Team:BU Wellesley Software/eLabNotebook
From 2011.igem.org
| (20 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<head> | <head> | ||
| - | <title>BU-Wellesley iGEM Team: | + | <title>BU-Wellesley iGEM Team: Meet the Team Members</title> |
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> | <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> | ||
<script src="http://cdn.jquerytools.org/1.2.5/full/jquery.tools.min.js?foo"></script> | <script src="http://cdn.jquerytools.org/1.2.5/full/jquery.tools.min.js?foo"></script> | ||
| - | |||
<style type="text/css"> | <style type="text/css"> | ||
/*hide default igem banner and reformat style into blank slate*/ | /*hide default igem banner and reformat style into blank slate*/ | ||
| Line 43: | Line 42: | ||
font-size: 32pt; | font-size: 32pt; | ||
} | } | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | .thumb { | ||
| + | width: 200px; | ||
| + | } | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| Line 51: | Line 53: | ||
<script src="http://cdn.jquerytools.org/1.2.5/full/jquery.tools.min.js"></script> | <script src="http://cdn.jquerytools.org/1.2.5/full/jquery.tools.min.js"></script> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://static.flowplayer.org/tools/css/scrollable-horizontal.css" /> | <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="http://static.flowplayer.org/tools/css/scrollable-horizontal.css" /> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 77: | ||
} | } | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| + | </head> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<body class="basiclayout"> | <body class="basiclayout"> | ||
<div id="bu-wellesley_wiki_content"> | <div id="bu-wellesley_wiki_content"> | ||
| Line 128: | Line 124: | ||
<a href="#bu-wellesley_wiki_content">Top</a><br> | <a href="#bu-wellesley_wiki_content">Top</a><br> | ||
<a href="#overview">Tool Overview</a><br> | <a href="#overview">Tool Overview</a><br> | ||
| + | <a href="#demo">Demo</a><br> | ||
<a href="#results">Results</a><br> | <a href="#results">Results</a><br> | ||
<a href="#futurework">Future Work</a> | <a href="#futurework">Future Work</a> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 133: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
The eLabNotebook is an electronic lab notebook that facilitates collaborative, effective, and safe assembly of biological systems. The eLabNotebook allows users to: | The eLabNotebook is an electronic lab notebook that facilitates collaborative, effective, and safe assembly of biological systems. The eLabNotebook allows users to: | ||
| + | <a href="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/System/elabnotebook.png"><img style="float:right; width:400px; margin:5px;" src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/System/elabnotebook.png"/></a> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 153: | Line 151: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
<p>The eLabNotebook will be initially prototyped on the iPad platform. | <p>The eLabNotebook will be initially prototyped on the iPad platform. | ||
| - | |||
<p> | <p> | ||
In this project, we were motivated by the disconnect that we observed between biologists' planning stages and their work in the lab, and by the large amount of time the biologists spent maintaining their notebooks during lab work. Often, when biologists planned for the future, they would create a long-term plan with multiple involved steps, each building on the last. However, there was much planning to be done before the biologists could begin their actual work: they had to figure out what protocols were necessary for each step of their work, check that there were enough supplies in the stock room for those protocols, and schedule lab time with other students to ensure that no two people needed to use a machine at the same time. While iGEM teams had many creative solutions to these problems, including the use of Google Docs and spreadsheets to share information about samples, or Doodle polls for lab scheduling, there was no simple way for them to accomplish all of these tasks simultaneously. | In this project, we were motivated by the disconnect that we observed between biologists' planning stages and their work in the lab, and by the large amount of time the biologists spent maintaining their notebooks during lab work. Often, when biologists planned for the future, they would create a long-term plan with multiple involved steps, each building on the last. However, there was much planning to be done before the biologists could begin their actual work: they had to figure out what protocols were necessary for each step of their work, check that there were enough supplies in the stock room for those protocols, and schedule lab time with other students to ensure that no two people needed to use a machine at the same time. While iGEM teams had many creative solutions to these problems, including the use of Google Docs and spreadsheets to share information about samples, or Doodle polls for lab scheduling, there was no simple way for them to accomplish all of these tasks simultaneously. | ||
| Line 159: | Line 156: | ||
