Team:Peking S/project/wire/harvest
From 2011.igem.org
(→salicylate system) |
Spring zhq (Talk | contribs) (→cin system) |
||
| (48 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
| - | + | Engineering microbial consortia provides us a vista for expanded genetic networks. However, organization of engineered consortia requires effective cell-cell communication and currently harnessed quorum sensing modules are far from sufficient, giving the engineering of cell-cell communication an emergent priority. An ideal communication system primarily consists of four elements: Production, Perception, Cell sensitivity and Detoxification. Natural quorum sensing systems is advantageous in production ,perception and cell sensitivity. As for detoxification, it wouldn’t be a major problem if the receiver module is sensitive enough, which frequently occurs to natural regulators. Thus, harvesting ‘chemical wires’ from natural systems would be a feasible strategy. | |
| - | + | Yet not every system composed of the elements above would give desired performance in engineered consortia. In order to achieve relatively apparent outcome, proper cell sensitivity is required. Also, because long-term monitoring of population behavior remains a challenge, responding time of the signalling system should be kept in a short period. We set our third criterion on the ability to coordinate population members so as to diminish fluctuations in the system. | |
| + | According to such criteria , we selected two signal generator-receiver systems as the positive regulating members of our 'chemical wire' toolbox. One employs auto-inducer N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis-tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (3OH-C14:1-HSL), as the signal molecule (Figure 1). The other system rewired the heterogeneous producing and receiving systems of Salicylate into a synthetic signaling system(molecule illustrated in Figure 2). | ||
| - | + | Correspondingly we designed experiment verifying the performance of our devices from three aspects, namely dose response, time dependence and coordination. | |
==== Cin system ==== | ==== Cin system ==== | ||
| - | This system was derived from | + | This system was derived from Gram-negative soil bacteria ''Rhizobium leguminosarum'' living in symbiotic association with legumes by forming nodules. In this system, cinI, pcin, cinR are core elements. CinI is a LuxI-family synthase, producing 3OH-C14:1-HSL and cinR is a LuxR-type transcriptional regulator responding to the molecules. Pcin will be activated by the binding of CinR -3OH-C14:1-HSL complex. |
| - | + | As one of the widely-used AHL autoinducing luxI/luxR family members, cinI/cinR system meets the four elements quite well. | |
| - | + | ||
<center>[[File:LM1.png]]</center> | <center>[[File:LM1.png]]</center> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
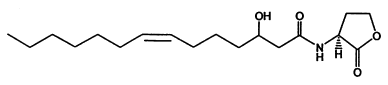
<center>''Figure 1. N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis-tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone chemical structure''</center> | <center>''Figure 1. N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis-tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone chemical structure''</center> | ||
| - | + | In order to verify our three criteria, we constructed 3OH-C14:1-HSL generator and receiver devices (shown in Figure 2) and experiments detecting dose response, time dependence and coordination of the device were performed. | |
| - | <center>[[File: | + | <center>[[File:Cin.png|600px]]</center> |
<center>(A) (B)</center> | <center>(A) (B)</center> | ||
| - | <center>[[File:LB2cbbb.png| | + | <center>[[File:LB2cbbb.png|600px]] |
(C) | (C) | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| - | ''Figure 2. | + | ''Figure 2.Schematic of Cin generator-receiver system. (A) CinI generator plasmid. (B) CinR regulated receiver plasmid. (C) Performance of cinI/cinR quorum sensing system.'' |
==== Salicylate system ==== | ==== Salicylate system ==== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
| - | <center>[[File:LM3.png]]</center> | + | <center>[[File:LM3.png|100px]]</center> |
| - | ''Figure 3. Chemical structure of salicylate'' | + | <center>''Figure 3. Chemical structure of salicylate'' </center> |
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
(C) | (C) | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| - | ''Figure 4. Scheme of salicylate system plasmids and mechanism of generator and receiver system. (A) Autoinducer generator plasmid. Core elements are plac promoter, | + | ''Figure 4. Scheme of salicylate system plasmids and mechanism of generator and receiver system. (A) Autoinducer generator plasmid. Core elements are plac promoter, ribosome binding site(RBS) B0034 and autoinducer synthase gene pchA and pchB. (B) Autoinducer receiver system plasmid. This plasmid contains 3 core parts:NahR, salicylate promoter psal and sal activated gfp. (C) mechanism of experiment system. IPTG with the help of lacI could induce the expression of Protein PchA,PchB. Then they synthesize the autoinducer. In receiver system the autoinducer binds to its receiver protein CinR and the complex actived GFP expression.'' |
== Results == | == Results == | ||
| Line 109: | Line 109: | ||
