Team:British Columbia/Notebook/Week 20
From 2011.igem.org
Watermelon (Talk | contribs) |
(→Diterpene production in yeast with LAS and ISO) |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
#bod {width:935px; float:left; background-color: white; margin-left: 15px; margin-top:10px;}</style> | #bod {width:935px; float:left; background-color: white; margin-left: 15px; margin-top:10px;}</style> | ||
<div id="bod"><b>Week 20: Oct 16-26</b> <html><a name="w20"></a></html> | <div id="bod"><b>Week 20: Oct 16-26</b> <html><a name="w20"></a></html> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
===Diterpene production in yeast with LAS and ISO=== | ===Diterpene production in yeast with LAS and ISO=== | ||
| - | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 74: | ||
Katrin showed Daisy how to make the data and how to analyze it. | Katrin showed Daisy how to make the data and how to analyze it. | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[File:LASSlide1. | + | [[File:LASSlide1.PNG]] |
| - | + | The GC data from yeast with levopimaradiene/abietadiene synthase (extracted from pellet), no extra CYP enzyme. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | [[File:LASSlide2.PNG]] | |
| + | The GC data from yeast with levopimaradiene/abietadiene synthase (extracted from pellet), with extra CYP enzyme . | ||
| + | [[File:LASSlide4.PNG]] | ||
| + | The GC data from yeast with levopimaradiene/abietadiene synthase (extracted from supernatant), no extra CYP enzyme. | ||
| - | + | [[File:LASSlide5.PNG]] | |
| + | The GC data from yeast with levopimaradiene/abietadiene synthase (extracted from Supernatant), with extra CYP enzyme. | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:LASSlide6.PNG]] |
| + | A comparison of the GC data from the yeast pellets with LAS synthase with and without the extra CYP enzyme. | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:LASSlide7.PNG]] |
| + | A comparison of the GC data from the yeast pellets with LAS synthase with and without the extra CYP enzyme. | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:LASSlide8.PNG]] |
| + | A comparison of the GC data from the yeast supernatant with LAS synthase with and without the extra CYP enzyme. | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:LASSlide9.PNG]] |
| + | A comparison of the GC data from the yeast pellet and supernatant with the LAS synthase and the extra CYP enzyme. | ||
| - | + | [[File:LASSlide10.PNG]] | |
| + | A comparison of the GC data from the various runs in the acid region. Green is the +LAS+CYP pellet and purple is the +LAS+CYP supernatant. | ||
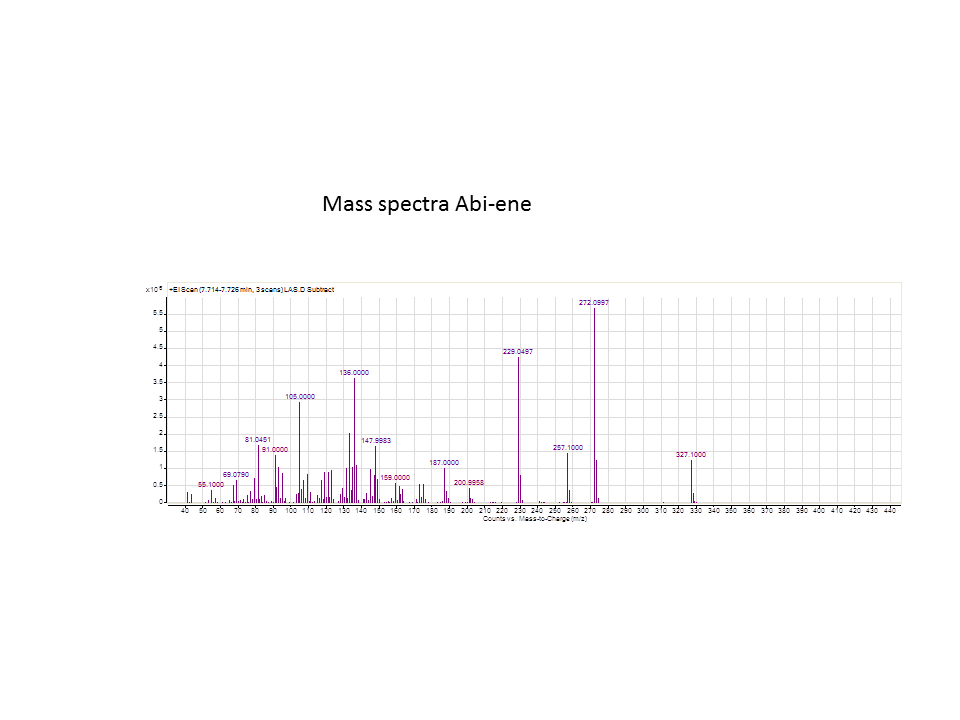
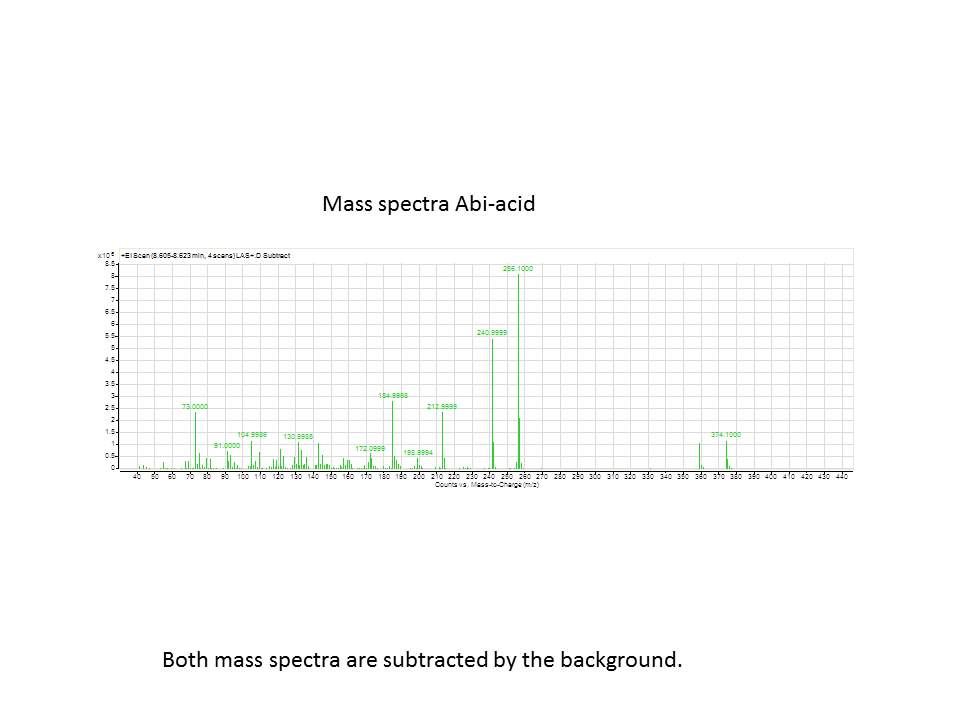
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:LASmass.png]] |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:LASslide12.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | These are the results from both runs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Katrin and Daisy finished at 9pm. Time for Daisy to go to Starbucks for coffee to fulfill my craving for caffeine. Daisy signing off.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Saccharomyces cerevisiae & Mountain Pine Beetle Co-culturing== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ubcigem2011beetleplatefungi.jpg | 300px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ubcigem2011beetleplatefungi1.jpg | 300px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ubcigem2011beetleplatefungi2.jpg |300px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ubcigem2011beetleplatefungi3.jpg | 300px]] | ||
| + | <center>[[File:Yst-MPB.jpg]]</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==G. clavigera and S. cerevisiae co-culture experiments== | ||
| - | + | We tested growth of G. clavigera and S. cerevisiae on both 1% OMEA and YPD. S. cerevisiae grows slower on 1% OMEA but the G.clavigera grows well. S. cerevisiae grows well on YPD media but the G.claviegera grows very slowly. We decided to use 1% OMEA so that both species could grow relatively well. | |
| + | [[File:5cocultureubcigem2011.jpg | thumb | right | 200px | G. clavigera mycelium growing very slowly outwards towards diterpenoid P40-producing S. cerevisiae on YPD.]] | ||
| - | + | ==Spore Co-culture== | |
| - | + | <b>Procedure</b> | |
| + | To determine if S. cerevisiae is a feasible chassis we tested its growth against G. clavigera in coculture. We used spores to simulate the conditions of a beetle entering a tree and inoculating fungal spores into the trunk. We plated the following of both on YPD and 1% OMEA plates for 4 days: | ||
| + | 1. 200 G. clavigera spores and 330 S. cerevisiae spores | ||
| + | 2. 200 G. clavigera spores | ||
| + | 3. 330 S. cerevisiae | ||
| - | + | <b>Results</b> | |
| + | When cocultured G.claviegera and S. cerevisiae mutually inhibit each other, as seen below. 54 G.claviegera spores grew on its own on 1% OMEA while 15 grew when cultured with S. cerevisiae on 1% OMEA. | ||
| - | 200 G. clavigera | + | [[File:cocultureubcigem2011.jpg | 200px ]] <br/> 200 G. clavigera spores plated on 1% OMEA for 4 days. |
| + | [[File:2cocultureubcigem2011.jpg | 200px ]] <br/> 330 S. cerevisiae spores plated on 1% OMEA for 4 days. | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:1cocultureubcigem2011.jpg | 200px ]] <br/> 200 G. clavigera + 330 S. cerevisiae spores + plated on 1% OMEA for 4 days. |
| - | + | <b>Conclusion</b> | |
| + | As the two species mutually inhibited each other's growth, S. cerevisiae may be a suitable chassis. | ||
