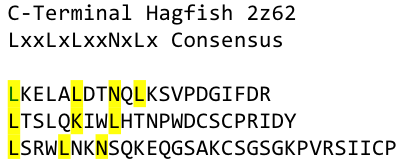Team:Freiburg/Modelling
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Modelling: Rational protein design) |
SophieCramer (Talk | contribs) (→imposing desired functions) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
|[[File:Freiburg11Modelling1.png|750px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11Modelling1.png|750px]] | ||
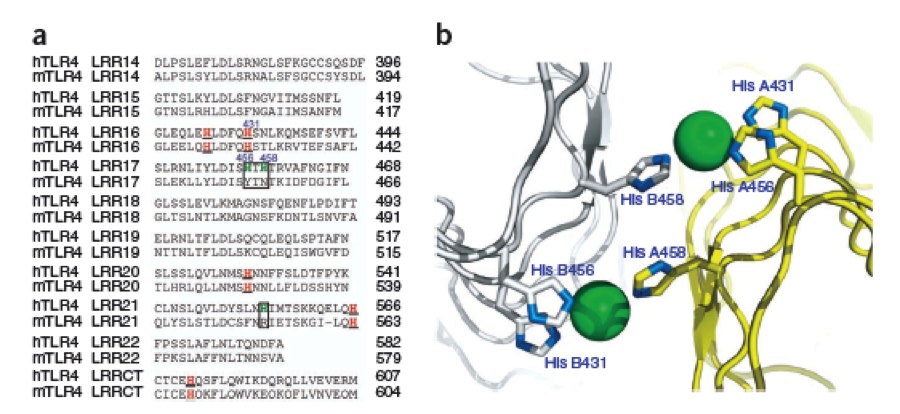
| - | + | Schmidt 2010 a) Two sequences of a TLR-4 from mice, one with mutations, a phenotype showing Nickel allergy(Histidines marked red), one wild-type without a Nickel allergy. b) assumed superimposition of Nickel ions binding on the LeucineRichRepeat structure of the TLR-4 | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | ===The core structure=== | ||
This was the necessary clue that gave answer to the question. | This was the necessary clue that gave answer to the question. | ||
In the following work, a lot of investigation about the perfect Nickel precipitating protein was done. It seemed that there is no optimal natural protein which would serves our needs. | In the following work, a lot of investigation about the perfect Nickel precipitating protein was done. It seemed that there is no optimal natural protein which would serves our needs. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 17: | ||
The Construction of a new protein | The Construction of a new protein | ||
After a long and detailed search, we found out that it is most reasonable to use bacterial LRR motifs, since they seemed very well conserved in sequence, and they are the shortest – with only 21 amino acids per LRR repeat. (Wei 2008, Kajava 1998). We wanted to have a protein as simple and as predictable in behavior and structure as possible. | After a long and detailed search, we found out that it is most reasonable to use bacterial LRR motifs, since they seemed very well conserved in sequence, and they are the shortest – with only 21 amino acids per LRR repeat. (Wei 2008, Kajava 1998). We wanted to have a protein as simple and as predictable in behavior and structure as possible. | ||
| - | Several search inquiries led to the most conserved and shortest of all bacterial LRR (PDB: | + | Several search inquiries led to the most conserved and shortest of all bacterial LRR (PDB: 3CVR), unluckily this protein is a toxin derived from ''Yersinia pestis''. We of course did not want to mess around with toxins, |
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align=right | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align=right | ||
|[[File:Freiburg11_Seq1.png|250px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11_Seq1.png|250px]] | ||
| - | + | The aminoacid sequence of a bacterial | |
| + | |||
| + | ligase we chose for our design (PDB:3CVR) | ||
|} | |} | ||
especially not with one of the black plague. We also did not know what amino acid pattern on the LRR motif would cause the toxic effect. Probably, there would have been no harm in using this protein alone, even if we did clone and express it, but why should we do that when we have a huge choice freely available anyway. Finally, we settled on the bacterial ligase PDB:3CVR. A ligase would be definitively harmless, especially since we planned to restructure it entirely. | especially not with one of the black plague. We also did not know what amino acid pattern on the LRR motif would cause the toxic effect. Probably, there would have been no harm in using this protein alone, even if we did clone and express it, but why should we do that when we have a huge choice freely available anyway. Finally, we settled on the bacterial ligase PDB:3CVR. A ligase would be definitively harmless, especially since we planned to restructure it entirely. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 32: | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" width="75%" | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" width="75%" | ||