Over the summer, we studied biologists in their lab and observed their work practices. We interviewed biologists and asked about the challenges they encountered in the lab. We brainstormed with them possible solutions to their problems. Largest among the challenges was the issue with contamination. Having to take gloves off to interact with a computer, to take notes, to handle certain things can lead to contamination of a sample. Our solution was a tablet interface that replaced the traditional lab notebook and improved the use experience by allowing hands-free interaction. The tablet was designed to display biological protocols, tasks, notes, lab status, and more. The switching of applications was streamlined by allowing voice activation. We also explored the possibility of using gestures to navigate the application as well. | Over the summer, we studied biologists in their lab and observed their work practices. We interviewed biologists and asked about the challenges they encountered in the lab. We brainstormed with them possible solutions to their problems. Largest among the challenges was the issue with contamination. Having to take gloves off to interact with a computer, to take notes, to handle certain things can lead to contamination of a sample. Our solution was a tablet interface that replaced the traditional lab notebook and improved the use experience by allowing hands-free interaction. The tablet was designed to display biological protocols, tasks, notes, lab status, and more. The switching of applications was streamlined by allowing voice activation. We also explored the possibility of using gestures to navigate the application as well. | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="demo"> | ||
| + | <h1>Demo Video</h1> | ||
<center><iframe width="560" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/7R5N7thoIWo" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></center> | <center><iframe width="560" height="315" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/7R5N7thoIWo" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></center> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 165: | ||
<div id="results"> | <div id="results"> | ||
<h1>Results</h1> | <h1>Results</h1> | ||
| - | + | <br><p>After our initial wetlab observations, the computational team created initial designs and concept ideas for the final eLabNoteook product. We took these initial designs back to the wetlab and showed them to the rest of our team, then took their feedback to create this series of wireframes using <a href="http://cacoo.com">Cacoo</a>. We continued to iterate on this design, bringing it to the <a href="https://2011.igem.org/Team:MIT">MIT iGEM team</a> to get their feedback, and also presenting it to <a href = "http://wyss.harvard.edu/viewpage/26/postdocs-and-students">Avi Robinson-Mosher</a> of the <a href="http://wyss.harvard.edu/">Wyss Institute</a>. From the MIT iGEM team, we got a better idea of which parts of our application were tailored specifically to our wetlab at BU, and which parts would be useful to iGEM teams in general. We also redesigned some parts of our application to be more broadly applicable: we recognized the necessity of changing the protocols between labs and for the same lab over time. Our meeting with Avi showed us the needs of users beyond iGEM students, and we hope to incorporate functionality more relevant to graduate and postgraduate work in future iterations of this project. | |
| + | <br> | ||
<div id="image_wrap"> | <div id="image_wrap"> | ||
| Line 172: | Line 173: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<a class="prev browse left"></a> | <a class="prev browse left"></a> | ||
| Line 185: | Line 188: | ||
<img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Scan in page.jpg" /> | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Scan in page.jpg" /> | ||
<img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Overview Schedule.jpg" /> | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Overview Schedule.jpg" /> | ||
| - | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Notebook | + | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Notebook%20page.jpg" /> |
| - | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/ | + | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Map_%20schedule_%20instructions.jpg" /> |
<img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Group awareness.jpg" /> | <img src="http://cs.wellesley.edu/~hcilab/iGEM_wiki/images/labnotebookpaperprototype/Group awareness.jpg" /> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 195: | Line 198: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<!-- "next page" action --> | <!-- "next page" action --> | ||
<a class="next browse right"></a> | <a class="next browse right"></a> | ||
| Line 244: | Line 252: | ||
}); | }); | ||
</script> | </script> | ||
| - | <br><br><br> | + | <p><p><p> <div><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br></div> |
| + | |||
<div id="futurework"> | <div id="futurework"> | ||
| + | <br><p><br> | ||
<h1>Future Work</h1> | <h1>Future Work</h1> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:17, 29 September 2011
eLabNotebook
Tool Overview
The eLabNotebook is an electronic lab notebook that facilitates collaborative, effective, and safe assembly of biological systems. The eLabNotebook allows users to:

- Capture multimodal data inside and outside the lab with minimal effort
- Follow a protocol in the lab while modifying and annotating steps as needed
- Access a wide variety of digital resources
- Get an overview of current activity and progress
- share physical and digital resources in real-time
The implementation of the eLabNotebook entails:
- Developing light-weight interaction techniques for capturing information
- Considering strategies for organizing and sharing heterogeneous information
- Visualizing current lab activity and progress
- Designing for multiple contexts and devices
The eLabNotebook will be initially prototyped on the iPad platform.
