Team:British Columbia/Data
From 2011.igem.org
(→Data for our Favourite New Parts) |
|||
| (38 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Template:Template_HD_1}} | {{Template:Template_HD_1}} | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <style> | ||
| + | #bod {width:935px; float:left; background-color: white; margin-left: 15px; margin-top:10px;}</style> | ||
| + | <div id="bod"></html> | ||
| + | ===Our System=== | ||
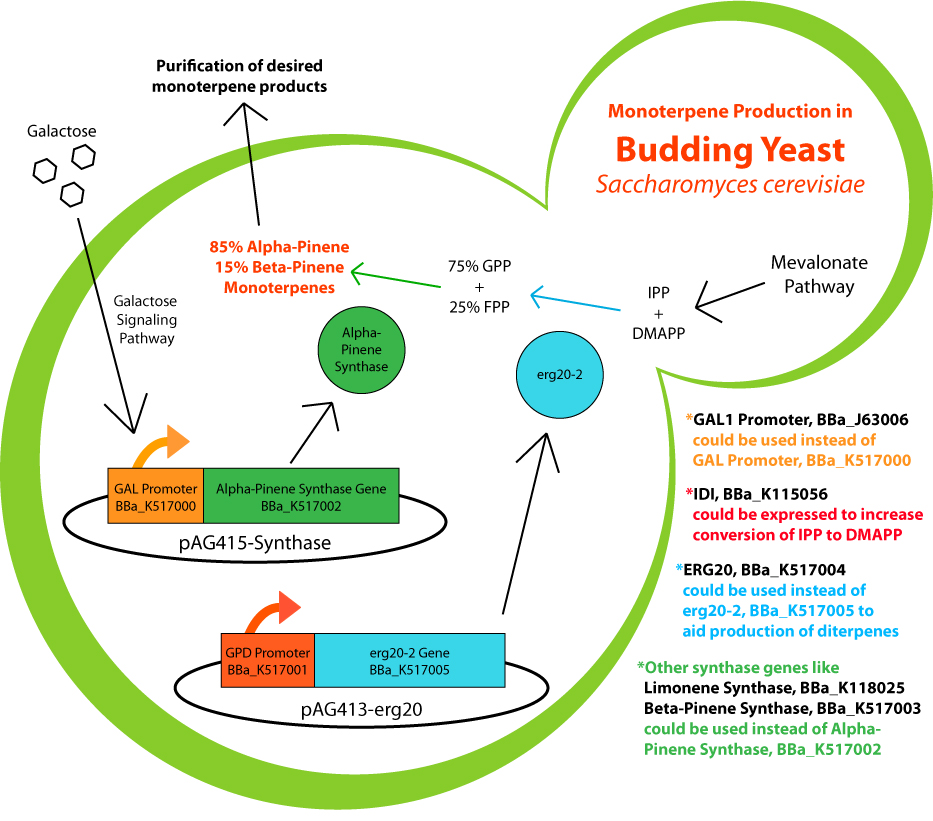
| - | + | [[File:ubcigem2011system.jpg]] | |
| - | ==Data for our Favourite New Parts== | + | ===Data for our Favourite New Parts=== |
| - | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part: | + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K517002"><b>Main Page</a> - Alpha-Pinene Synthase Gene, BBa_K517002:</b> The (-)-a-pinene synthase (PsTPS-Pin) was isolated from Sitka spruce and converts geranyl pyrophosphate to 83.4%(-)-alpha-pinene, 12.6%(-)-beta-pinene, 2.1% Linalool, 1.0% (-)-beta-phellandrene, 0.4% Camphene, and 0.4% myrcene. We characterized it by expression in C41 DE3 E. coli followed by a His-tag purification. The purified enzymes were assayed in vitro with GPP and sent for GC-MS, which confirmed alpha- and beta-pinene as products. </br></br> |
| - | |||
| - | <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part: | + | <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K517003"><b>Main Page</a> - Beta-Pinene Synthase Gene, BBa_K517003:</b> The (-)-b-pinene synthase (PsTPS-Pin2) synthase is a monoterpene synthase isolated from Sitka spruce converts geranyl pyrophosphate to 70.5%(-)-beta-pinene, 29.5%(-)-alpha-pinene. (-)-b-pinene synthase has been previously characterized by expression in C41 DE3 E. coli followed by a His-tag purification. The purified enzymes were assayed in vitro with GPP and sent for GC-MS, which confirmed alpha- and beta-pinene as products. </br></br> |
| - | + | ||
| - | <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part: | + | <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K517000"><b>Main Page</a> - GAL galactose-inducible yeast promoter, BBa_K517000:</b> Promoter can be induced when exposed to galactose in the absence of glucose. We characterized this part by placing a reporter GFP gene downstream of the promoter and determined that GFP expression was up-regulated when the yeast was shifted to galactose media.</br></br> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | ==Data for Pre-Existing Parts== | + | ===Data for Pre-Existing Parts=== |
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | <b><a href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K118025:Experience">Experience</a> - Limonene Synthase Composite + Lac promotor, BBa_K118025 (Edinburgh, iGEM 2008):</b> We expressed | + | <b><a href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K118025:Experience">Experience</a> - Limonene Synthase Composite + Lac promotor, BBa_K118025 (Edinburgh, iGEM 2008):</b> This part was previously uncharacterized. We expressed it in C41 <i>E. coli</i> that possesses a pRARE plasmid that enables it to translate proteins with rare codons. The limonene synthase was purified from a culture and subjected to an enzymatic assay for its ability to synthesize limonene monoterpene from GPP substrate. GC-MS analysis showed that limonene was produced, demonstrating that this part works!</br> |
</br> | </br> | ||
| - | <b><a href="http://partsregistry.org/Part: | + | <b><a href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J63006:Experience">Experience</a> - Yeast GAL1 Promoter, BBa_J63006:</b> We characterized this part by placing a reporter GFP gene downstream of the promoter. However, using the same protocol that successfully characterized our newly submitted BBa_K517000 GAL promoter and BBa_K517001 GPD promoter, we were not able to obtain clear evidence of BBa_J63006 promoter induction under exposure to galactose. Instead, for induction by galactose, we recommend using the BBa_K517000 GAL promoter created by our team until more evidence of BBa_J63006 functionality is obtained.</br></br> |