|[[File:Freiburg11Modelling2.png|750px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11Modelling2.png|750px]] | ||
| - | + | Consensus sequences derived from the repeating loops of the 3CVR ligase to work out the conserved aminoacids and shared chemical properties of the different positions in the loops. | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
By analyzing the logo it was obvious which positions of the LRR motif were conserved and which not – AND: which of the non-conserved amino acids appeared in what kind of pattern. Were there positions in the protein that required a polar amino acid? Or a non-polar, hydrophobic /-philic, charged, non-charged one?. We compared the consensus sequence with the 3D structure, using PYMOL, to extract as much information as possible, and then came up with this ideal consensus sequence: | By analyzing the logo it was obvious which positions of the LRR motif were conserved and which not – AND: which of the non-conserved amino acids appeared in what kind of pattern. Were there positions in the protein that required a polar amino acid? Or a non-polar, hydrophobic /-philic, charged, non-charged one?. We compared the consensus sequence with the 3D structure, using PYMOL, to extract as much information as possible, and then came up with this ideal consensus sequence: | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
|[[File:Freiburg11_Seq2.png|300px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11_Seq2.png|300px]] | ||
| - | + | ideal consensus sequence extracted from the consensus motif above | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | ===imposing desired functions=== | ||
The next consideration we had to do was: how many Nickel do we need on the surface of our ideal Nickel binding protein, in what pattern, with what distances between, and at which angles toward each other to allow proper ion complexion? | The next consideration we had to do was: how many Nickel do we need on the surface of our ideal Nickel binding protein, in what pattern, with what distances between, and at which angles toward each other to allow proper ion complexion? | ||
| - | Nickel can be complexed by imidazole structures from 4 planar orthogonal directions, as well as to axial positions. It can, however, only take four ligands at once - preferably in a planar orientation. Cobalt has a bipyramidal setup for ligand-binding, too, but can take up to six ligands. The distances from an N-atom in the Imidazole ring to the ion had to be between 3 and 6 Angström. We found a crystal structure of a different protein | + | Nickel can be complexed by imidazole structures from 4 planar orthogonal directions, as well as to axial positions. It can, however, only take four ligands at once - preferably in a planar orientation. Cobalt has a bipyramidal setup for ligand-binding, too, but can take up to six ligands. The distances from an N-atom in the Imidazole ring to the ion had to be between 3 and 6 Angström. We found a crystal structure of a different protein which was resolved with three Histidines complexing a Nickel ion for a comparison, as well as some old publications that analyzed peptide ion bonds that taught us how the complex should look like. (Jordan 1974) |
