Team:ITESM Mexico/Abstract
From 2011.igem.org
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Team:ITESM_Mexico/Top}} | {{Team:ITESM_Mexico/Top}} | ||
| - | '''Dual light controlled arabinose biosensor''' | + | <html><h1 class="myowntitle">Abstract</h1> </html> |
| - | [[File:Construct.jpg| | + | ---- |
| + | : | ||
| + | : | ||
| + | : | ||
| + | : | ||
| + | : | ||
| + | : | ||
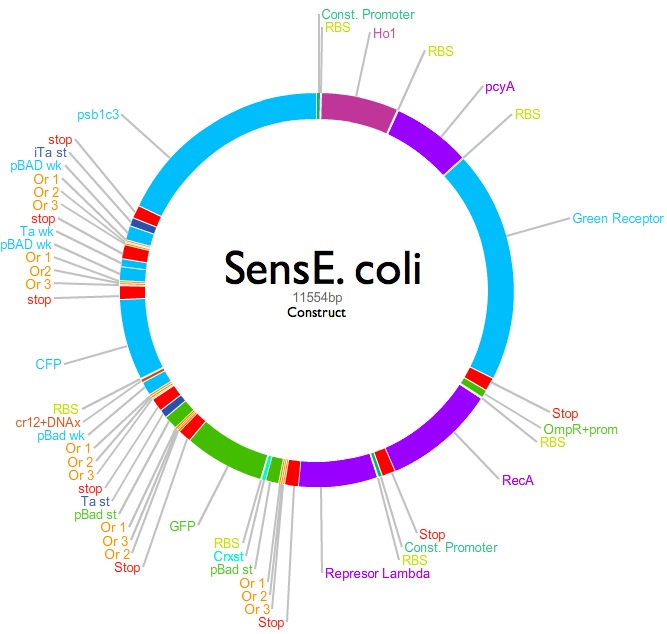
| + | ::::::::::::::::::::::'''Dual light controlled arabinose biosensor''' | ||
| + | [[File:Construct.jpg|300px|left]] | ||
'''Integrating the work of many other previous iGEM teams (Tokyo NoKoGen 2010, Chiba 2009, 2010, British Columbia 2009, Cambridge 2010, UNAM-Genomics México 2010, ITESM Monterrey 2010), the aim of this project is to develop a way of giving a cell the command to perform a function at user’s will, improving current lock-and-key designs. A novel mechanism based on an ''E.coli'' chassis, was designed with two main objectives: to sense arabinose reporting its concentration and to use light receptors to trigger the expression of the required pathways. The first receptor enables ''E.coli'' to activate (express), the arabinose sensing mechanism; whereas the second receptor activates a quick deactivation(degradation), of the sensing mechanism depriving the cell of that capability.''' | '''Integrating the work of many other previous iGEM teams (Tokyo NoKoGen 2010, Chiba 2009, 2010, British Columbia 2009, Cambridge 2010, UNAM-Genomics México 2010, ITESM Monterrey 2010), the aim of this project is to develop a way of giving a cell the command to perform a function at user’s will, improving current lock-and-key designs. A novel mechanism based on an ''E.coli'' chassis, was designed with two main objectives: to sense arabinose reporting its concentration and to use light receptors to trigger the expression of the required pathways. The first receptor enables ''E.coli'' to activate (express), the arabinose sensing mechanism; whereas the second receptor activates a quick deactivation(degradation), of the sensing mechanism depriving the cell of that capability.''' | ||
Latest revision as of 03:13, 29 September 2011
Abstract
-
- Dual light controlled arabinose biosensor
Integrating the work of many other previous iGEM teams (Tokyo NoKoGen 2010, Chiba 2009, 2010, British Columbia 2009, Cambridge 2010, UNAM-Genomics México 2010, ITESM Monterrey 2010), the aim of this project is to develop a way of giving a cell the command to perform a function at user’s will, improving current lock-and-key designs. A novel mechanism based on an E.coli chassis, was designed with two main objectives: to sense arabinose reporting its concentration and to use light receptors to trigger the expression of the required pathways. The first receptor enables E.coli to activate (express), the arabinose sensing mechanism; whereas the second receptor activates a quick deactivation(degradation), of the sensing mechanism depriving the cell of that capability.
 "
"