a large amount of Delta. However, some Notch still remains in the cells, and is strongly activated; Delta production rates begin to drop because of the LacI. Some cells gain significant amounts of Notch before others, due to the random movements of the cells. Once a cell gains a significant amount of Notch, it's Delta level drops off sharply, and it ceases to activate cells in its vincinity. Thus, once a cell is fully "activated", other cells around it are much less likely to be. The stable state of such dynamics is a mosaic pattern, in which single cells are activated and are surrounded by a sea of inactivated cells.
But what if they are not sticky?
There is a very large discrepancy between the behavior of the circuit in HEK cells in CHO cells, which are modeled with no adhesion and are initialized with gaps in between them. In CHO cells, the following ensues:
Movie
Analysis
Bimodality almost completely drops off in this model. This is clear from the video; looking at the histograms, we can see that only an extremely small hump develops at the end in place of where the hump for the activated mode should be. The cells drift around randomly, most of the far away from others and thus inactivated; sometimes they bump in to one another, and a cell or two begins the road to activation, but they never stay together for long enough for the dominance of the activated cell to be established and for bimodality to be enforced.Adding in NCAD
Now, we add in the NCad. Using the AdhesionFlex plugin, we set the adhesion strength of NCad to 1 (modifying this within reasonable bounds does not really change things much) and set the amount of NCad in CompuCell3D to equal the amount of Reporter in our BionetSolver circuit. This created the following results:
Movie
Analysis
This circuit never really settles down into any clear behavior. Looking at the histograms, we can see that there is a fairly large gap between most "activated" and "non-activated" cells, but the "activated" cells have a much wider range of Reporter values and the range drifts over time. Looking at the video, one can see certain cells that end up always being unactivated, certain cells that are always activated, and certain cells with a moderate Reporter level that oscillates in a complicated fashion. What seems to be happening is that as a cell randomly becomes activated, it causes other cells to stick to it; this creates enough cells in close proximity to one another to cause more cells to activate, which weakens the aggregate structure, causing the cells to start drifting apart. Analysis of this model is ongoing. We tried clustering the cells, but standard algorithms did not do a very good job in clustering cells into groups that share the same behavior. This may be because cells seem to change behaviors -- a cell that looks like it is always off can, in the middle of the simulation, become an always on cell.
[1] Sprinzak, et al. Cis-interactions between Notch and Delta generate mutually exclusive signalling states. Nature 465:86-90
Patterning Experimental Results
One of the key modules in our self-organizing cell project is intercellular communication. We achieved this through the use of the Notch/Delta signalling system. As described under the Project page, Notch/Delta is a cell-cell contact based signalling system with Delta acting as the sending ligand and Notch as the receiver. The Notch we used was a fusion of the Notch extracellular domain with an intracellular Gal4 domain. Upon Delta binding, the intracellular domain is cleaved and Gal4 can migrate to the nucleus and activate UAS. In the following experiments, we tested out this interaction ----TO-DMC (Sender) cells
CHO T-REx stably integrated with: pcDNA5/TO‐Deltamcherry
Purpose: These cells normally inhibit expression of Delta-mCherry. However, doxycyline can relieve this repression and start expression of Delta. These cells can only send using their Delta ligand, so we termed them "senders".
hN1G4esn‐No‐Delta (Receiver Type)
CHO T-REx stably integrated with: CMV-Cerulean, UAS-H2B-Citrine, pcDNA3‐hNECD‐Gal4esn
Purpose: These cells express Notch constitutively and have a Histone-Citrine fusion under UAS control as the readout. We termed these cells as receivers.
hN1G4esn (Cis-inhibitor Type)
CHO T-REx stably integrated with: CMV-Cerulean, UAS-H2B-Citrine, pcDNA3‐hNECD‐Gal4esn, pcDNA5/TO‐Deltamcherry
Purpose: These cells express Notch constitutively and inhibit Delta expression in the absence of doxycycline. In this state, they are effectively receiver type. However, as dox levels increase, we see more and more Delta expression and due to cis-inhibition, we see a switch to sender state. Because these cells allow us to observe and modulate cis-inhibition, we termed them "cis-inhibitor type".





Explanation:
We decided to test our Notch/Delta constructs by performing a co-culture experiment. We transfected our Hef1a:Delta-mCherrry construct into Hek293 cells. We mixed these Hek sender cells with receiver CHO cells in the specified ratios. The results of flow cytometry are displayed above.
From the microscopy images above, we can see clear expression of Delta-mCherry by our HEK cells. In addition, we can see activation of Notch on adjacent CHO receiver cells as seen by the presence of Citrine (yellow signal). This spatial correlation is strong evidence showing Notch activation by Delta.