We wanted our protein to be short. First in order to cause as little unspecific binding as possible and further to allow an easy expression as well as for keeping costs low for gene synthesis. For a proper purification of His-tagged proteins in Ni-NTA columns we knew that there are up to three Nickel involved in the interaction between the His tag (which consists of 6 or 7 Histidines) and the column. These have to be in close proximity to one another. There are always two Histidines of the tag binding to one ion. | We wanted our protein to be short. First in order to cause as little unspecific binding as possible and further to allow an easy expression as well as for keeping costs low for gene synthesis. For a proper purification of His-tagged proteins in Ni-NTA columns we knew that there are up to three Nickel involved in the interaction between the His tag (which consists of 6 or 7 Histidines) and the column. These have to be in close proximity to one another. There are always two Histidines of the tag binding to one ion. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 50: | ||
To get a first impression how Histidines are positioned in a bacterial Ligase, we replaced all non conserved amino acids by Histidines and sent the sequence for a 3D sequence prediction to I-TASSER, an online structure prediction software tool. | To get a first impression how Histidines are positioned in a bacterial Ligase, we replaced all non conserved amino acids by Histidines and sent the sequence for a 3D sequence prediction to I-TASSER, an online structure prediction software tool. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| Line 57: | Line 59: | ||
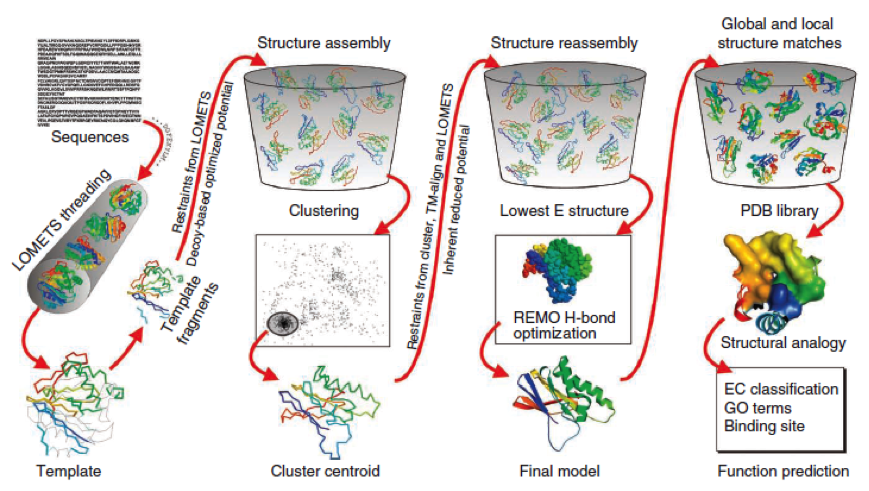
The community-wide Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) ranked the I-Tasser as the best protein prediction method in the server section. | The community-wide Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) ranked the I-Tasser as the best protein prediction method in the server section. | ||
The method of the I-Tasser can be divided into 4 stages: | The method of the I-Tasser can be divided into 4 stages: | ||
| - | Stage 1 is called threading. In this stage the sequence or parts of the sequence or motifs are compared with already known protein structures to identify evolutionary relatives and predict secondary structures. This gives a sequence profile and together with the query sequence it is threaded by LOMETS, a server combining seven threading programs which evaluate the sequence respectively the templates with an individual score | + | Stage 1 is called threading. In this stage the sequence or parts of the sequence or motifs are compared with already known protein structures to identify evolutionary relatives and predict secondary structures. This gives a sequence profile and together with the query sequence it is threaded by LOMETS, a server combining seven threading programs which evaluate the sequence respectively the templates with an individual score . The top templates are selected for further consideration. |
Stage 2 is responsible for structural assembly. The structure is modeled ab initio by aligning different templates from the threading. This is a very complex process and different programs are involved. | Stage 2 is responsible for structural assembly. The structure is modeled ab initio by aligning different templates from the threading. This is a very complex process and different programs are involved. | ||
Stage 3 is a model selection of the achievements of stage 2 with a following refinement of the predicted models. | Stage 3 is a model selection of the achievements of stage 2 with a following refinement of the predicted models. | ||
Stage 4 announces the function of the predicted molecule by its structural conformation comparing with already known proteins of PDB database. | Stage 4 announces the function of the predicted molecule by its structural conformation comparing with already known proteins of PDB database. | ||
| - | The predicted models are all evaluated by the C-Score, which assesses the quality of the prediction. It has a value from -5 to 2; the more positive the C-Score the merrier | + | The predicted models are all evaluated by the C-Score, which assesses the quality of the prediction. It has a value from -5 to 2; the more positive the C-Score the merrier and more plausible the predicted structure is. |