In this project, we were motivated by the disconnect that we observed between biologists' planning stages and their work in the lab, and by the large amount of time the biologists spent maintaining their notebooks during lab work. Often, when biologists planned for the future, they would create a long-term plan with multiple involved steps, each building on the last. However, there was much planning to be done before the biologists could begin their actual work: they had to figure out what protocols were necessary for each step of their work, check that there were enough supplies in the stock room for those protocols, and schedule lab time with other students to ensure that no two people needed to use a machine at the same time. While iGEM teams had many creative solutions to these problems, including the use of Google Docs and spreadsheets to share information about samples, or Doodle polls for lab scheduling, there was no simple way for them to accomplish all of these tasks simultaneously.
Over the summer, we studied biologists in their lab and observed their work practices. We interviewed biologists and asked about the challenges they encountered in the lab. We brainstormed with them possible solutions to their problems. Largest among the challenges was the issue with contamination. Having to take gloves off to interact with a computer, to take notes, to handle certain things can lead to contamination of a sample. Our solution was a tablet interface that replaced the traditional lab notebook and improved the use experience by allowing hands-free interaction. The tablet was designed to display biological protocols, tasks, notes, lab status, and more. The switching of applications was streamlined by allowing voice activation. We also explored the possibility of using gestures to navigate the application as well.
Demo Video
Results
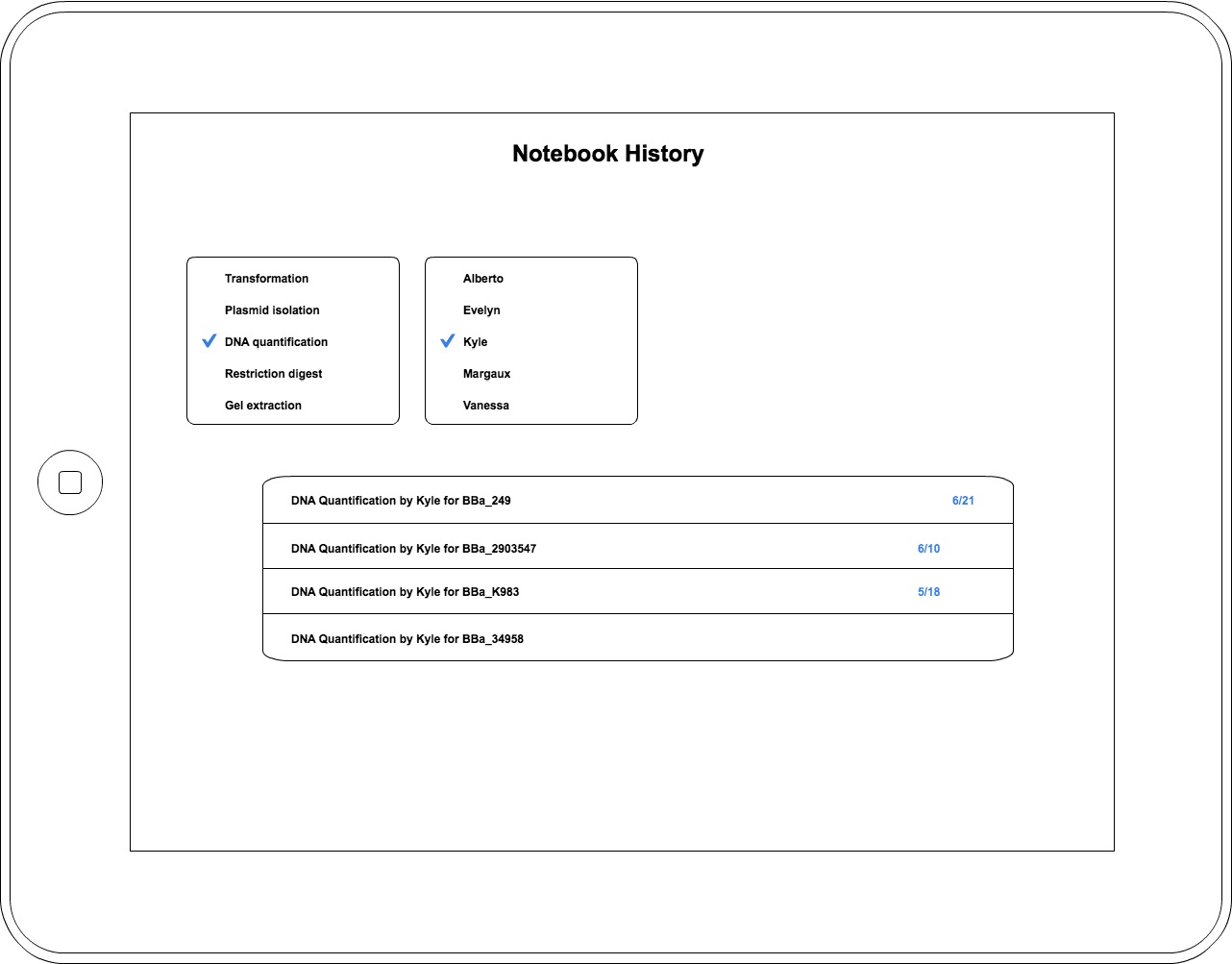
After our initial wetlab observations, the computational team created initial designs and concept ideas for the final eLabNoteook product. We took these initial designs back to the wetlab