In order to comfirm the system work or not. We put generator and recevier cultivate together for 3 hours, then centrifuged cells and resuspended them in phosphate buffer solution (PBS)(Figure.5). Experment result testify salicylate system work. | In order to comfirm the system work or not. We put generator and recevier cultivate together for 3 hours, then centrifuged cells and resuspended them in phosphate buffer solution (PBS)(Figure.5). Experment result testify salicylate system work. | ||
| - | <center>[[File: | + | <center>[[File:LM5a.JPG|300px]]</center> |
| - | + | Figure 5. Salicylate verify experiment result. The tube on the left side is control and tubes 2,3,4 on the right contain mix of Salicylate generator and Salicylate recevier. | |
| - | Figure 5. Salicylate verify experiment result. The tube on the left side is control and | + | |
=== Dose Response === | === Dose Response === | ||
==== cin system ==== | ==== cin system ==== | ||
| - | First, we | + | First, we cultivated generator cell with 10-3M IPTG for 16 hours, then centrifuged cells and collect the supernatant. We use this supernatant as original 3OH-C14:1-HSL solution,then we diluted it to 10-7, 5×10-7, 10-6, 5×10-6, 10-5, 6×10-5, 8×10-5, 10-4, 2×10-4, 4×10-4, 7×10-4, 10-3, 3×10-3, 6×10-3, 8×10-3, 10-2 of original solution concentration respectively.Induction was performed with the dilutions at 37℃ for 3 hours, then receiver cells are centrifuged and resuspended in PBS. The GFP fluorescence of each culture was obtained using enzyme-labeled assay. The result is shown in figure 6. |
| - | <center>[[File:LM6.png| | + | <center>[[File:LM6.png|430px]]</center> |
Figure 6. Dose Response Curve. Vertical axis RFU/OD represents GFP expression measured through enzyme-labeled assay and the Horizontal axis represent different relative dilution concentration of 3OH-C14:1-HSL. Data was fitted with Hill function. | Figure 6. Dose Response Curve. Vertical axis RFU/OD represents GFP expression measured through enzyme-labeled assay and the Horizontal axis represent different relative dilution concentration of 3OH-C14:1-HSL. Data was fitted with Hill function. | ||
| Line 127: | Line 126: | ||
We cultivate the recevier E.coli until the OD up to 0.4 and add salicylateinto 16 EP tube containing aforementioned E.coli respectively. Different concentration of salicylate solution will be added, that is 10-7 M, 10-6 M, 5×10-6 M, 10-5 M, 2.5×10-5 M, 5×10-5 M, 7.5×10-5 M, 10-4 M, 2.5×10-4 M, 5×10-4 M, 7.5×10-4 M, 10-3 M. Cultivate the cell for 3 hours at 37℃. Then centrifuged cells and resuspended in phosphate buffer solution (PBS). The GFP fluorescence of each culture was obtained using FCM(flow cytometry). The result is shown in figure 7. | We cultivate the recevier E.coli until the OD up to 0.4 and add salicylateinto 16 EP tube containing aforementioned E.coli respectively. Different concentration of salicylate solution will be added, that is 10-7 M, 10-6 M, 5×10-6 M, 10-5 M, 2.5×10-5 M, 5×10-5 M, 7.5×10-5 M, 10-4 M, 2.5×10-4 M, 5×10-4 M, 7.5×10-4 M, 10-3 M. Cultivate the cell for 3 hours at 37℃. Then centrifuged cells and resuspended in phosphate buffer solution (PBS). The GFP fluorescence of each culture was obtained using FCM(flow cytometry). The result is shown in figure 7. | ||
| - | <center>[[File:LM7b.png| | + | <center>[[File:LM7b.png|420px]]</center> |
Figure 7. Dose response curve. Horizontal axis represents GFP expression measured by flow cytometry and the vertical axis represen different salicylate concentration. Data was fitted with Hill function. | Figure 7. Dose response curve. Horizontal axis represents GFP expression measured by flow cytometry and the vertical axis represen different salicylate concentration. Data was fitted with Hill function. | ||
| Line 133: | Line 132: | ||
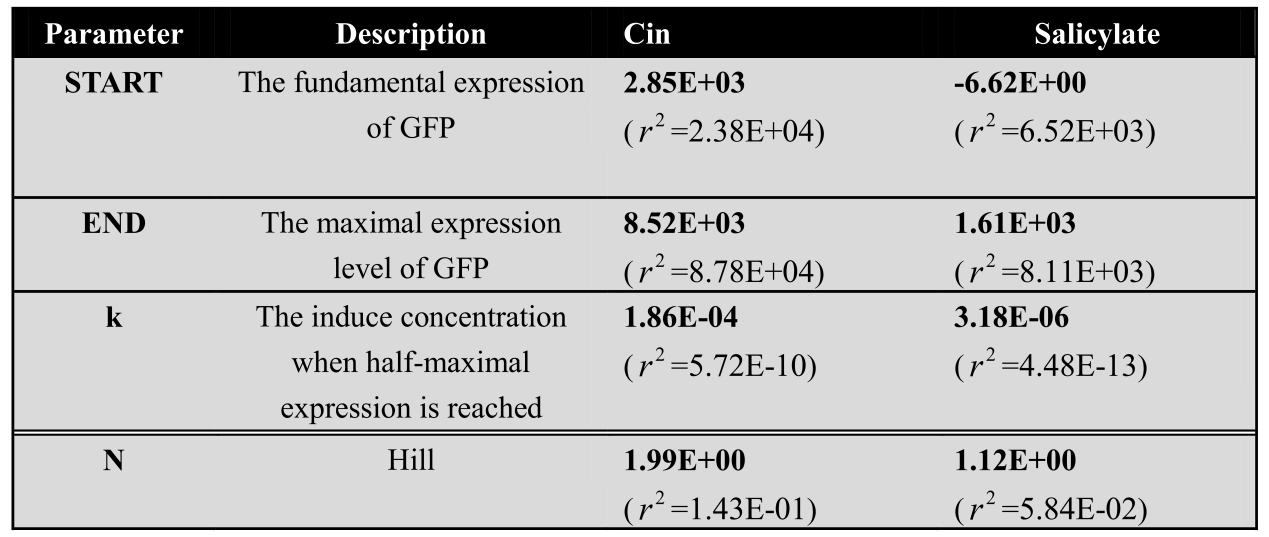
| - | <center> | + | <center>Table 1: Corresponding fitting parameters of the dose response curves for each system</center> |
| - | <center>[[File:LM8.png| | + | <center>[[File:LM8.png|550px]]</center> |
| - | *Hill function: [[File:LMe1.png| | + | *Hill function: [[File:LMe1.png|200px]] |
=== Time Dependence === | === Time Dependence === | ||
==== cin system ==== | ==== cin system ==== | ||
| - | + | Cin AHL receiver was induced with filtered culture broth diluted in a fold of 100. | |
| - | <center>[[File:LM9.png| | + | <center>[[File:LM9.png|420px]]</center> |
| - | Figure 9. Time | + | Figure 9. Time dependence of cin receiver. Fluorescence was recorded with micro plate reader every 15 mins. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | ==== Salicylate System ==== | ||
| + | Overnight culture was diluted in a fold of 1000 with fresh LB. When OD600 reached 0.4~0.6, salicylate was supplied and cell culture was then cultivated at 37 degree, 250rpm. Fluorescence of bacterial cell was measured with Flow Cytometry at fixed time interval. | ||
| - | <center>[[File:LM10.png| | + | <center>[[File:LM10.png|400px]]</center> |
| - | Figure 10. Time | + | Figure 10. Time dependence of salicylate inducement. Horizontal axis represents time while the vertical axis represents fluorescence intensity recorded by flow cytometry. |
| - | <center>The modeling parameter of time dependence | + | <center>Table 2: The modeling parameter of time dependence of salicylate inducement and cin system</center> |
| - | <center>[[File:LM11.png| | + | <center>[[File:LM11.png|550px]]</center> |
| - | *Fitted function:<center>[[File:LMe2.png| | + | *Fitted function:<center>[[File:LMe2.png|100px]] </center> |