[[File:Freiburg11Modelling3.png|750px]] | [[File:Freiburg11Modelling3.png|750px]] | ||
| Line 72: | Line 74: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="left" | ||
| + | |[[File:Freiburg11_Seq7.png|300px]] | ||
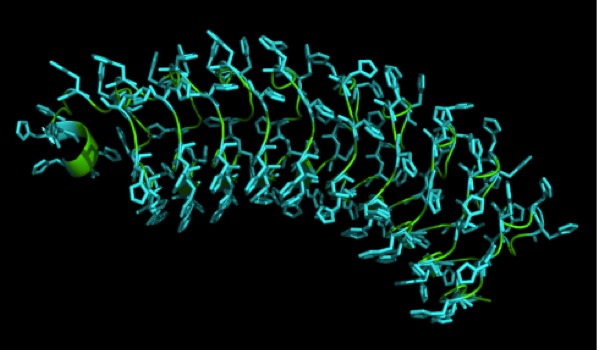
| + | first aminoacid sequence submitted to I-TASSER to determine | ||
| + | |||
| + | proper Histidine patterns on the LRR backbone's surface | ||
| + | |} | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="right" | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="right" | ||
|[[File:Freiburg11Modelling4.png|250px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11Modelling4.png|250px]] | ||
| - | + | first predicted structure used to determine proper Histidine | |
| + | |||
| + | patterns on the LRR backbone's surface | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
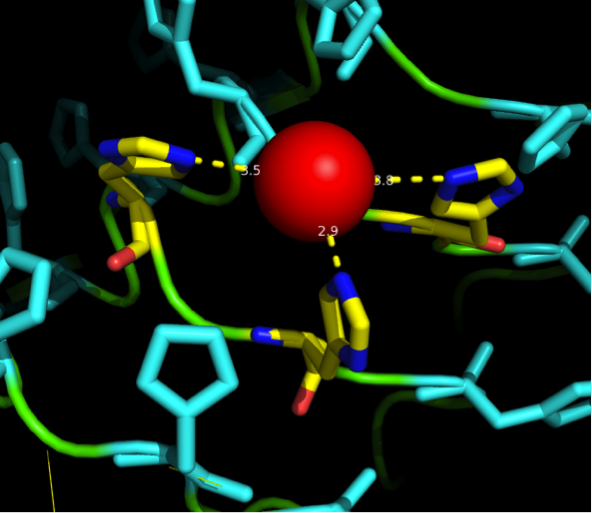
We received this pdb file with a C-score of 0.53. Obviously this was not a realistic model, since the folding would obviously be impaired by so many Histidines everywhere. But is was useful for finding several good locations where the Nickel could fit in in respect to the requirements it has for binding ligands. We manually fit in a Nickel ion, as it was crystallized in the mentioned PDB file, and measured the distances and evaluated the 3dimensional orientation of the Histidines towards the Nickel. Histidines can coordinate ligands with their free electron pair pointing planar away from the imidazole ring. What we further realized from the structure file was, that the ends of the LRR segments were “open”, meaning the hydrophobic core of the protein was exposed and as it is visible in the prediction, curled in on one end into a sort of helix. This means the protein folding is not reliable and the structure needs some sor of cap on either end in order to stabilize the LRR core motif. | We received this pdb file with a C-score of 0.53. Obviously this was not a realistic model, since the folding would obviously be impaired by so many Histidines everywhere. But is was useful for finding several good locations where the Nickel could fit in in respect to the requirements it has for binding ligands. We manually fit in a Nickel ion, as it was crystallized in the mentioned PDB file, and measured the distances and evaluated the 3dimensional orientation of the Histidines towards the Nickel. Histidines can coordinate ligands with their free electron pair pointing planar away from the imidazole ring. What we further realized from the structure file was, that the ends of the LRR segments were “open”, meaning the hydrophobic core of the protein was exposed and as it is visible in the prediction, curled in on one end into a sort of helix. This means the protein folding is not reliable and the structure needs some sor of cap on either end in order to stabilize the LRR core motif. | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="right" | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="right" | ||
|[[File:Freiburg11Modelling5.png|250px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11Modelling5.png|250px]] | ||
| - | + | superimposition of a Nickel ion into our first I-TASSER structure. | |
| + | |||
| + | Dotted lines show the distances between the atoms, angles were | ||
| + | |||
| + | analysed to see whether binding is likely to happen or not. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Histidine residues were analysed for flexibility in the backbone | ||
| + | |||
| + | and their potential to orient towards optimal binding. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
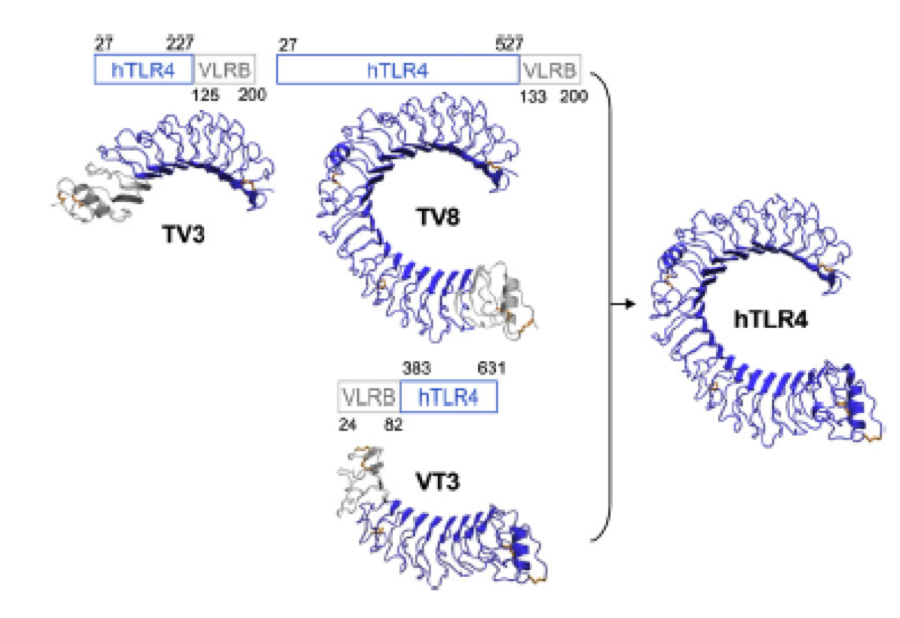