and showed them to the rest of our team, then took their feedback to create this series of wireframes using Cacoo. We continued to iterate on this design, bringing it to the MIT iGEM team to get their feedback, and also presenting it to Avi Robinson-Mosher of the Wyss Institute. From the MIT iGEM team, we got a better idea of which parts of our application were tailored specifically to our wetlab at BU, and which parts would be useful to iGEM teams in general. We also redesigned some parts of our application to be more broadly applicable: we recognized the necessity of changing the protocols between labs and for the same lab over time. Our meeting with Avi showed us the needs of users beyond iGEM students, and we hope to incorporate functionality more relevant to graduate and postgraduate work in future iterations of this project.


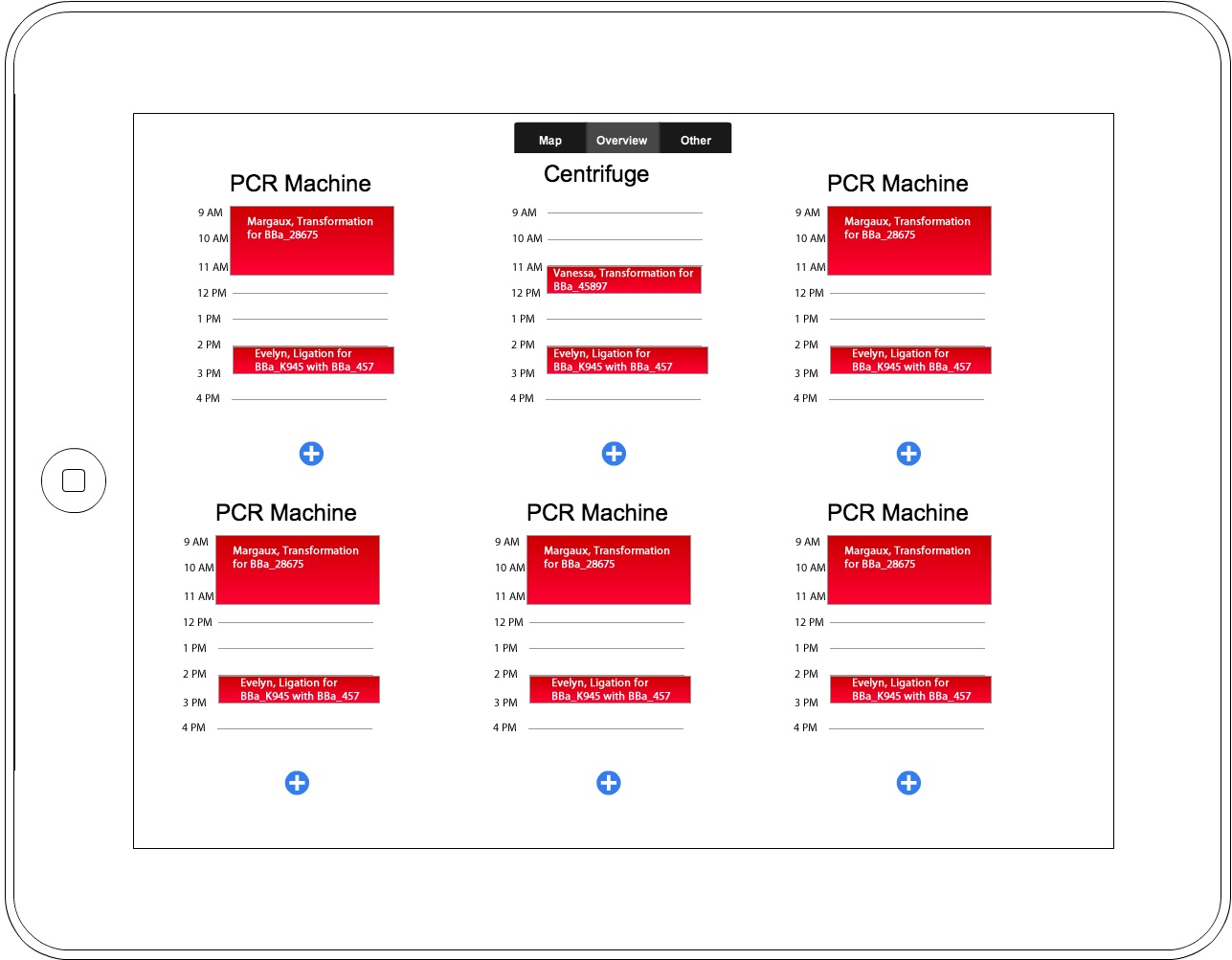
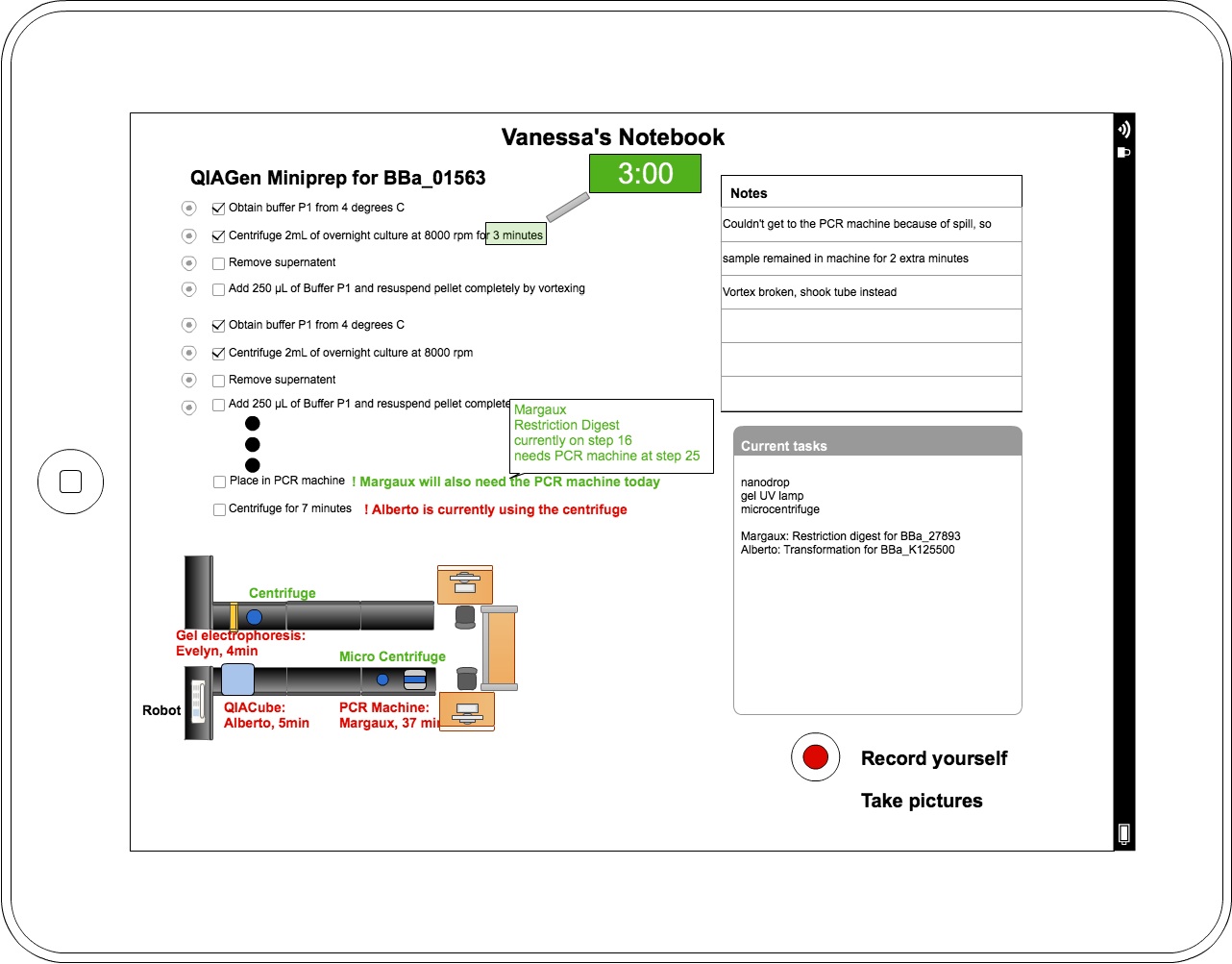
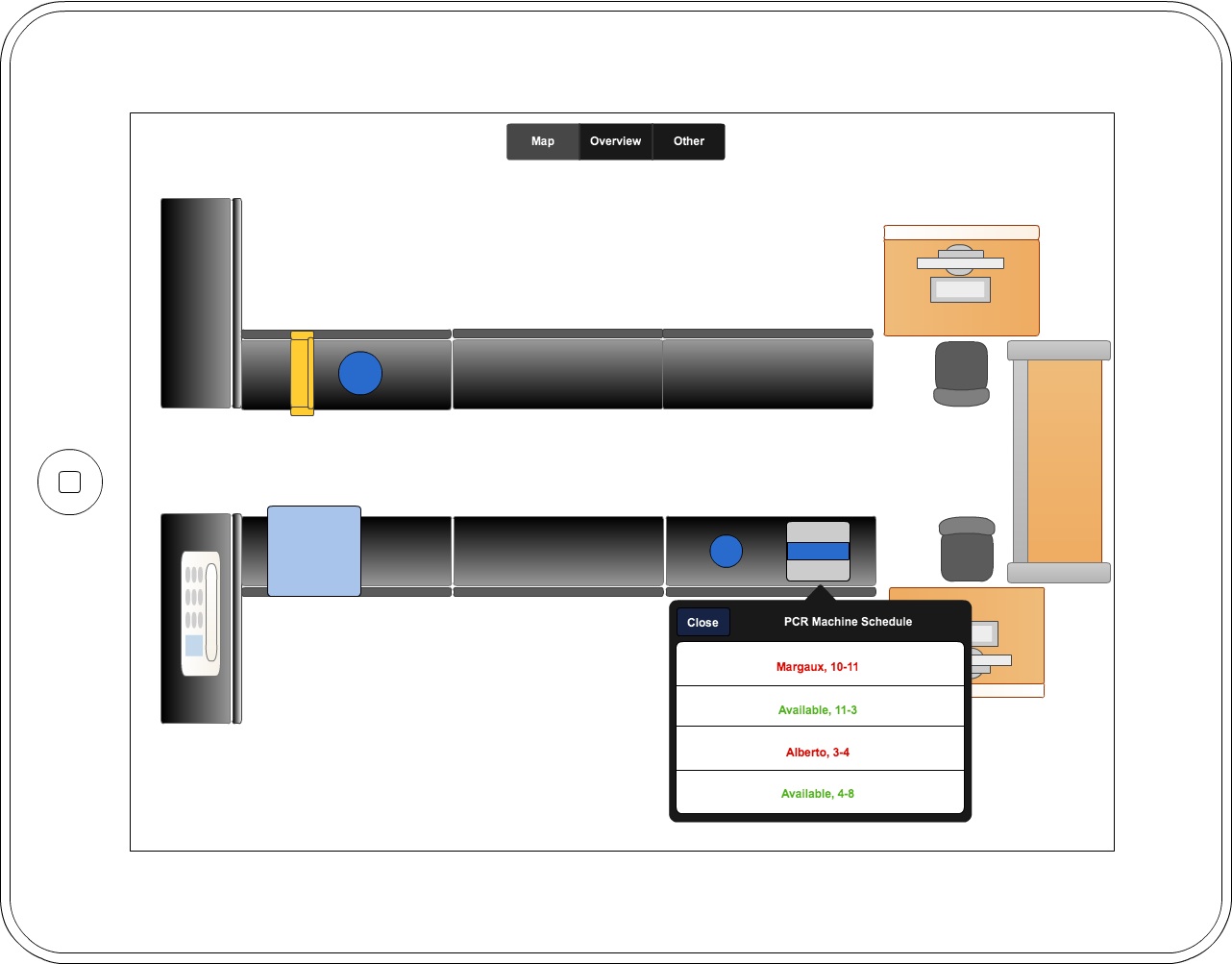
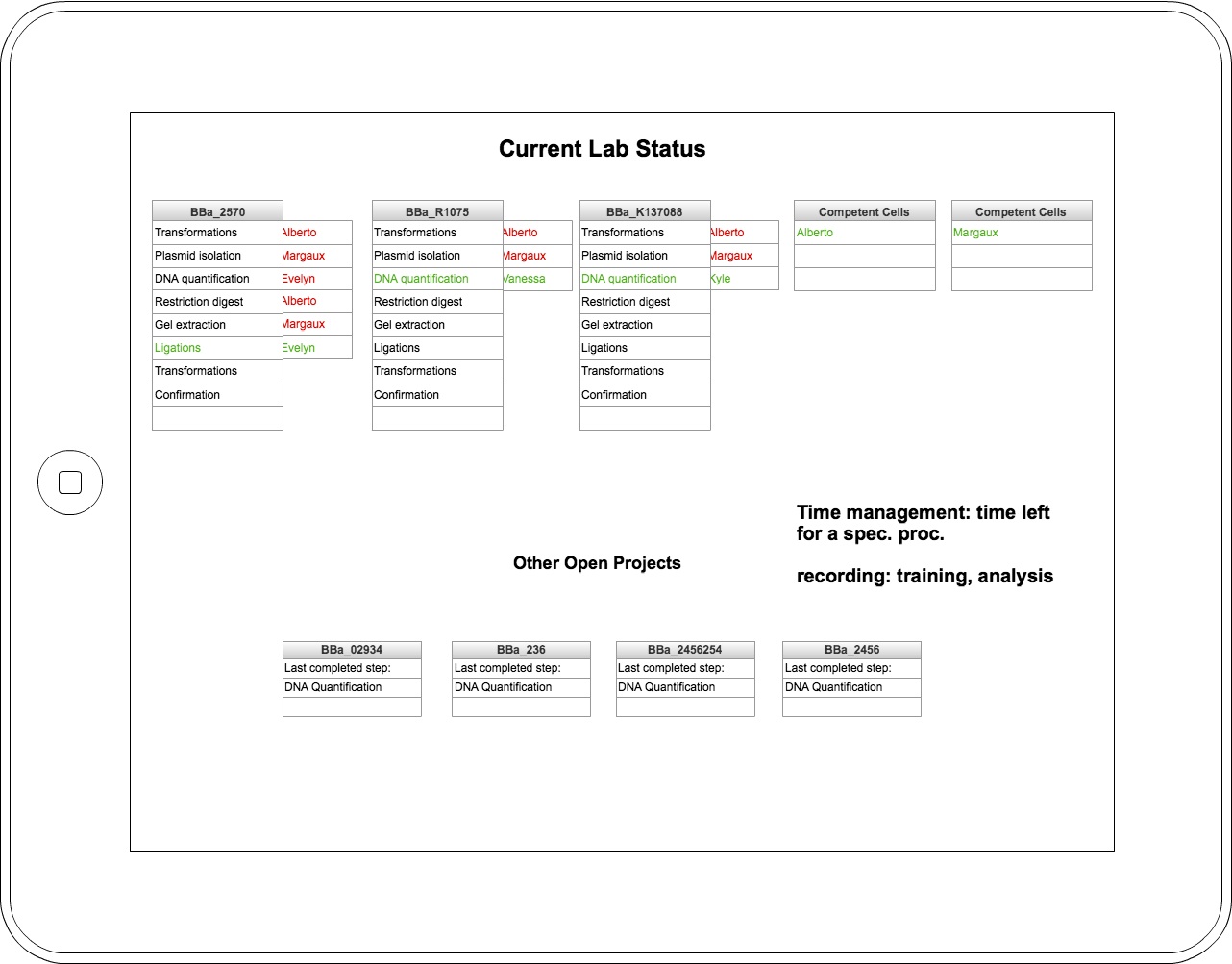
Future Work
- Add connectivity between multiple iPads
- Create multiple interfaces for different hardware (i.e., PC access, iPad access, mobile phone access)
- Create specialized functions for an advisor vs. a student
- Improve the user interface
- Use gesture based input or voice commands instead of touch to control the iPad
- Add reference materials for use in lab setting
 "
"