| - | </br></br | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <b><a href="http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K115056:Experience">Experience</a> - <i>E. coli</i> Isopentenyl Diphosphate Isomerase, BBa_K115056 (TU Delft 2008):</b> We sequenced this part using the VF2 and VR primers and found that the sequence between the original EcoRI and PstI restriction enzyme sites (1) did not contain the XbaI or SpeI sites and (2) was not homologous to any part of the IDI gene. We recommend that this part is removed from the registry and taken off distribution. | |
| + | </br></br></html> | ||
| - | + | ===We've also characterized the following parts=== | |
| - | + | <html><a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K517001"><b>Main Page</a> - GPD constitutive yeast promoter, BBa_K517001:</b> Promoter for constitutively high expression. We characterized this part by placing a reporter GFP gene downstream of the promoter and determined that GFP was expressed regardless of whether the yeast was in glucose, raffinose or galactose media.</html> | |
Latest revision as of 03:56, 18 October 2011

Contents |
Our System
Data for our Favourite New Parts
Main Page - Alpha-Pinene Synthase Gene, BBa_K517002: The (-)-a-pinene synthase (PsTPS-Pin) was isolated from Sitka spruce and converts geranyl pyrophosphate to 83.4%(-)-alpha-pinene, 12.6%(-)-beta-pinene, 2.1% Linalool, 1.0% (-)-beta-phellandrene, 0.4% Camphene, and 0.4% myrcene. We characterized it by expression in C41 DE3 E. coli followed by a His-tag purification. The purified enzymes were assayed in vitro with GPP and sent for GC-MS, which confirmed alpha- and beta-pinene as products. Main Page - Beta-Pinene Synthase Gene, BBa_K517003: The (-)-b-pinene synthase (PsTPS-Pin2) synthase is a monoterpene synthase isolated from Sitka spruce converts geranyl pyrophosphate to 70.5%(-)-beta-pinene, 29.5%(-)-alpha-pinene. (-)-b-pinene synthase has been previously characterized by expression in C41 DE3 E. coli followed by a His-tag purification. The purified enzymes were assayed in vitro with GPP and sent for GC-MS, which confirmed alpha- and beta-pinene as products. Main Page - GAL galactose-inducible yeast promoter, BBa_K517000: Promoter can be induced when exposed to galactose in the absence of glucose. We characterized this part by placing a reporter GFP gene downstream of the promoter and determined that GFP expression was up-regulated when the yeast was shifted to galactose media.
Data for Pre-Existing Parts
Experience - Limonene Synthase Composite + Lac promotor, BBa_K118025 (Edinburgh, iGEM 2008): This part was previously uncharacterized. We expressed it in C41 E. coli that possesses a pRARE plasmid that enables it to translate proteins with rare codons. The limonene synthase was purified from a culture and subjected to an enzymatic assay for its ability to synthesize limonene monoterpene from GPP substrate. GC-MS analysis showed that limonene was produced, demonstrating that this part works! Experience - Yeast GAL1 Promoter, BBa_J63006: We characterized this part by placing a reporter GFP gene downstream of the promoter. However, using the same protocol that successfully characterized our newly submitted BBa_K517000 GAL promoter and BBa_K517001 GPD promoter, we were not able to obtain clear evidence of BBa_J63006 promoter induction under exposure to galactose. Instead, for induction by galactose, we recommend using the BBa_K517000 GAL promoter created by our team until more evidence of BBa_J63006 functionality is obtained. Experience - E. coli Isopentenyl Diphosphate Isomerase, BBa_K115056 (TU Delft 2008): We sequenced this part using the VF2 and VR primers and found that the sequence between the original EcoRI and PstI restriction enzyme sites (1) did not contain the XbaI or SpeI sites and (2) was not homologous to any part of the IDI gene. We recommend that this part is removed from the registry and taken off distribution.
We've also characterized the following parts
Main Page - GPD constitutive yeast promoter, BBa_K517001: Promoter for constitutively high expression. We characterized this part by placing a reporter GFP gene downstream of the promoter and determined that GFP was expressed regardless of whether the yeast was in glucose, raffinose or galactose media.
 "
"