| - | + | ==Terpene Co-culture== | |
| - | + | <b>Procedure</b> | |
| + | To determine if terpene producing yeast could inhibit G. clavigera growth, we smeared rings of 5 types of yeast onto 1% OMEA and placed plugs of G. clavigera mycelium in the centre of the plate. We wish to evaluate if the mycelium can grow past the terpenoid-producing yeast rings; this is done after a week. | ||
| + | 1. Wildtype | ||
| + | 2. ISO | ||
| + | 3. ISO P4 | ||
| + | 4. LAS | ||
| + | 5. LAS P40 | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:3cocultureubcigem2011.jpg | 200px ]] <br/> Assorted plates of G. clavigera mycelium plugs and terpenoid-producing S. cerevisiae rings. |
| - | G. clavigera mycelium growing outwards towards diterpenoid ISO-producing S. cerevisiae on 1% OMEA. | + | [[File:4cocultureubcigem2011.jpg | 200px ]] <br/>G. clavigera mycelium growing outwards towards diterpenoid ISO-producing S. cerevisiae on 1% OMEA. |
| + | <b>Results</b> | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:OMEA WT.JPG | 200px ]] 1. Wildtype <br/> |
| + | [[File:OMEA ISO.JPG | 200px ]] 2. ISO <br/> | ||
| + | [[File:OMEA ISOP4.JPG | 200px ]] 3. ISO P4 <br/> | ||
| + | [[File:OMEA LAS.JPG | 200px ]] 4. LAS <br/> | ||
| + | [[File:OMEA LASP40.JPG | 200px ]] 5. LAS P40 <br/> | ||
| - | + | ==Human Practices: Expert Opinions on Synthetic Biology Gone Wild== | |
| + | To obtain expert opinions on releasing synthetic organisms into the wild and initiate discourse on this topic, our team interviewed many experts across numerous fields at UBC. | ||
| + | For the interview transcripts and some of the key take-home messages, please view [[Team:British Columbia/Wild|Expert Opinions on Synthetic Biology Gone Wild]]! | ||
| + | <br/><br/> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:British_Columbia/Notebook"><center><b>Back to the Notebook</b></center></a> | <a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:British_Columbia/Notebook"><center><b>Back to the Notebook</b></center></a> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:45, 29 October 2011

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Contents |
Diterpene production in yeast with LAS and ISO
We obtained four yeast strains from Katrin and Niels (from Bohlmann lab).
The yeast strains contained
- Levoabietadiene synthase + CYP720B4
- Levoabietadiene synthase
- Isopimaradiene synthase + CYP720B4
- Isopimaradiene synthase
These are diterpene synthases which convert GGPP to the diterpinols, which are hydrolyzed to form diterpenes. These diterpenes can be further hydroxylated to form resin acids. CYP720B4 is an enzyme isolated by members of Bohlmann lab. This enzyme plays a key role in the production of specific acids that have been shown to have anti-white pine weevil effects.
The goal is to express diterpenes and show secretion into the media.
LAS/ISO were on pESC-HIS. GGPP synthase is also on the same plasmid as the synthases.
CYP720B4 is on another vector, -URA marked.
These experiments were conducted twice.
We obtained the protocol from Anne (Thanks anne!). There was also an extra derivitization step to produce the resin acids that required the addition of trimethylsilane (or is it Trimethylsilyl chloride). This is to ensure that the resin acids were detected (?).
Katrin was really helpful and showed Daisy and Jacob the derivization step.
After we got our first round of results, our ISO results were rather odd. Katrin was really nice and went through our results with us. She helped explain what the various peaks were and how to interpret the data and how to use the program. Katrin suggested Daisy and Marianne redo the experiments. Marianne recultured the yeast but put them in -Leu. These yeast are not -leu marked. The cultures did not grow the next day.
Another 5mL yeast culture was started. We need to transfer to 50 mL of SD media.
However, because we lacked some of the proper media, the yeast were put to SD -His -Leu media. The yeast are not -Leu marked. The yeast did not grow.
Now, another 5ml culture was started by Joe or Jacob.
The yeast were accidentally put in -His and -Leu media. However, Joe and Jacob only put it in for an hour before they realized it. The yeast were spun down and the incorrect media was poured out. Joe and Jacob were looking for SD -His media but it was Sunday and Alina was not there. Instead, they grew the yeast in YPD.
Then they switched it back to SG -His.
Daisy went to talk to Katrin and Anne the next day. Daisy explained what went wrong with the yeast. We looked at the yeast cultures and the ones without the CYP720B4 were growing fairly dense. Katrin and Anne were quite shocked at what we put the yeast through.
By putting the yeast into YPD, we are removing the selective marker. This means that the yeast can choose to get rid of the plasmid that it once needed when it was in the selective media.
Katrin then asked Daisy why it was not grown in -His and -Ura. Daisy was quite confused until she realized that the CYP720B4 was on a seperate vector that was -URA marked.
Because the entire time the yeast were not grown on -URA, it is possible that some yeast got rid of the plasmid that contained the CYP720B4 enzyme. This means that there would be less cells that would be able to produce the resin acids.
Daisy and Jacob extracted the samples. However, there was some odd contamination in the LAS sample. It appeared to be agar or some form of agarose gel.
When Daisy reported this to Katrin and Anne, both were again flabbergasted and quite shocked!