The above bar chart displays average FITC signal of our cells as determined by flow cytometry. We can see an increase in fluorescence in the test samples compared to the controls. This suggests that our Delta construct is also capable of signaling to Notch.
Mammalian Cell Adhesion Results
Cadherins are a medically important calcium-dependent surface protein that can bind to same-type cadherins on other cells. The existence of different types of cadherins allows for the development of highly organized tissues, as the differential expression of different types of cadherins in various cells drives the development of complex three-dimensional structures.
We incorporated cadherins into our existing characterized signaling work, with the goal of achieving control of cadherin expression in mammalian cells. By integrating cadherins into our pattern-formation mechanism, we will be able to create patterns based on differential adhesion strengths between cells.
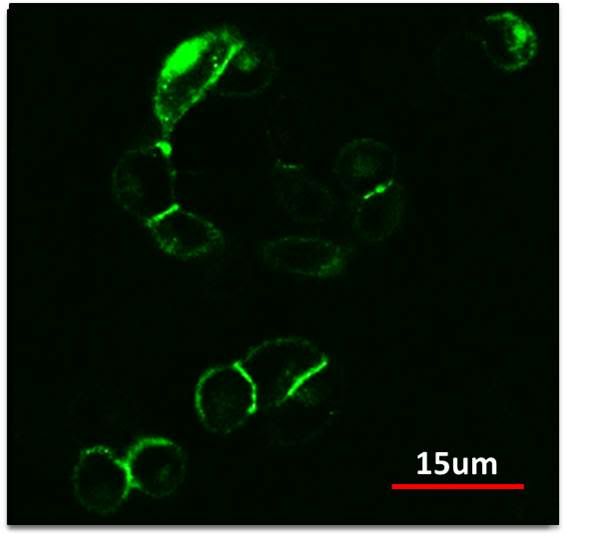
The construct shown above uses a Ncadherin eGFP fusion protein that allows us to visualize localization of Ncadherin. Using confocal microscopy, we were able to observe membrane localization of our Ncadherin protein as expected. Additionally, we can also observe very bright signal at the cell interfaces, showing clustering of Ncad at these interfaces and thus adhesion.
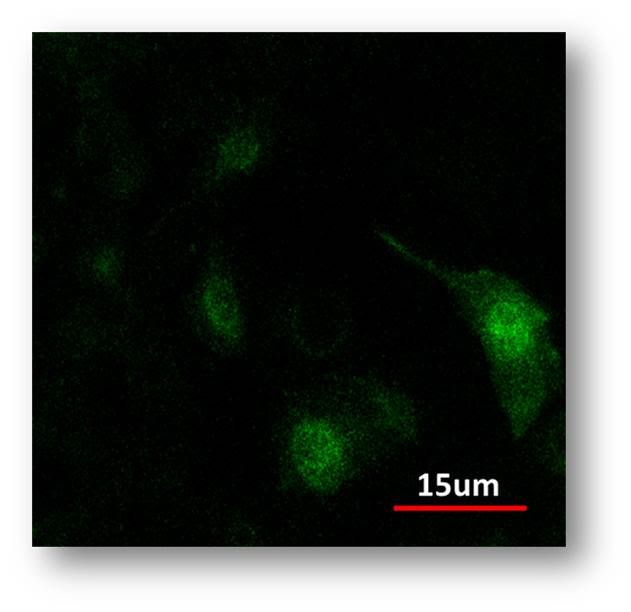
Meanwhile, in our control, we transfected a constitutive GFP construct. We can see diffuse cytoplasmic localization versus membrane localization.
This series of experiments show that our Ncad construct does display expected behavior and provides a promising start to incorporating adhesion into our designs. We observe membrane localization and sticking which is what we were looking for.
Attributions
Our instructors were very helpful not only in giving feedback on our designs, cloning strategies, and data, but also in training us for lab work.
The training for tissue culture work was conducted by Linda Stockdale in the Griffiths lab.
Gibson assembly techniques and FACS training from Deepak Mishra, one of our instructors.
Jonathan Babb, another one of our instructors helped us with setting up the robot.
Other than the initial training, all programming, DNA, and transfection work was done by our undergraduate team.
Special credit belongs to Semon Rezchikov for simulations and modeling, Jenny Cheng for animations, and Tiffany Huang and Jenny Cheng for wiki design.
Special thanks to Michael Elowitz for generously providing not only the CMV:hN1ECD-Gal4esn, CMV-TO:Delta-mCherry, and UAS:H2B-Citrine constructs, but also the stably integrated cell lines. We could not have implemented the Notch-Delta system without these valuable contributions.
 "
"