| - | The Fluorescence intensity X obeys:<center>[[File:LMe3.png| | + | The Fluorescence intensity X obeys:<center>[[File:LMe3.png|100px]]</center> |
| - | After integration, we | + | After integration, we got:<center>[[File:LMe4.png|100px]]</center> |
=== Coordinatiblity === | === Coordinatiblity === | ||
| - | We induced cin and salicylate cell with Dose Response experiment | + | We induced cin and salicylate receiver cell with Dose Response experiment protocol. The ability of AHL produced by cin and salicylate to coordinate population was recorded with FACS. Result has been shown in Figure 10 |
<center>[[File:LM12a.png|340px]][[File:LM12b.png|340px]]</center> | <center>[[File:LM12a.png|340px]][[File:LM12b.png|340px]]</center> | ||
| - | <center>(A) | + | <center>(A) (B)</center> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | Figure 12. Distribution of Fluorescence Intensity of cin receiver and salicylate receiver | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | == Reference == | |
| - | + | Craig M and Allan D. Co-ordination of quorum-sensing regulation in Rhizobium leguminosarum by induction of an anti-repressor. Molecular Microbiology,81(4),994–100(2011). | |
| - | + | Florence W & Allan D.Quorum-sensing in Rhizobium. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek,81,397-407(2002). | |
| - | + | Gary SR and J. AD. Quorum-sensing-regulated transcriptional initiation of plasmid transfer and replication genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. Microbiology,153,2074–2082(2007). | |
| - | Adam PA, Christopher AV. Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate J Christopher Anderson. J. Mol. Biol | + | Adam PA, Christopher AV. Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate J Christopher Anderson. J. Mol. Biol,355,619–627(2006). |
| - | Mark AS and Elizabeth FP. Demonstration, Characterization, and Mutational Analysis of NahR Protein Binding to nah and sal Promoters. Journal of Bacteriology | + | Mark AS and Elizabeth FP. Demonstration, Characterization, and Mutational Analysis of NahR Protein Binding to nah and sal Promoters. Journal of Bacteriology,171,837-846(1989). |
| - | Mark AS and paul EW. Identification of the nahR Gene Product and Nucleotide Sequences Required for Its Activation of the sal Operon. Journal of Bacteriology | + | Mark AS and paul EW. Identification of the nahR Gene Product and Nucleotide Sequences Required for Its Activation of the sal Operon. Journal of Bacteriology,166,9-14(1986). |
| - | Jose LR and Carlos AG. Exploitation of prokaryotic expression systems based on the salicylate-dependent control circuit encompassing nahR/Psal::xylS2for biotechnological applications. Bioengineered Bugs | + | Jose LR and Carlos AG. Exploitation of prokaryotic expression systems based on the salicylate-dependent control circuit encompassing nahR/Psal::xylS2for biotechnological applications. Bioengineered Bugs,1:4,244-251(2010). |
| - | Woon KL, Hae JS. In vitro binding of purified NahR regulatory protein with promoter Psal. Biochimica et Biophysica | + | Woon KL, Hae JS. In vitro binding of purified NahR regulatory protein with promoter Psal. Biochimica et Biophysica,1725,247 – 255(2005) |
Latest revision as of 04:02, 6 October 2011
Template:Https://2011.igem.org/Team:Peking S/bannerhidden Template:Https://2011.igem.org/Team:Peking S/back2
Template:Https://2011.igem.org/Team:Peking S/bannerhidden

Chemical Wire Toolbox
Introduction|Harvesting ‘Chemical Wires’ From Nature|Synthesizing Quorum Sensing Inverters|Orthogonal Activating Matrix
Contents |
Introduction
Engineering microbial consortia provides us a vista for expanded genetic networks. However, organization of engineered consortia requires effective cell-cell communication and currently harnessed quorum sensing modules are far from sufficient, giving the engineering of cell-cell communication an emergent priority. An ideal communication system primarily consists of four elements: Production, Perception, Cell sensitivity and Detoxification. Natural quorum sensing systems is advantageous in production ,perception and cell sensitivity. As for detoxification, it wouldn’t be a major problem if the receiver module is sensitive enough, which frequently occurs to natural regulators. Thus, harvesting ‘chemical wires’ from natural systems would be a feasible strategy.
Yet not every system composed of the elements above would give desired performance in engineered consortia. In order to achieve relatively apparent outcome, proper cell sensitivity is required. Also, because long-term monitoring of population behavior remains a challenge, responding time of the signalling system should be kept in a short period. We set our third criterion on the ability to coordinate population members so as to diminish fluctuations in the system.
According to such criteria , we selected two signal generator-receiver systems as the positive regulating members of our 'chemical wire' toolbox. One employs auto-inducer N-(3-hydroxy-7-cis-tetradecenoyl)-L-homoserine lactone (3OH-C14:1-HSL), as the signal molecule (Figure 1). The other system rewired the heterogeneous producing and receiving systems of Salicylate into a synthetic signaling system(molecule illustrated in Figure 2).
Correspondingly we designed experiment verifying the performance of our devices from three aspects, namely dose response, time dependence and coordination.