Daisy and Jacob decided not to run the LAS sample, which contained the contamination.
The samples were prepared.
Katrin helped run our samples. However Joe also wanted to run his monoterpene samples. However, this required a different program. However, none of us knew what the program was because Lina usually does it, but Lina is on vacation. Joe went to ask Chris and Chris says that we need to look at how Lina did it.
Katrin and Daisy and Joe went to go look for the program. Most of the programs were run on a DBWAX column. There was one protocol that ran on a Solgel column. However, someone was using it at the time.
Note: at this point, it is around 6pm.
Katrin and Anne try to add on the sample and do some crazy magic but somehow it does not work. It takes us another hour before we can get Joe's cineole samples to start running.
At this point, everyone is extremely tired and probably needs a coffee.
Katrin and Daisy now go and analyze the data from the latest diterpene results. The results were very interesting! Katrin did a very good job explaining to Daisy what the peaks were and how the results should be interpreted. Katrin also explained a lot of what she thinks the results may mean.
There was not any diterpenes produced from the ISO. LAS did produce diterpenes.
Katrin showed Daisy how to make the data and how to analyze it.
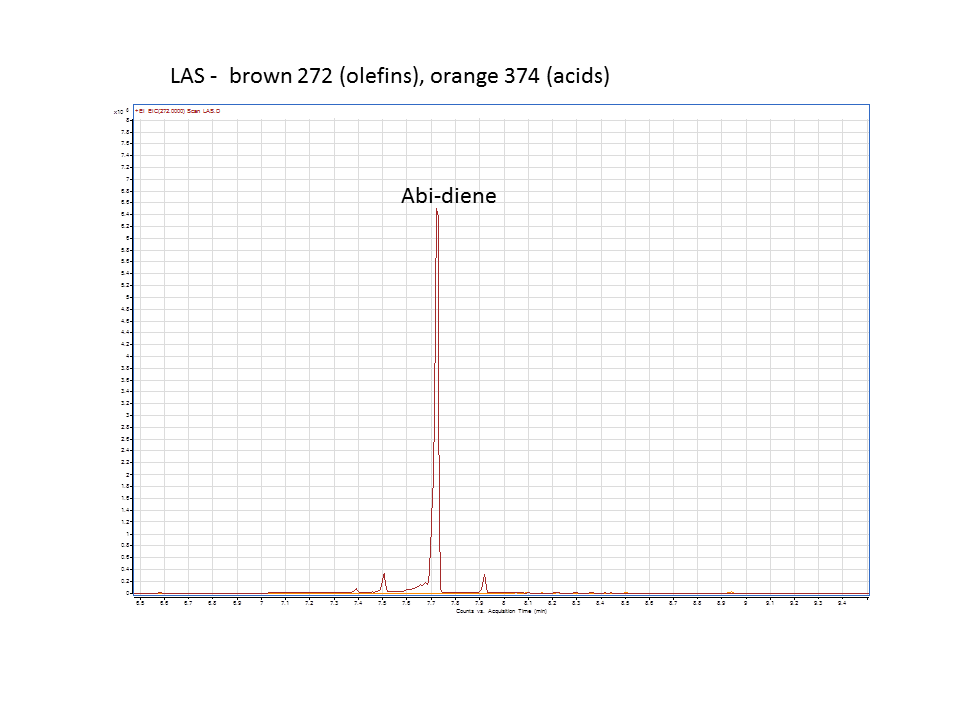
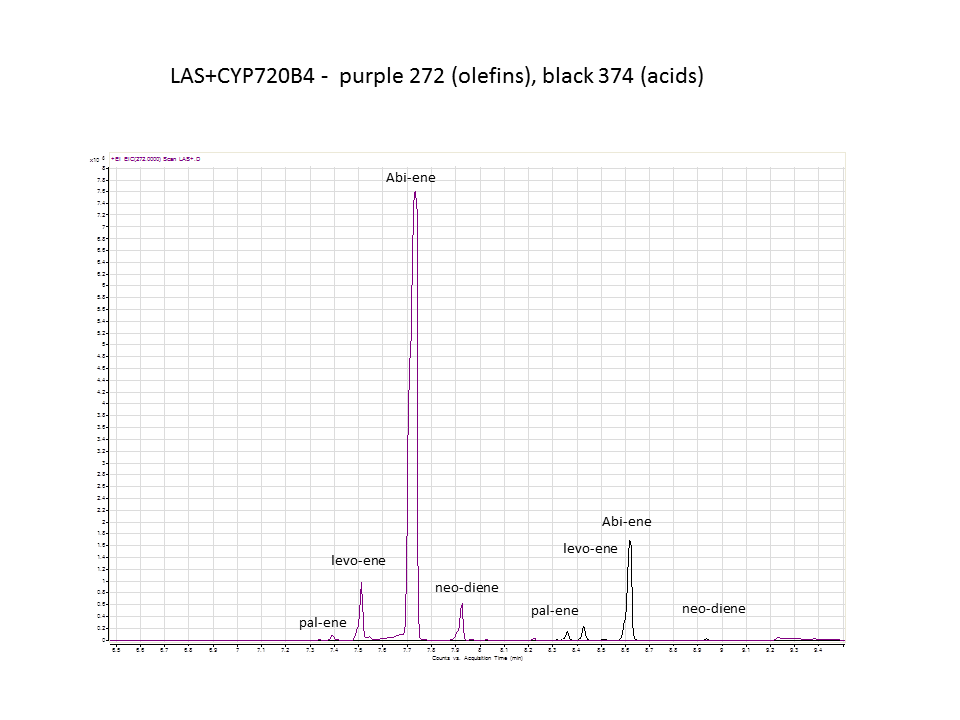
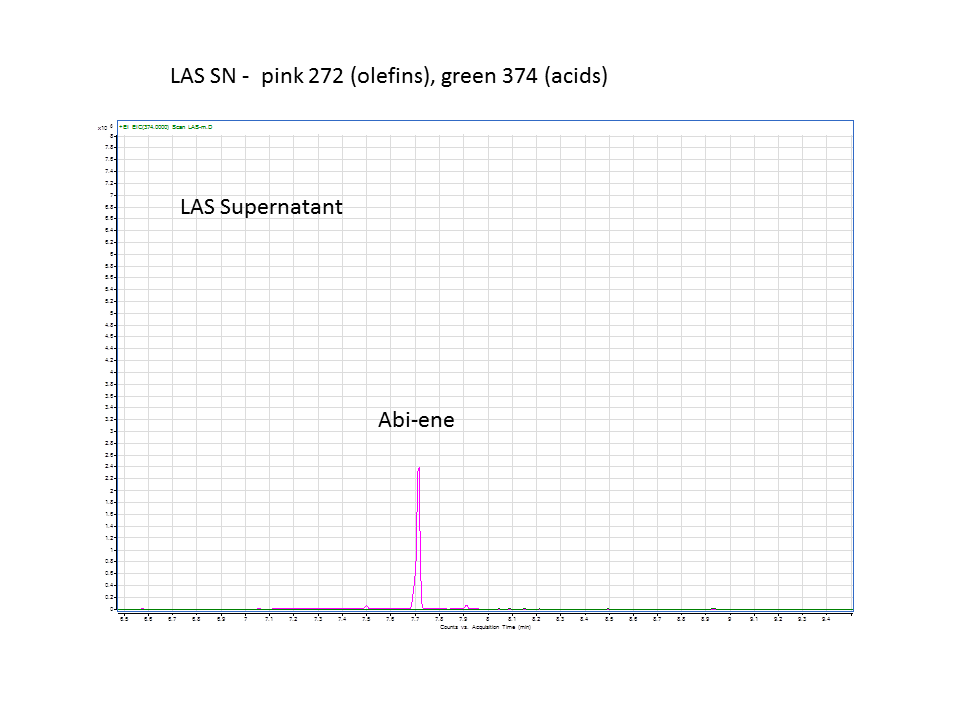
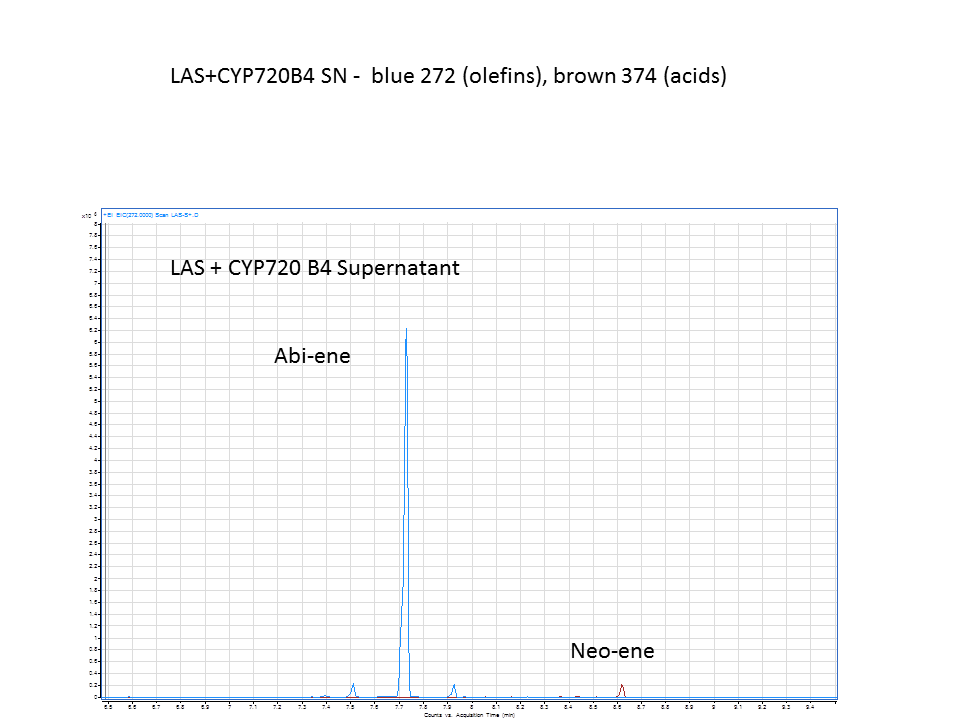
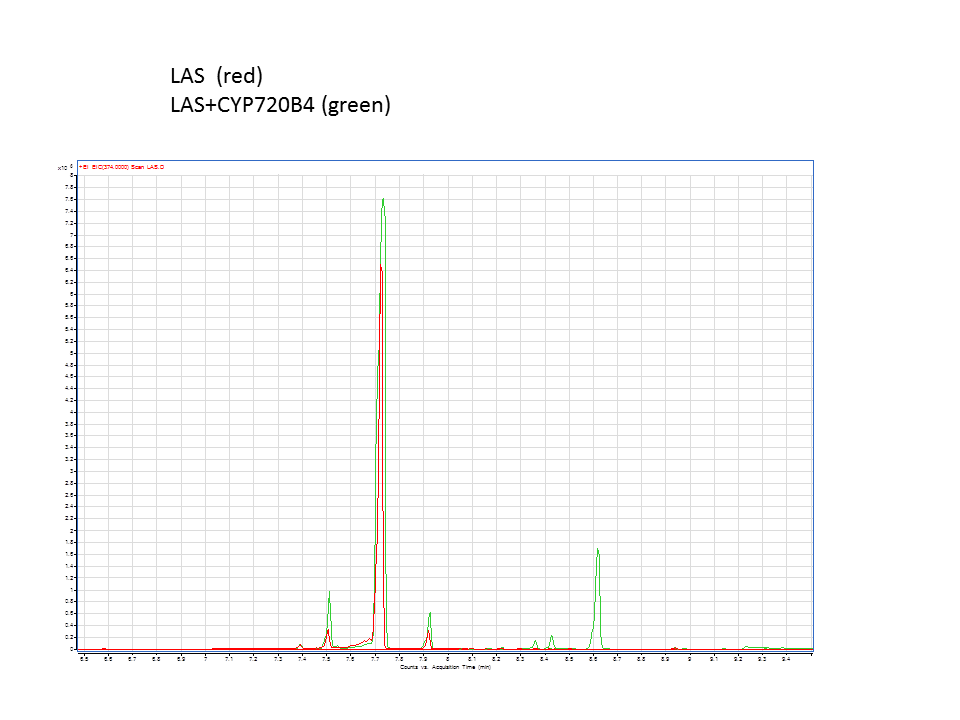
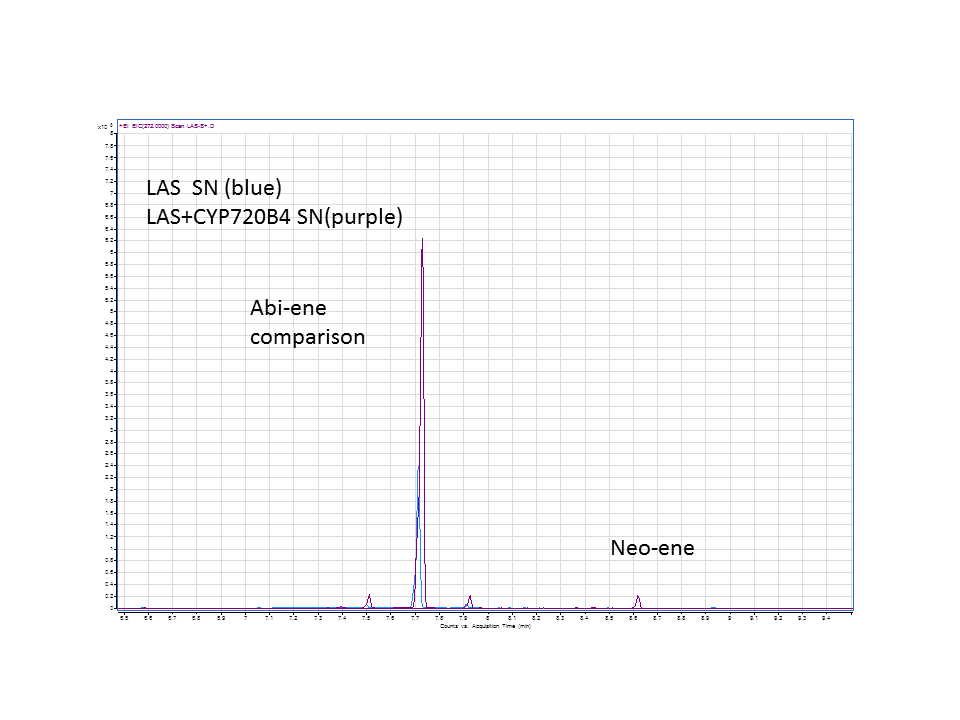
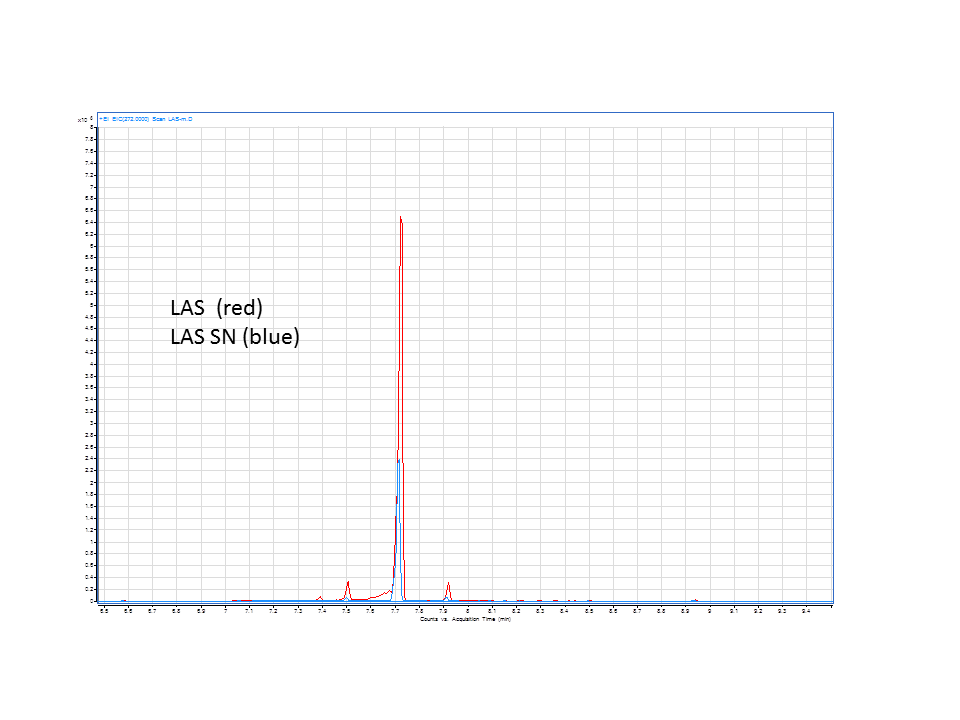
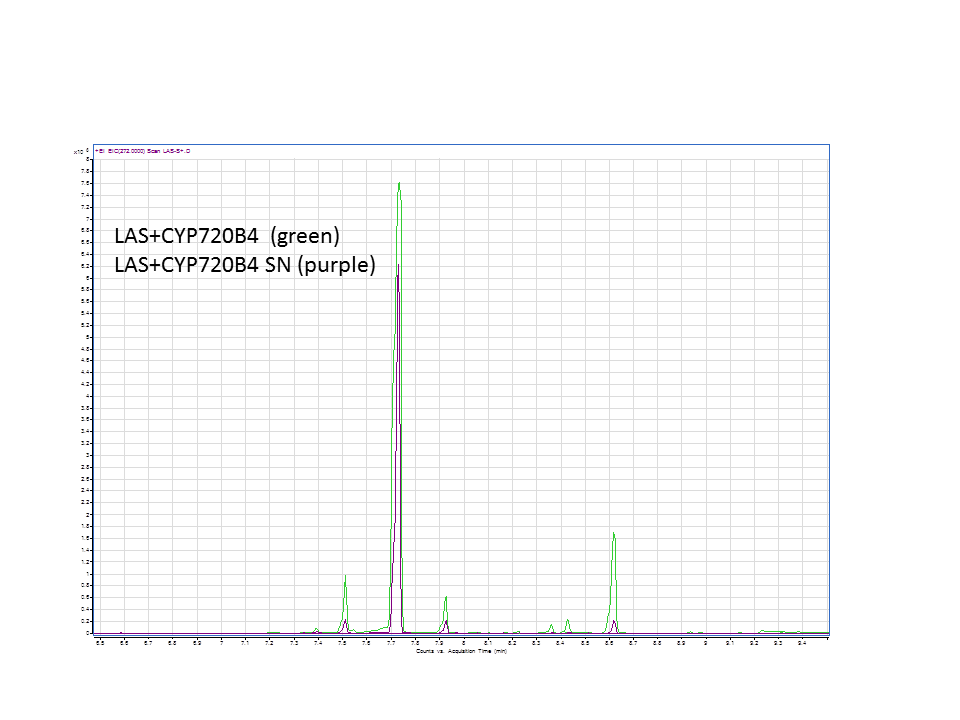
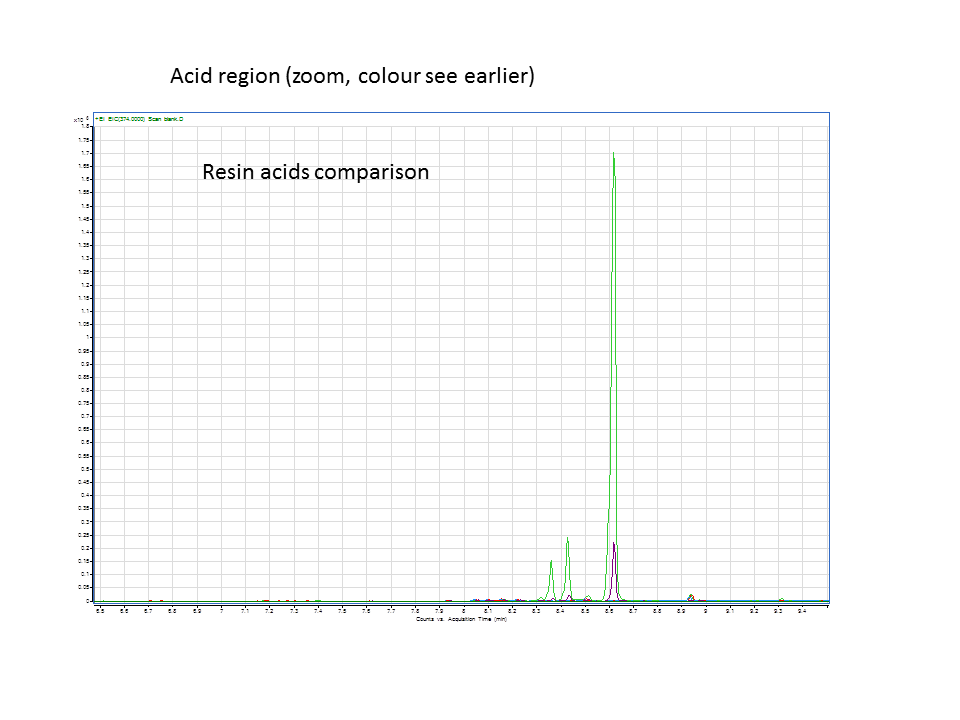
These are the results from both runs.
Katrin and Daisy finished at 9pm. Time for Daisy to go to Starbucks for coffee to fulfill my craving for caffeine. Daisy signing off.