A solution to this was shown by Schmidt et. al. 2010, who crystallized the TLR-4 receptor. | A solution to this was shown by Schmidt et. al. 2010, who crystallized the TLR-4 receptor. | ||
| - | In this very useful work he dissected the TLR4(PDB: 3FXI) | + | In this very useful work he dissected the TLR4(PDB: 3FXI) into 3 parts, since it was too large and unhandy to be crystallized at once.. |
| Line 103: | Line 132: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | + | ===stabilizing the structure=== | |
| - | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align=" | + | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="right" |
|[[File:Freiburg11Modelling6.png|500px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11Modelling6.png|500px]] | ||
| - | + | Kim, Ho Min 2007: TLR-4 receptor in 3 pieces for crystallisation. Each piece was capped by Hagfish domains. Afterwards all three pieces were assembled by superimposition. | |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
To overcome this problem of an exposed hydrophobic core, he used the N- and C-terminal protein fragments of a LRR protein derived from hagfish. They tried a variety of different versions of how to glue together his fragments and these N- and C-terminal caps until they found a working one. | To overcome this problem of an exposed hydrophobic core, he used the N- and C-terminal protein fragments of a LRR protein derived from hagfish. They tried a variety of different versions of how to glue together his fragments and these N- and C-terminal caps until they found a working one. | ||
| Line 118: | Line 148: | ||
| style="width: "30%";background-color:lightgrey;" | | | style="width: "30%";background-color:lightgrey;" | | ||
; [[File:Freiburg11_Seq4.png|200px]] | ; [[File:Freiburg11_Seq4.png|200px]] | ||
| - | |||
| style="width: "30%";background-color:lightgrey;" | | | style="width: "30%";background-color:lightgrey;" | | ||
; [[File:Freiburg11_Seq5.png|200px]] | ; [[File:Freiburg11_Seq5.png|200px]] | ||
| - | |||
|[[File:Freiburg11_Seq3.png|200px]] | |[[File:Freiburg11_Seq3.png|200px]] | ||
| - | |||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | ===optimzing the sequence=== | |
| - | + | ||
After combining these caps with our structural analysis for possible Nickel binding sites and filling the empty positions of the consensus sequence with the ideal sequence derived from the ligase sequence (see above), we were still unsure whether this would work out. To increase our chances of success we designed six different versions with distinct Histidine patterns on the LRR core. | After combining these caps with our structural analysis for possible Nickel binding sites and filling the empty positions of the consensus sequence with the ideal sequence derived from the ligase sequence (see above), we were still unsure whether this would work out. To increase our chances of success we designed six different versions with distinct Histidine patterns on the LRR core. | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" width="85%" | {| style="color:black; background-color:lightgrey;" cellpadding="10%" cellpadding="15%" cellspacing="0" border="1" width="85%" | ||
| style="width: 100%;background-color:lightgrey;" | | | style="width: 100%;background-color:lightgrey;" | | ||
;[[File:Freiburg11_Seq6.png|700px]] | ;[[File:Freiburg11_Seq6.png|700px]] | ||
| - | + | Six different Histidine patterns inserted into our ideal LRR sequence, capped by Hagfish domain fragments were sent for I-TASSER structure prediction. C-Score shown under the sequence. | |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 311: | Line 337: | ||
| - | + | Nieba, L. et al BIACORE analysis of histidine-tagged proteins using a chelating NTA sensor chip. Analytical Biochemistry 252: 217-228; (1997). | |
Latest revision as of 03:54, 22 September 2011
 "
"
 Contact
Contact