Team:ETH Zurich/Biology/Validation
From 2011.igem.org
(→Expression of AlcR in E.coli) |
(→Expression of AlcR in E. coli) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
== Expression of AlcR in ''E. coli'' == | == Expression of AlcR in ''E. coli'' == | ||
| - | Given that codon usage is not the same in ''E.coli'' and ''aspergillus nidulans'', we analyzed codon usage of AlcR. | + | Given that codon usage is not the same in ''E. coli'' and ''aspergillus nidulans'', we analyzed codon usage of AlcR. |
| - | We obtained a Codon adaptation index (CAI) of 0.7 for the aspergillus nidulans protein in E.coli, especially at the beginning of the gene a few very rare codons were included. To get a fully E.coli optimized | + | We obtained a Codon adaptation index (CAI) of 0.7 for the aspergillus nidulans protein in ''E. coli'', especially at the beginning of the gene a few very rare codons were included. To get a fully ''E. coli''-optimized gene, we ordered the gene codon optimized. To make some first test, we exchanged the rare codons at the beginning of the ''aspergillus nidulans'' protein with PCR. With these protein we made same first Test of the expression of AlcR. |
To monitor the expression of AlcR a His-tag was introduced in the test system. | To monitor the expression of AlcR a His-tag was introduced in the test system. | ||
Revision as of 15:54, 20 September 2011
| Validation |
| ||||
| Experimental setups... | |||||
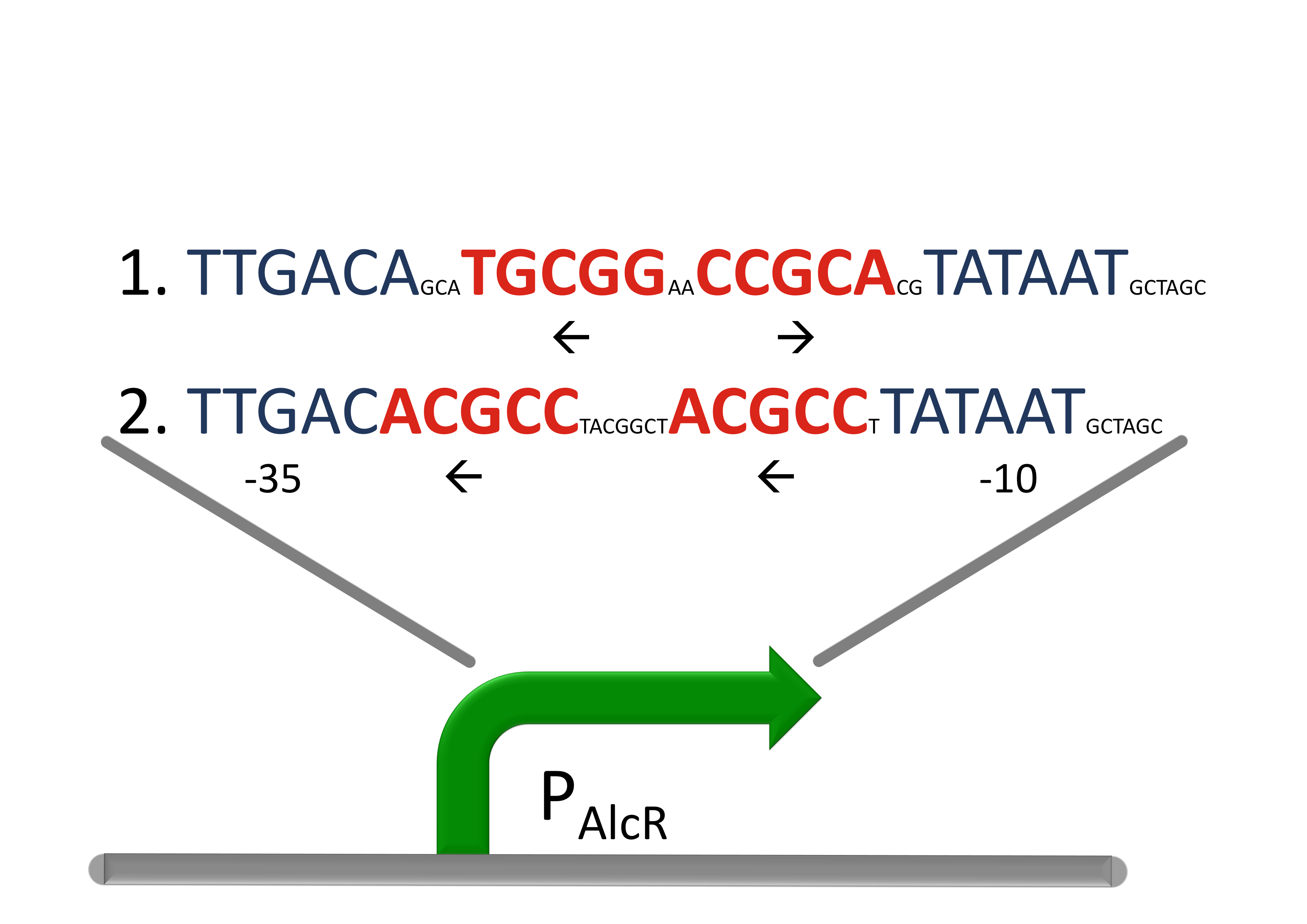
Sensor AlcRDesign of a AlcR/acetaldehyde repressed promoter PAlcRBecause funghi activator normally does not work in e.coli, we modified AlcR in a way that it acts as a repressor. The mechanism of how AlcR activates transcription is not completely known what makes the process of redesigning it very challenging. For the promoter PAlcR the operator site of AlcR from apergillus nidulans was placed between the -10 and -35 region of the bacterial promoter. As DNA targets we used two different versions, one with direct-repeat targets and one with inverted [1]. The idea is that in present of acetaldehyde AlcR will bind to the operon and block the binding of the RNA-polymerase. This only works if the mechanism of AlcR binding does not involves conformational changes or something similar. Expression of AlcR in E. coliGiven that codon usage is not the same in E. coli and aspergillus nidulans, we analyzed codon usage of AlcR. We obtained a Codon adaptation index (CAI) of 0.7 for the aspergillus nidulans protein in E. coli, especially at the beginning of the gene a few very rare codons were included. To get a fully E. coli-optimized gene, we ordered the gene codon optimized. To make some first test, we exchanged the rare codons at the beginning of the aspergillus nidulans protein with PCR. With these protein we made same first Test of the expression of AlcR. To monitor the expression of AlcR a His-tag was introduced in the test system. western blot Repression test of AlcRTo test our designed AlcR-promotors the following system was designed (see Figure). In present of acetaldeyhde AlcR binds to the AlcR operon and inhibits the expression of GFP. For a better signal assam gfp was used. results |
Sensor XylR |
Xylene degradation |
Bandpass |
References[1] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11550794 Beatrice Felenbok, Michel Flipphi and Igor Nikolaev: Ethanol Catabolism in Aspergillus nidulans: A Model System for Studying Gene Regulation, Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology, 69: 149-204] |
 "
"