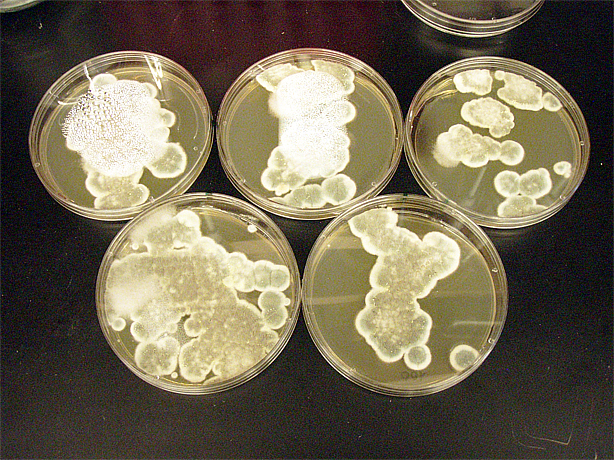
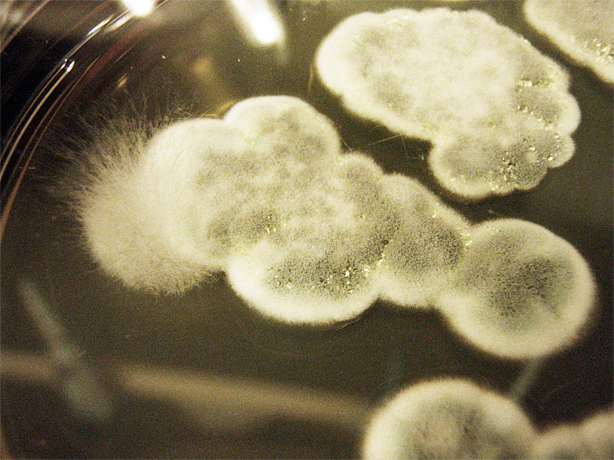
Saccharomyces cerevisiae & Mountain Pine Beetle Co-culturing
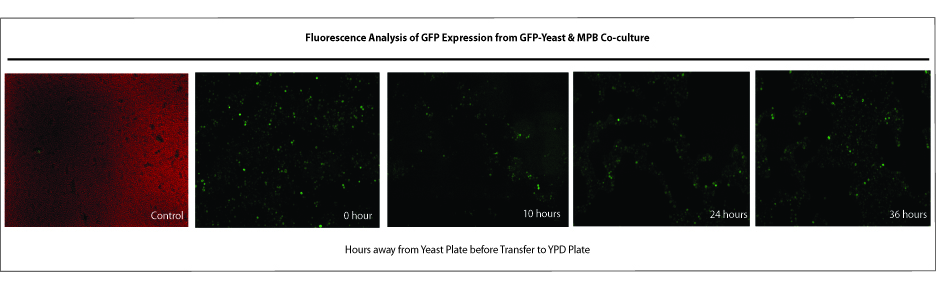
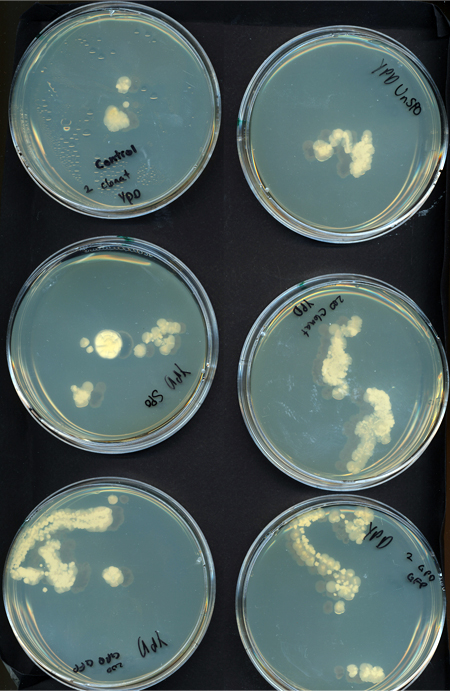
G. clavigera and S. cerevisiae co-culture experiments
We tested growth of G. clavigera and S. cerevisiae on both 1% OMEA and YPD. S. cerevisiae grows slower on 1% OMEA but the G.clavigera grows well. S. cerevisiae grows well on YPD media but the G.claviegera grows very slowly. We decided to use 1% OMEA so that both species could grow relatively well.
Spore Co-culture
Procedure To determine if S. cerevisiae is a feasible chassis we tested its growth against G. clavigera in coculture. We used spores to simulate the conditions of a beetle entering a tree and inoculating fungal spores into the trunk. We plated the following of both on YPD and 1% OMEA plates for 4 days:
1. 200 G. clavigera spores and 330 S. cerevisiae spores 2. 200 G. clavigera spores 3. 330 S. cerevisiae
Results When cocultured G.claviegera and S. cerevisiae mutually inhibit each other, as seen below. 54 G.claviegera spores grew on its own on 1% OMEA while 15 grew when cultured with S. cerevisiae on 1% OMEA.
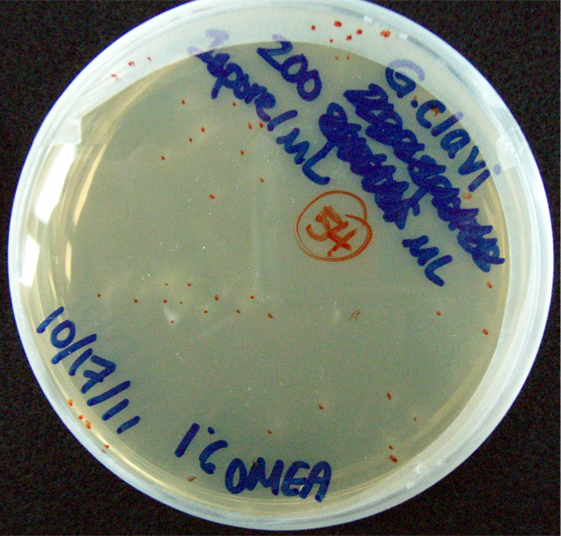
200 G. clavigera spores plated on 1% OMEA for 4 days.
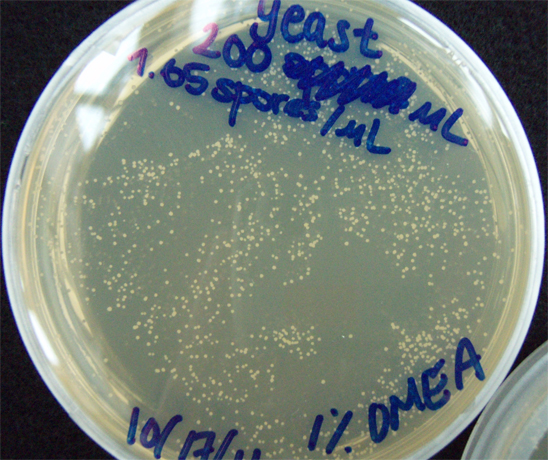
330 S. cerevisiae spores plated on 1% OMEA for 4 days.
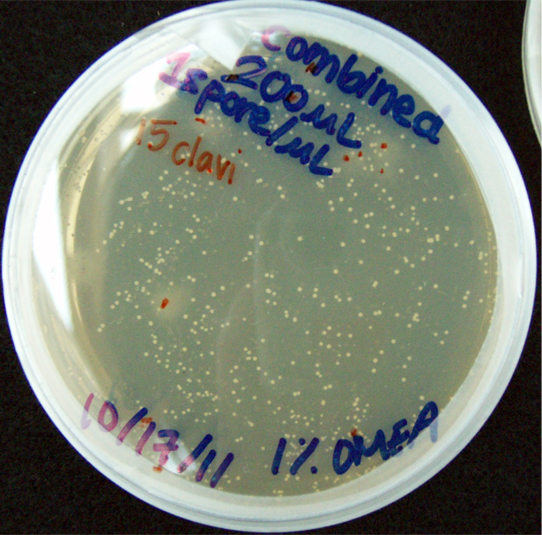
200 G. clavigera + 330 S. cerevisiae spores + plated on 1% OMEA for 4 days.
Conclusion As the two species mutually inhibited each other's growth, S. cerevisiae may be a suitable chassis.