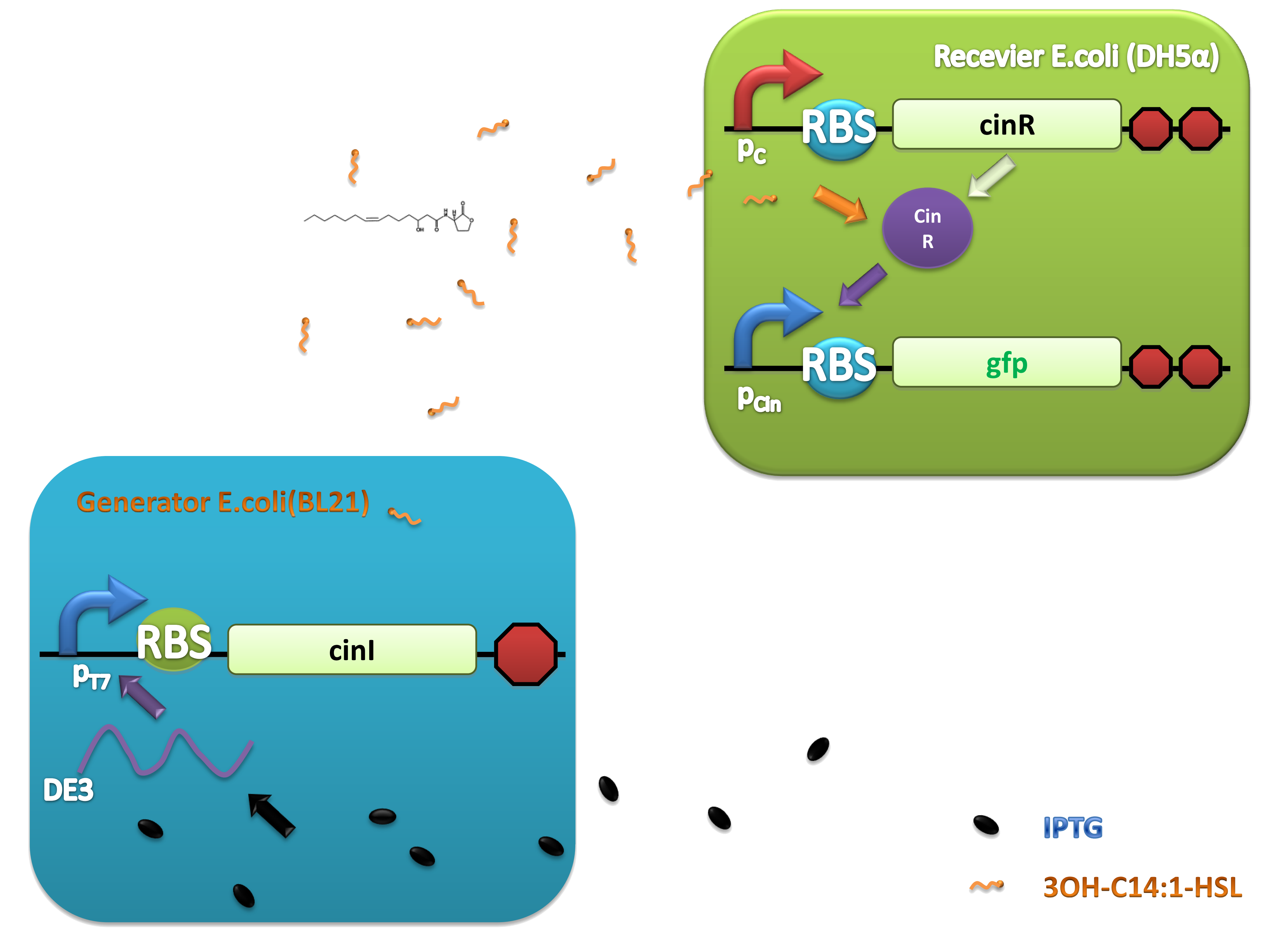
Cin system
This system was derived from Gram-negative soil bacteria Rhizobium leguminosarum living in symbiotic association with legumes by forming nodules. In this system, cinI, pcin, cinR are core elements. CinI is a LuxI-family synthase, producing 3OH-C14:1-HSL and cinR is a LuxR-type transcriptional regulator responding to the molecules. Pcin will be activated by the binding of CinR -3OH-C14:1-HSL complex.
As one of the widely-used AHL autoinducing luxI/luxR family members, cinI/cinR system meets the four elements quite well.
In order to verify our three criteria, we constructed 3OH-C14:1-HSL generator and receiver devices (shown in Figure 2) and experiments detecting dose response, time dependence and coordination of the device were performed.
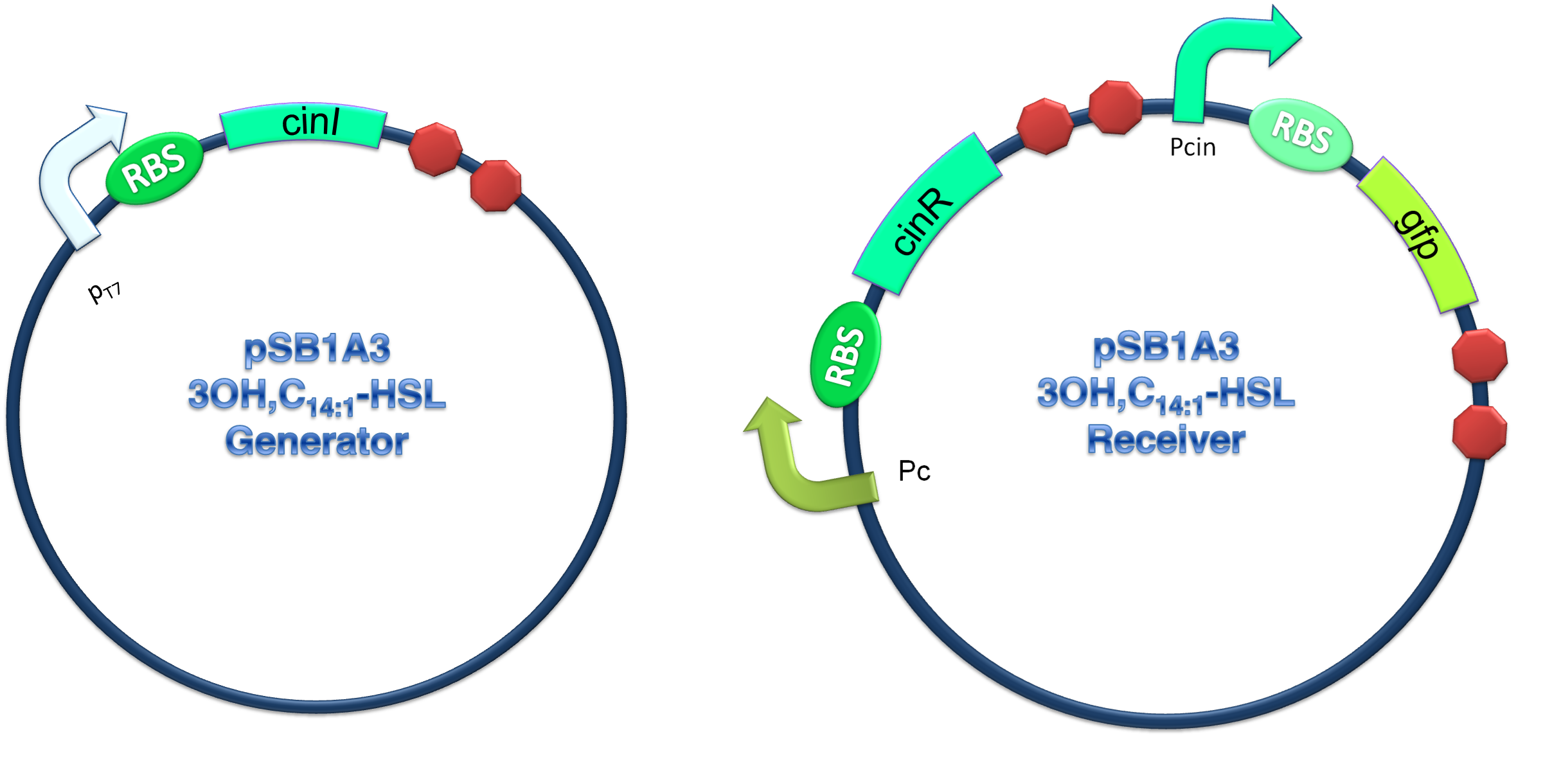
(C)
Figure 2.Schematic of Cin generator-receiver system. (A) CinI generator plasmid. (B) CinR regulated receiver plasmid. (C) Performance of cinI/cinR quorum sensing system.
