Team:UCL London/Research/Supercoiliology/Experiments
From 2011.igem.org
Supercoiliology in the Lab
Making Top10 E. coli cells
Test competency by transforming pUC19 plasmid into E. coli cells and determining the CFU/ml, making sure it falls within an adequate range.
Extraction
Design primers (introducing EX and SP restriction sites upstream and downstream of the gyrase ORFs) for gyrase a and b, forward and reverse based on EcoCyc and Eurofin from the E. coli genome.
Use polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to isolate genes for gyrase a and gyrase b in order to extract them from the wild type E.coli genome.
Check EX SP restriction sites in wild type gyrase genes (using the NEB cutter 2.0 website, checks the restriction sites we have in the DNA sequence we want to study). This is done in order to assess whether or not the cutting sites are located on the gene of interest which would help us determine which restriction enzymes we must use to excise the desired gene.
Do PCR to extract and amplify the wild type gyrase A and B genes.
Purify the PCR product.
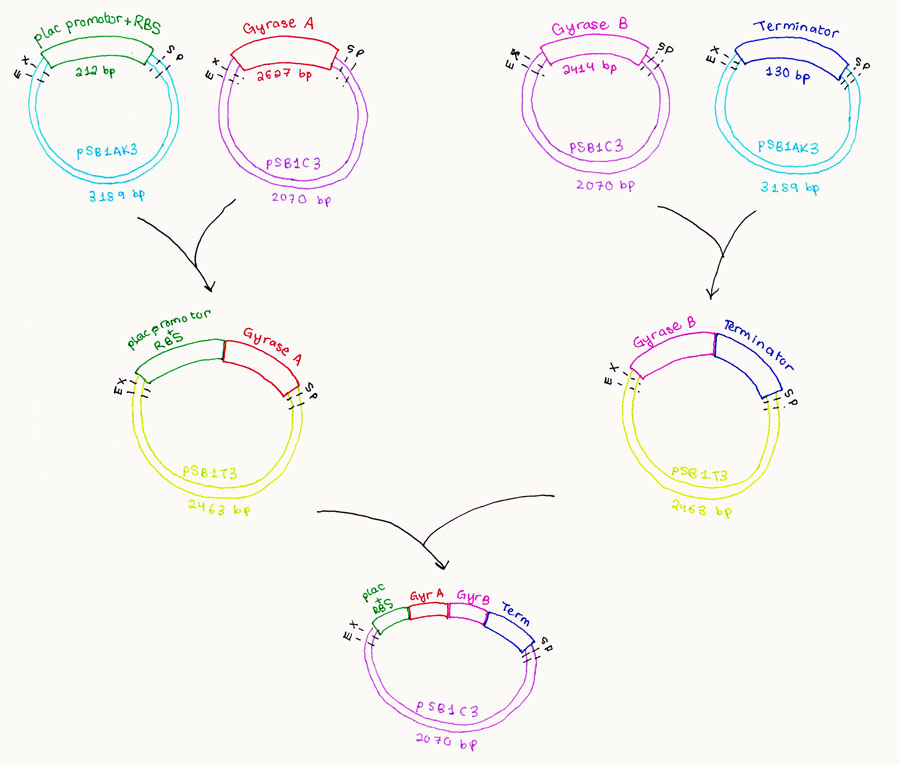
Ligate the PCR product of the wild type genes into a single plasmid backbone, PSB1C3.
In order to better determine whether or not we had successful ligations of our PCR product into the PSB1C3 backbone, we used a BBa_Jo4450 RFP expression cassette for the ligation of the psb1C3 backbone.
Modification
After ligating, we transform bacteria with plasmid to find out which culture has right insert. Plate out on a chloramphenicol (Cm) plate. The bacterium which has the right insert will turn white, whereas the ones which have taken up the wrong insert or have self ligated will stay red.
Do an overnight culture of the successfully ligated colonies and mini prep them in order to purify the DNA so that it can be used for subsequent procedures.
Digest DNA samples using EcoR1 and Pst1. Then check digested product on gel to make sure that the insert is the correct size. This is to be followed up by doing DNA sequencing.
After obtaining the correct gyrase insert we do site directed mutagenesis again.
In gyrase A, Pst1 cuts at 1612th base pair position while for gyrase B, Ecor1 cuts at 6th base pair position. This was a rather large issue as it meant any further digestions done with on these inserts using the aforementioned enzymes would destroy the genes.
A site directed mutagenesis was done using the Stratagem kit to remove these cutting sites from the gyrase genes of both the A and B subunits.
We took the plac IPTG inducible promoter with RBS, BBa_J04500 from the iGEM registry plates and transformed it and extracted the required gene.
The plac promoter+ RBS was ligated together with gyrase A.
Gyrase B is to be ligated with the terminator BBa_B0015 obtained from the Registry plates.
A 3A assembly is done with all the parts.
 "
"