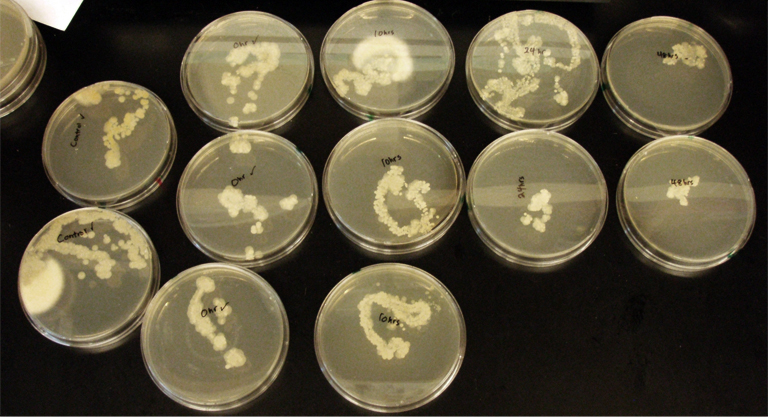
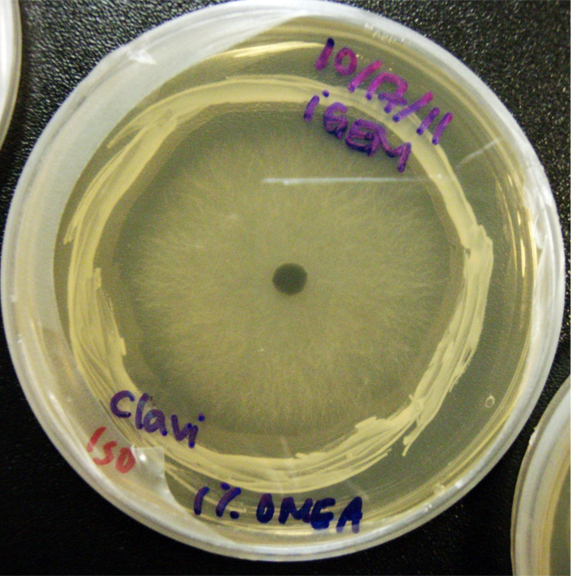
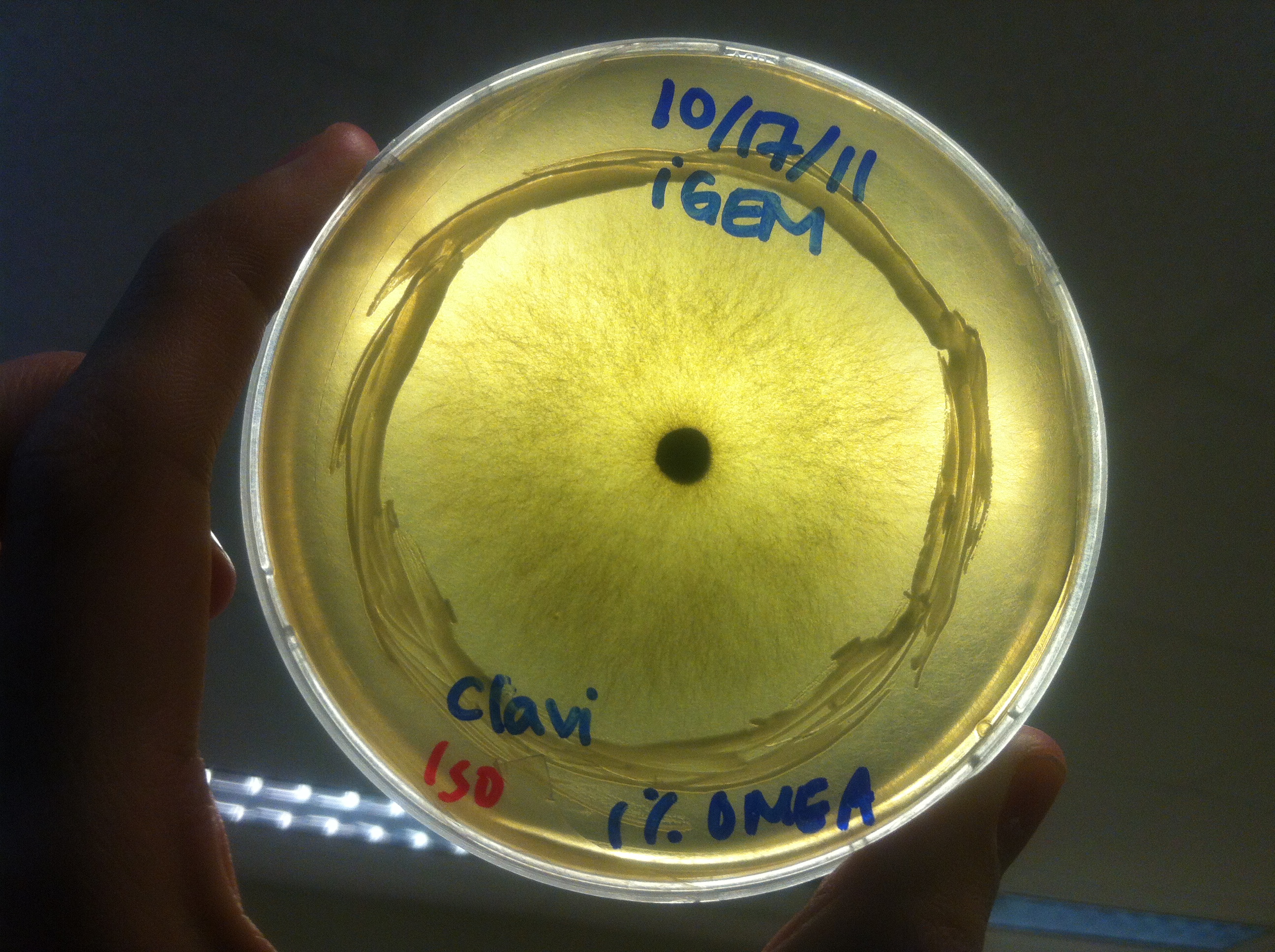
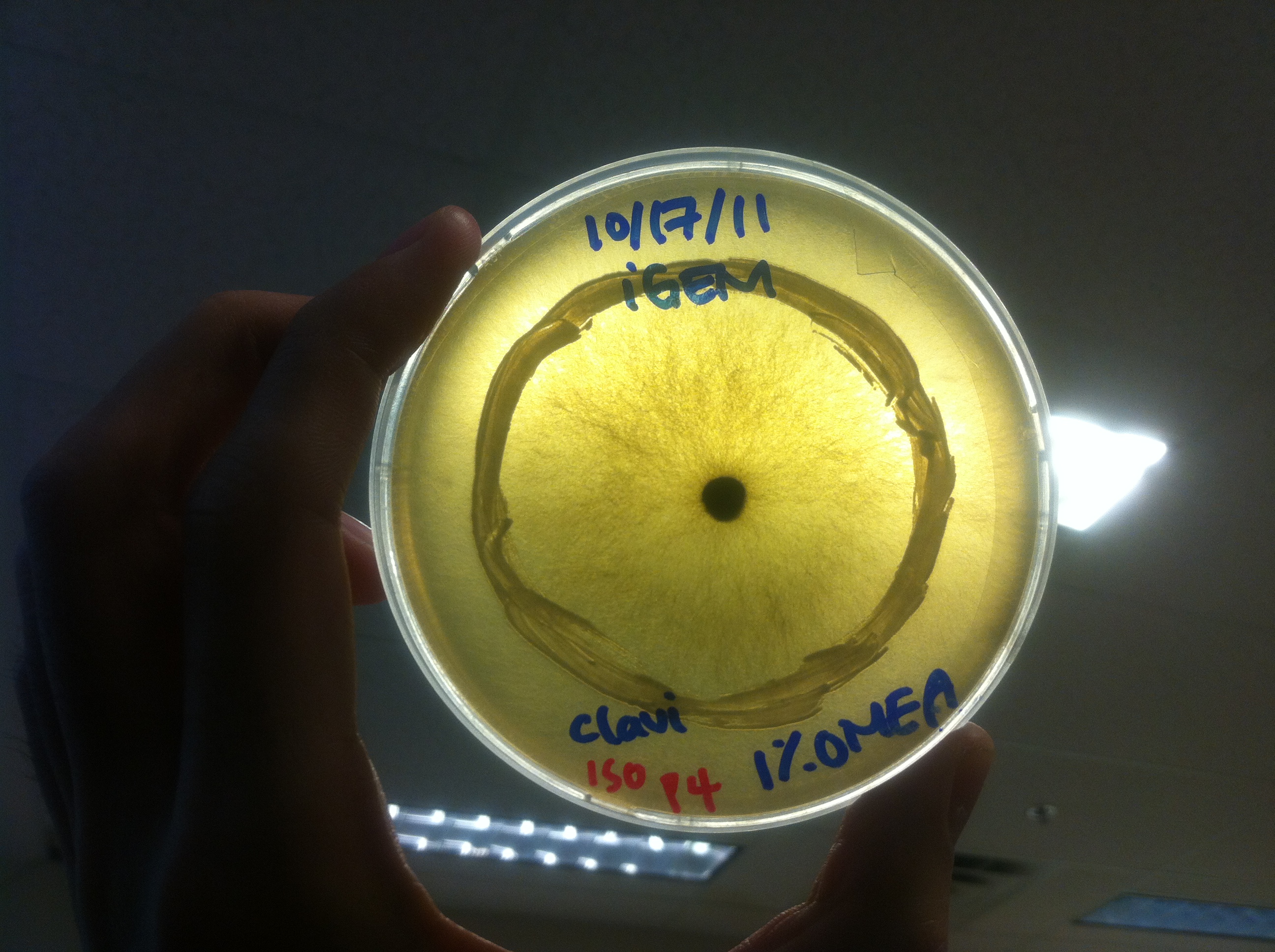
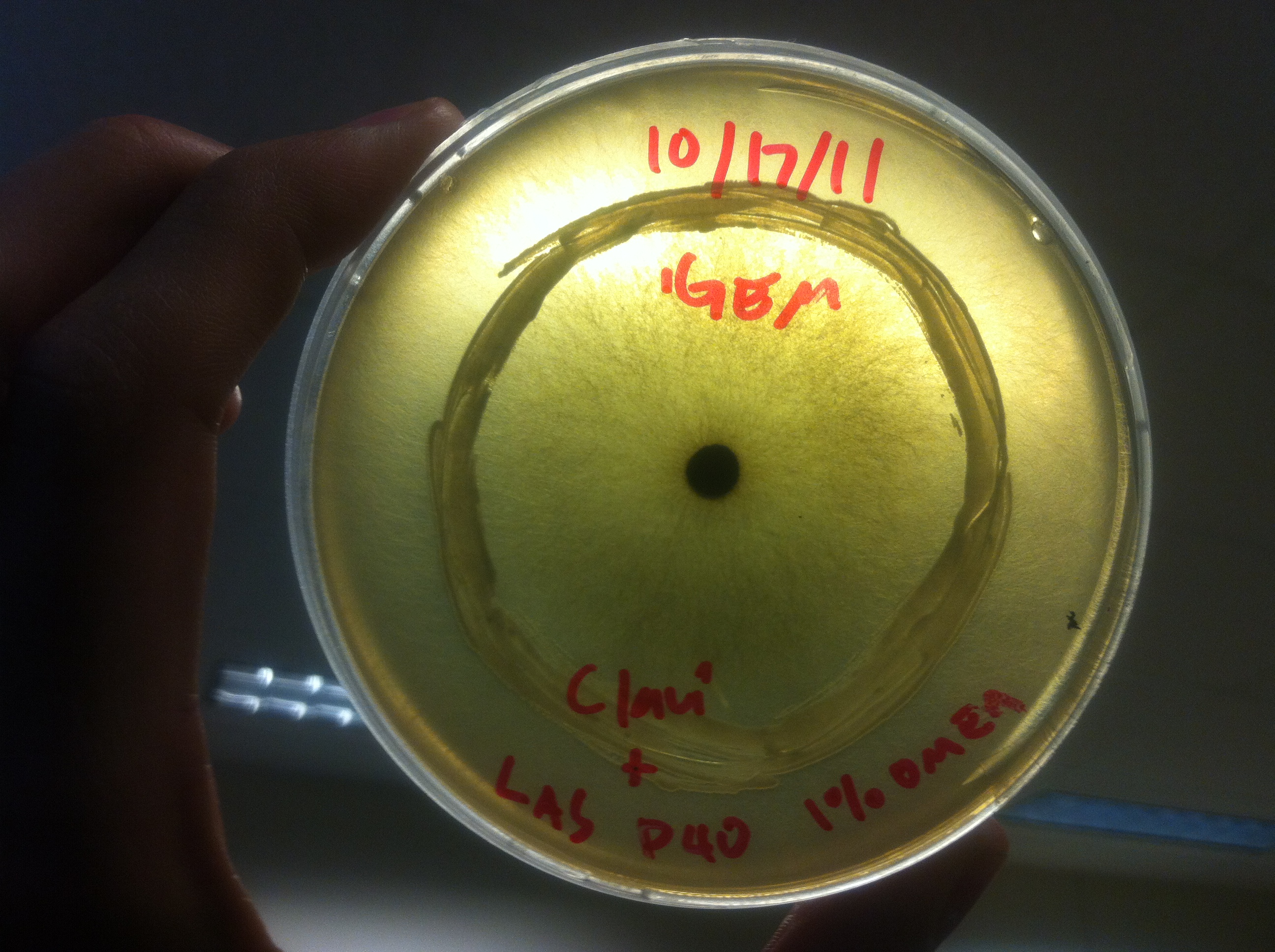
Terpene Co-culture
Procedure To determine if terpene producing yeast could inhibit G. clavigera growth, we smeared rings of 5 types of yeast onto 1% OMEA and placed plugs of G. clavigera mycelium in the centre of the plate. We wish to evaluate if the mycelium can grow past the terpenoid-producing yeast rings; this is done after a week.
1. Wildtype 2. ISO 3. ISO P4 4. LAS 5. LAS P40

Assorted plates of G. clavigera mycelium plugs and terpenoid-producing S. cerevisiae rings.
G. clavigera mycelium growing outwards towards diterpenoid ISO-producing S. cerevisiae on 1% OMEA.
Results


Human Practices: Expert Opinions on Synthetic Biology Gone Wild
To obtain expert opinions on releasing synthetic organisms into the wild and initiate discourse on this topic, our team interviewed many experts across numerous fields at UBC.
For the interview transcripts and some of the key take-home messages, please view Expert Opinions on Synthetic Biology Gone Wild!
 "
"