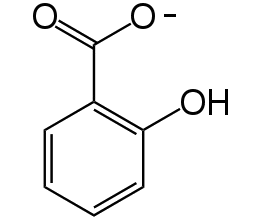
Salicylate system
Some microorganisms can degrade salicylate and the mechanism has been studied extensively in Pseudomonas putida. Interestingly, there is a bacterium species named Pseudomonas aeruginosa which can synthesize salicylate. These two bacteria strains provide the possibility of constructing an artificial quorum sensing system.
1. Salicylate operon has a broad concentration response curve
We found that salicylate sensor NahR is able to response to salicylate among a wide concentration range. When induced with high concentration of salicylate, for instance, 10^-3M, the gene of interest regulated by pSal promoter will be dramatically expressed, while NahR could still sense salicylate even as low as 10^-6M.
2. Salicylate would not cause huge burden on the cell metabolism
As a chemical wire, salicylate has small molar mass and simple chemical structure. The synthesis pathway of salicylate only involves two genes. As a result, metabolic burden will not be a hurdle when using salicylate as artificial quorum sensing molecules.
3. Salicylate has a unique chemical feature making it more stable
Benzene ring and carboxyl make salicylate more stable than other quorum-sensing small molecules.
In order to characterize the system, generator device and receiver device were transformed into different strains.
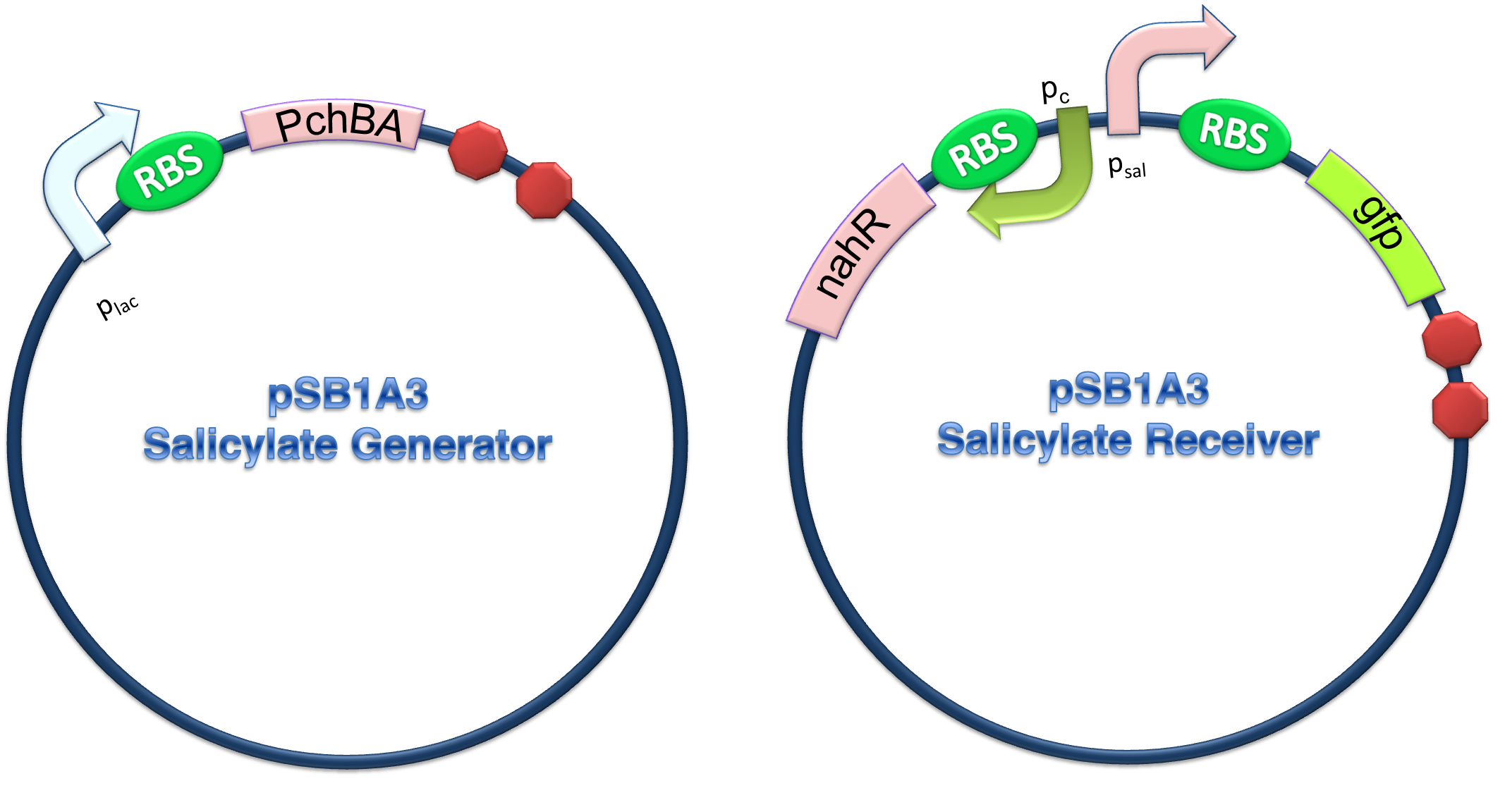
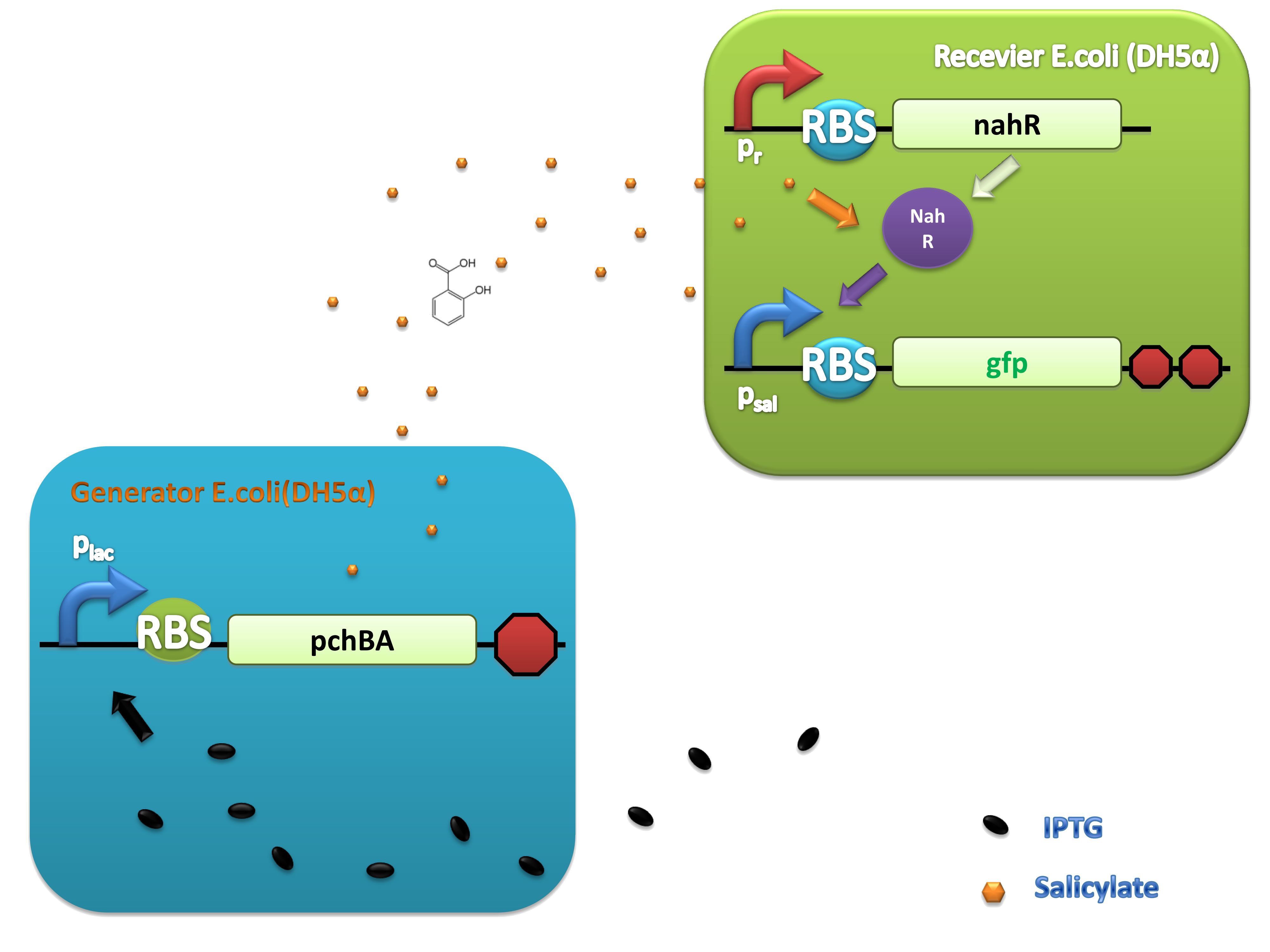
PchBA which locates at generator plasmid encodes an isochorismate pyruvate-lyase and an isochorismate synthase derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PchA, an isochorismate synthase, catalyzes the conversion of chorismate to isochorismate. The enzyme PchB, catalyzes the conversion of isochorismate to salicylate.
NahR is a polypeptide which plays an important role in salicylate operon. The polypeptide can exerts its salicylate-dependent activation sal operon by interacting with the promoter sequence in the region of -83 to -45 base pairs before the transcription start site. Binding of the inducer to the central domain of NahR is thought to cause additional interactions of