Team:NYC Wetware/Deinococcus/Cell Damage
From 2011.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
Fe3+ + H2O2 → Fe2+ + OOH· + H+<br/> | Fe3+ + H2O2 → Fe2+ + OOH· + H+<br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | The hydroxyl radical is very | + | The hydroxyl radical is very reactive, and can cause damage to DNA and proteins by reducing them. In addition to producing a hydroxyl radical, ionizing radiation produces many other reactive, potentially damaging molecules, including ·O2- (Superoxide). <br/> |
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | Non-ionizing radiation, such as UV radiation, can directly rearrange a molecule’s structure, leading to base damage as well as single strand breaks in the DNA. However, Non-ionizing radiation doesn’t produce the reactive molecules, because it doesn’t remove electrons from molecules. Therefore the only damage is through rearrangement of the structure of DNA and proteins.<br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <h3>And now its time for Radiation Trivia!</h3> | ||
| + | Did you know that nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain are usually seen within one to two hours of an acute 6 –10 Gray radiation exposure. (Source: Donnelly EH, Nemhauser JB, Smith JM,et al. (June 2010). "Acute radiation syndrome: assessment and management". South. Med. J. 103 (6): 541–6.)<br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | or that Average annual total radiation dose for the US: 6.2 x 10^-3 Gray/year. (Source: | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://web.princeton.edu/sites/ehs/osradtraining/backgroundradiation/background.htm)<br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | Activity and Typical Dose<br/> | ||
| + | Smoking = 2.8 x 10^-3 Gray/year<br/> | ||
| + | Using radioactive materials in a Princeton University lab = <1 x 10^-4 Gray/year<br/> | ||
| + | Dental x-ray = 1 x 10^-4 Gray per x-ray<br/> | ||
| + | Chest x-ray = 8 x 10^-5 Gray per x-ray<br/> | ||
| + | Drinking water = 5 x 10^-5 Gray per year<br/> | ||
| + | Cross country round trip by air = 5 x 10^-5 Gray per year<br/> | ||
| + | Coal burning power plant = 1.65 x 10^-6 Gray/year<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Source: http://web.princeton.edu/sites/ehs/osradtraining/backgroundradiation/background.htm<br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <h3>Cellular Protection</h3> | ||
| + | The cell has various mechanisms for protecting itself.<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | (1) Increasing Mn/Fe ratio<br/> | ||
| + | The cell is able to limit the number of free radicals produced by limiting the exposure of iron, a player in the Fenton reaction. The production of hydroxyl radicals, outlined in the Damage section, by the Fenton reaction, leads to cellular damage, both in the destruction of DNA and in the incapacitation of proteins. To limit the occurrence of the Fenton reaction, the cell replaces Fe with Mn in what would otherwise be otherwise Fe-cofactored enzymes. This adjustment of the Mn/Fe ratio protects the cell from oxidative damage.<br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | (2) DNA Repair<br/> | ||
| + | 1. To Base Damage [Base Damage.png]<br/> | ||
| + | The cell employs an enzyme, DNA glycosylase, to remove the damaged base. AP endonuclease cuts the DNA backbone, essentially forming a Single Strand Break. DNA polymerase then resynthesizes the base. The single strand break is repaired as in Step 2 (below).<br/> | ||
| + | 2. To Single Strand Breaks [SSb.png]<br/> | ||
| + | A nick in the backbone of a single strand can be easily ligated by DNA ligase. | ||
| + | [http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/46/DNA_Repair.jpg] - DNA Ligase at work | ||
| + | 3. To Double Strand Breaks [DSb.png]<br/> | ||
| + | One of the primary methods of repairing double strand breaks is known as homologous recombination. The broken DNA fragment is connected to a complete DNA strand by a junction (a “Holliday junction.”) The DNA repair mechanism restores the damaged DNA.<br/> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | (3) Anti-Oxidant Enzymes | ||
| + | |||
| + | A group of enzymes known as Antioxidants can have a preventative effect on radiation damage via reactive molecules. the reactive molecules reduce the antioxidant before having a chance to reduce DNA or sensitive proteins. Two examples are the Superoxide dismutase family (e.g., Manganese-SOD)and Catalase family (e.g., KatE), which react with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydroxyl radical, respectively. Because the output of Superoxide dismutase is Hydroxyl radical, therefore only Superoxide dismutase combined with Catalase neutralizes Hydrogen Peroxide.<br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
Revision as of 05:02, 28 September 2011

Normal Cell Function
The prokaryotic cell carries on as if it were a normal day. The DNA, the string of code with information to direct the cell’s daily activities, floats freely in the cytoplasm. It allows itself to be transcribed by the RNA into proteins, which reside casually in the cytoplasm, the intracellular environment of the cell.