NahR with sequences near the -35 and DNA bending, both of which promote transcriptional activation, therefore, so if there are no salicylate in the liquid nutrient medium, NahR will not binding on the promoter and lead to RNA ploymerase can not work normally, otherwise, transcription will be actived and downstream of the promoter will be transcripted, in our case, GFP will be expressed.
(C)
Figure 4. Scheme of salicylate system plasmids and mechanism of generator and receiver system. (A) Autoinducer generator plasmid. Core elements are plac promoter, ribosome binding site(RBS) B0034 and autoinducer synthase gene pchA and pchB. (B) Autoinducer receiver system plasmid. This plasmid contains 3 core parts:NahR, salicylate promoter psal and sal activated gfp. (C) mechanism of experiment system. IPTG with the help of lacI could induce the expression of Protein PchA,PchB. Then they synthesize the autoinducer. In receiver system the autoinducer binds to its receiver protein CinR and the complex actived GFP expression.
Results
Salicylate Testing experiment
In order to comfirm the system work or not. We put generator and recevier cultivate together for 3 hours, then centrifuged cells and resuspended them in phosphate buffer solution (PBS)(Figure.5). Experment result testify salicylate system work.
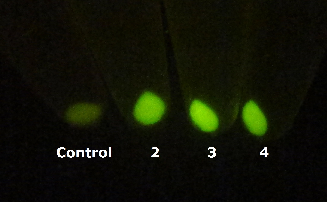
Figure 5. Salicylate verify experiment result. The tube on the left side is control and tubes 2,3,4 on the right contain mix of Salicylate generator and Salicylate recevier.
Dose Response
cin system
First, we cultivated generator cell with 10-3M IPTG for 16 hours, then centrifuged cells and collect the supernatant. We use this supernatant as original 3OH-C14:1-HSL solution,then we diluted it to 10-7, 5×10-7, 10-6, 5×10-6, 10-5, 6×10-5, 8×10-5, 10-4, 2×10-4, 4×10-4, 7×10-4, 10-3, 3×10-3, 6×10-3, 8×10-3, 10-2 of original solution concentration respectively.Induction was performed with the dilutions at 37℃ for 3 hours, then receiver cells are centrifuged and resuspended in PBS. The GFP fluorescence of each culture was obtained using enzyme-labeled assay. The result is shown in figure 6.

Figure 6. Dose Response Curve. Vertical axis RFU/OD represents GFP expression measured through enzyme-labeled assay and the Horizontal axis represent different relative dilution concentration of 3OH-C14:1-HSL. Data was fitted with Hill function.
salicylate system
We cultivate the recevier E.coli until the OD up to 0.4 and add salicylateinto 16 EP tube containing aforementioned E.coli respectively. Different concentration of salicylate solution will be added, that is 10-7 M, 10-6 M, 5×10-6 M, 10-5 M, 2.5×10-5 M, 5×10-5 M, 7.5×10-5 M, 10-4 M, 2.5×10-4 M, 5×10-4 M, 7.5×10-4 M, 10-3 M. Cultivate the cell for 3 hours at 37℃. Then centrifuged cells and resuspended in phosphate buffer solution (PBS). The GFP fluorescence of each culture was obtained using FCM(flow cytometry). The result is shown in figure 7.

Figure 7. Dose response curve. Horizontal axis represents GFP expression measured by flow cytometry and the vertical axis represen different salicylate concentration. Data was fitted with Hill function.
Time Dependence
cin system
Cin AHL receiver was induced with filtered culture broth diluted in a fold of 100.
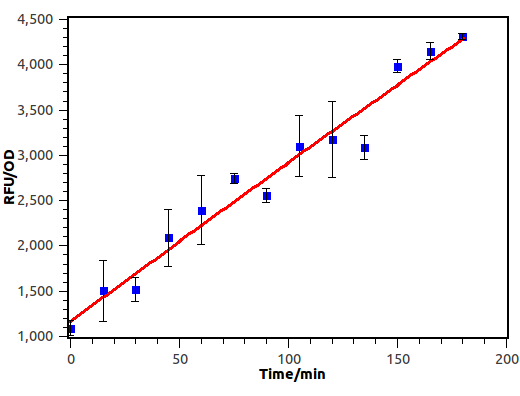
Figure 9. Time dependence of cin receiver. Fluorescence was recorded with micro plate reader every 15 mins.
Salicylate System
Overnight culture was diluted in a fold of 1000 with fresh LB. When OD600 reached 0.4~0.6, salicylate was supplied and cell culture was then cultivated at 37 degree, 250rpm. Fluorescence of bacterial cell was measured with Flow Cytometry at fixed time interval.
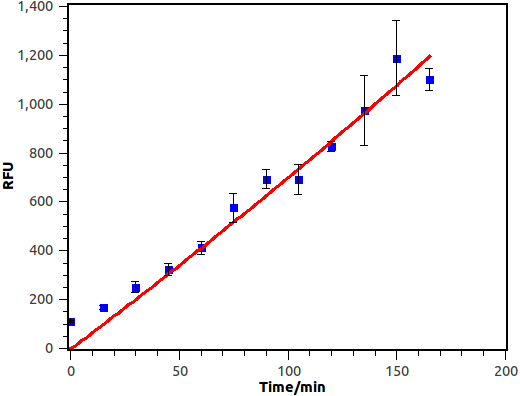
Figure 10. Time dependence of salicylate inducement. Horizontal axis represents time while the vertical axis represents fluorescence intensity recorded by flow cytometry.

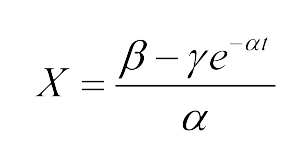