[Image of Protein with Iron]

Damage to the DNA and Proteins
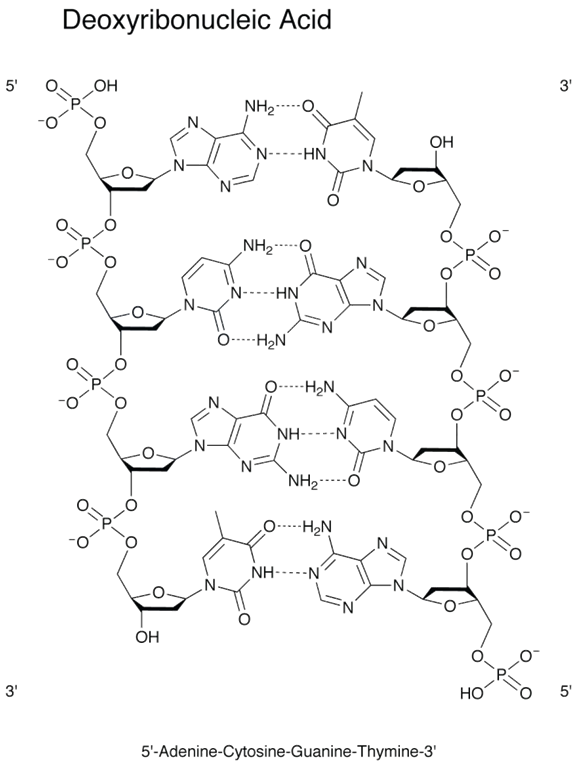
The cell is hit repeatedly with radiation, causing extensive damage to the DNA and proteins. The damage to the DNA includes:1. Base Damage

DNA is composed of a backbone attached to nucleobases. Damage may occur to the bases.
2. Single Strand Breaks

The backbone of DNA is made up of a repeating pattern of sugar and phosphate. A single strand break occurs when this backbone is broken.
3. Double Strand Breaks

DNA is commonly found as a double strand. If the opposing strands both develop single strand breaks, this double strand break may cause the separation of the two fragments of DNA.
Damage to the protein may include:

Ionizing radiation is radiation with sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom.

Ionizing radiation has the power to cause Double Strand Breaks, as well as initiate the Fenton Reaction, which can cause damage to proteins as well as DNA.
Fenton Chemistry results in the production of a hydroxyl radical through the oxidation of ferrous iron to ferric iron by means of hydrogen peroxide.
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + OH· + OH−
The ferrous iron is recycled by hydrogen peroxide.
Fe3+ + H2O2 → Fe2+ + OOH· + H+
The hydroxyl radical is very reactive, and can cause damage to DNA and proteins by reducing them. In addition to producing a hydroxyl radical, ionizing radiation produces many other reactive, potentially damaging molecules, including ·O2- (Superoxide).
Non-ionizing radiation, such as UV radiation, can directly rearrange a molecule’s structure, leading to base damage as well as single strand breaks in the DNA. However, Non-ionizing radiation doesn’t produce the reactive molecules, because it doesn’t remove electrons from molecules. Therefore the only damage is through rearrangement of the structure of DNA and proteins.
And now its time for Radiation Trivia!
Did you know that nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain are usually seen within one to two hours of an acute 6 –10 Gray radiation exposure. (Source: Donnelly EH, Nemhauser JB, Smith JM,et al. (June 2010). "Acute radiation syndrome: assessment and management". South. Med. J. 103 (6): 541–6.)or that Average annual total radiation dose for the US: 6.2 x 10^-3 Gray/year. (Source: http://web.princeton.edu/sites/ehs/osradtraining/backgroundradiation/background.htm)
Activity and Typical Dose
Smoking = 2.8 x 10^-3 Gray/year
Using radioactive materials in a Princeton University lab = <1 x 10^-4 Gray/year
Dental x-ray = 1 x 10^-4 Gray per x-ray
Chest x-ray = 8 x 10^-5 Gray per x-ray
Drinking water = 5 x 10^-5 Gray per year
Cross country round trip by air = 5 x 10^-5 Gray per year
Coal burning power plant = 1.65 x 10^-6 Gray/year
Source: http://web.princeton.edu/sites/ehs/osradtraining/backgroundradiation/background.htm
Cellular Protection
The cell has various mechanisms for protecting itself.(1) Increasing Mn/Fe ratio
The cell is able to limit the number of free radicals produced by limiting the exposure of iron, a player in the Fenton reaction. The production of hydroxyl radicals, outlined in the Damage section, by the Fenton reaction, leads to cellular damage, both in the destruction of DNA and in the incapacitation of proteins. To limit the occurrence of the Fenton reaction, the cell replaces Fe with Mn in what would otherwise be otherwise Fe-cofactored enzymes. This adjustment of the Mn/Fe ratio protects the cell from oxidative damage.
(2) DNA Repair
1. To Base Damage [Base Damage.png]
The cell employs an enzyme, DNA glycosylase, to remove the damaged base. AP endonuclease cuts the DNA backbone, essentially forming a Single Strand Break. DNA polymerase then resynthesizes the base. The single strand break is repaired as in Step 2 (below).
2. To Single Strand Breaks [SSb.png]
A nick in the backbone of a single strand can be easily ligated by DNA ligase. [http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/46/DNA_Repair.jpg] - DNA Ligase at work 3. To Double Strand Breaks [DSb.png]
One of the primary methods of repairing double strand breaks is known as homologous recombination. The broken DNA fragment is connected to a complete DNA strand by a junction (a “Holliday junction.”) The DNA repair mechanism restores the damaged DNA.
(3) Anti-Oxidant Enzymes A group of enzymes known as Antioxidants can have a preventative effect on radiation damage via reactive molecules. the reactive molecules reduce the antioxidant before having a chance to reduce DNA or sensitive proteins. Two examples are the Superoxide dismutase family (e.g., Manganese-SOD)and Catalase family (e.g., KatE), which react with Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydroxyl radical, respectively. Because the output of Superoxide dismutase is Hydroxyl radical, therefore only Superoxide dismutase combined with Catalase neutralizes Hydrogen Peroxide.
 "
"