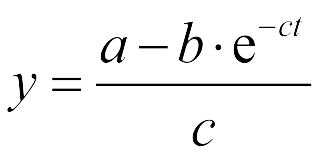
Coordinatiblity
We induced cin and salicylate receiver cell with Dose Response experiment protocol. The ability of AHL produced by cin and salicylate to coordinate population was recorded with FACS. Result has been shown in Figure 10
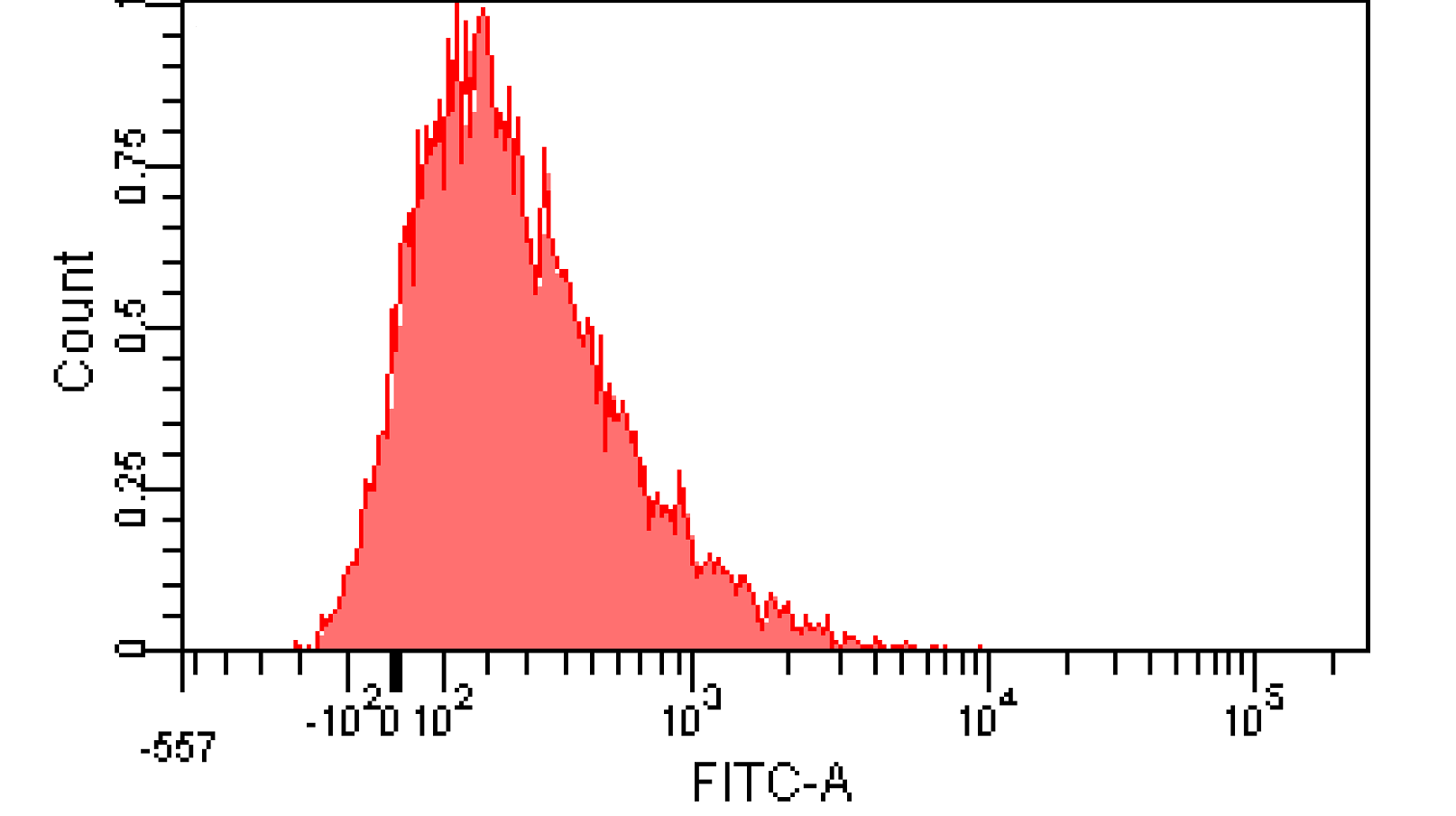
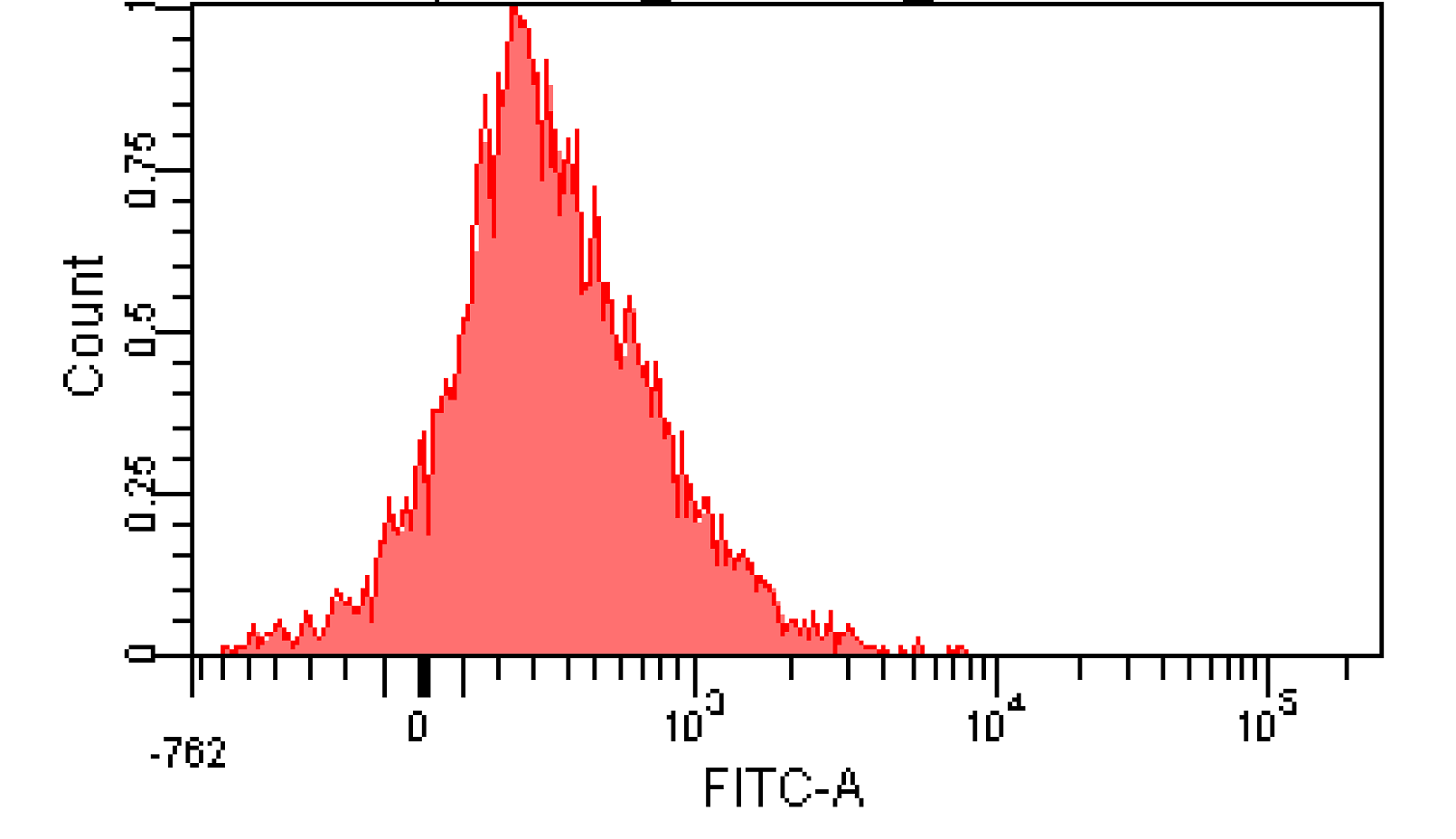
Figure 12. Distribution of Fluorescence Intensity of cin receiver and salicylate receiver
Reference
Craig M and Allan D. Co-ordination of quorum-sensing regulation in Rhizobium leguminosarum by induction of an anti-repressor. Molecular Microbiology,81(4),994–100(2011).
Florence W & Allan D.Quorum-sensing in Rhizobium. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek,81,397-407(2002).
Gary SR and J. AD. Quorum-sensing-regulated transcriptional initiation of plasmid transfer and replication genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. Microbiology,153,2074–2082(2007).
Adam PA, Christopher AV. Environmental signal integration by a modular AND gate J Christopher Anderson. J. Mol. Biol,355,619–627(2006).
Mark AS and Elizabeth FP. Demonstration, Characterization, and Mutational Analysis of NahR Protein Binding to nah and sal Promoters. Journal of Bacteriology,171,837-846(1989).
Mark AS and paul EW. Identification of the nahR Gene Product and Nucleotide Sequences Required for Its Activation of the sal Operon. Journal of Bacteriology,166,9-14(1986).
Jose LR and Carlos AG. Exploitation of prokaryotic expression systems based on the salicylate-dependent control circuit encompassing nahR/Psal::xylS2for biotechnological applications. Bioengineered Bugs,1:4,244-251(2010).
Woon KL, Hae JS. In vitro binding of purified NahR regulatory protein with promoter Psal. Biochimica et Biophysica,1725,247 – 255(2005)
 "
"
